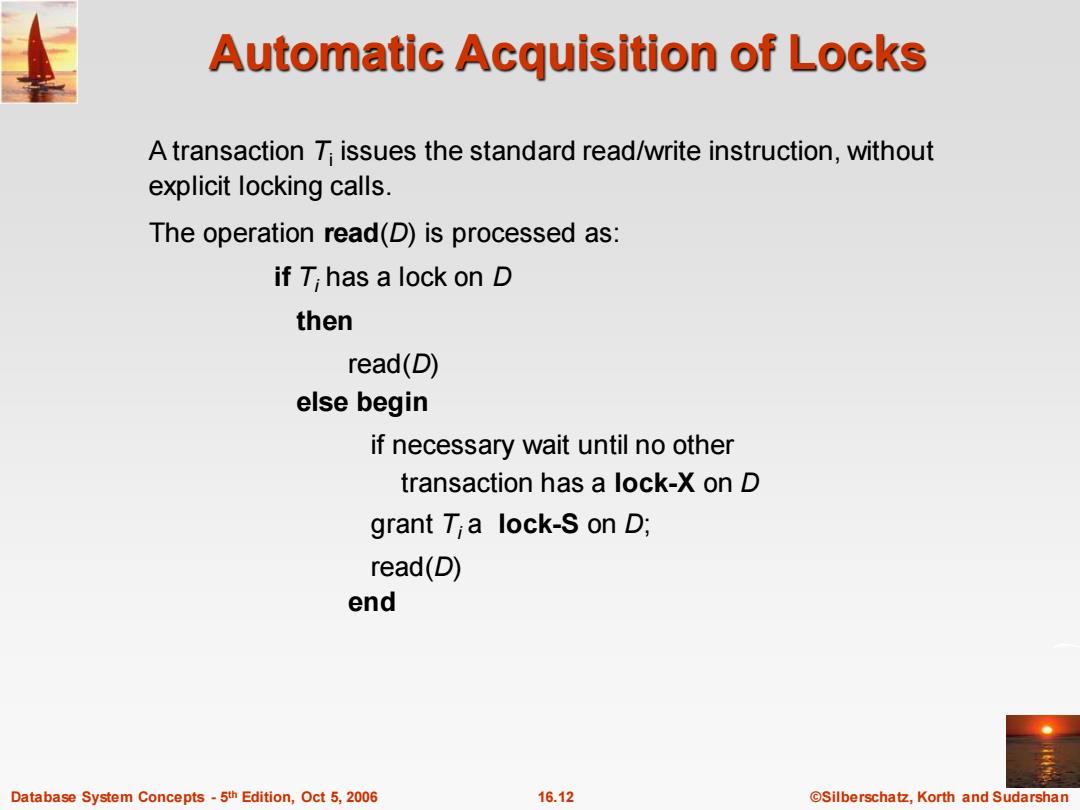
Automatic Acquisition of Locks A transaction T issues the standard read/write instruction,without explicit locking calls. The operation read(D)is processed as: if T;has a lock on D then read(D) else begin if necessary wait until no other transaction has a lock-X on D grant Ti a lock-S on D; read(D) end Database System Concepts-5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 16.12 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 16.12 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 Automatic Acquisition of Locks A transaction Ti issues the standard read/write instruction, without explicit locking calls. The operation read(D) is processed as: if Ti has a lock on D then read(D) else begin if necessary wait until no other transaction has a lock-X on D grant Ti a lock-S on D; read(D) end
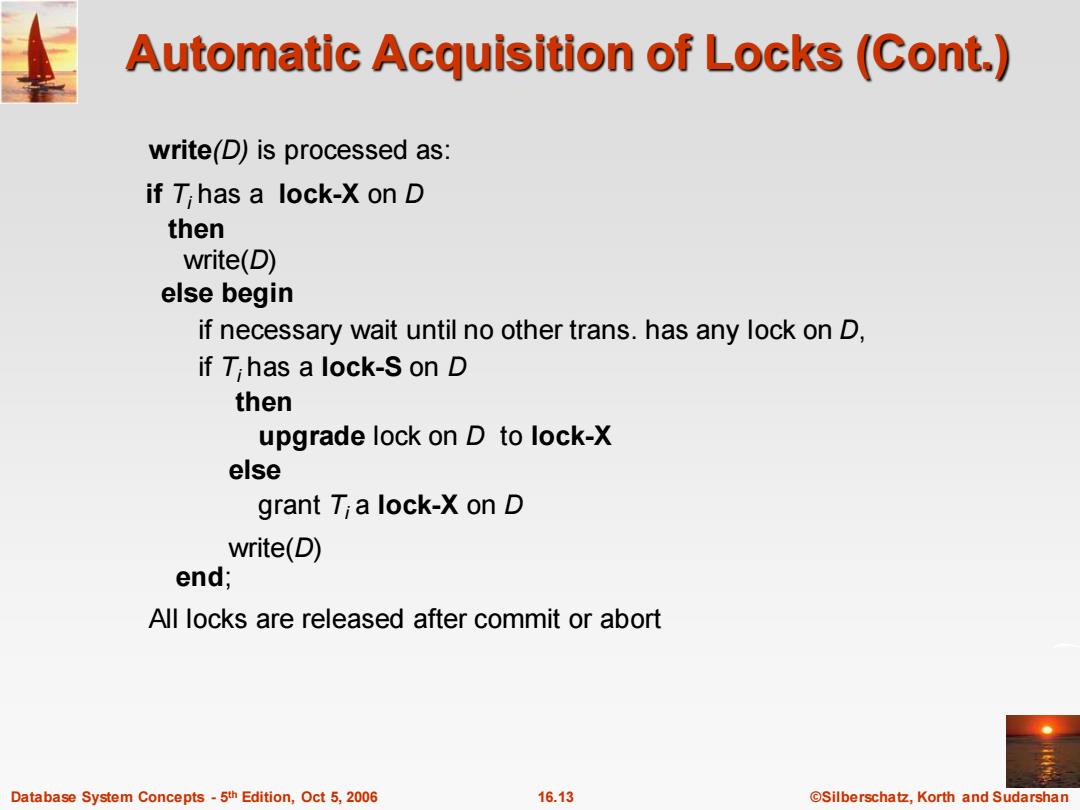
Automatic Acquisition of Locks (Cont.) write(D)is processed as: if T;has a lock-X on D then write(D) else begin if necessary wait until no other trans.has any lock on D, if T;has a lock-S on D then upgrade lock on D to lock-X else grant T;a lock-X on D write(D) end; All locks are released after commit or abort Database System Concepts-5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 16.13 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 16.13 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 Automatic Acquisition of Locks (Cont.) write(D) is processed as: if Ti has a lock-X on D then write(D) else begin if necessary wait until no other trans. has any lock on D, if Ti has a lock-S on D then upgrade lock on D to lock-X else grant Ti a lock-X on D write(D) end; All locks are released after commit or abort

Implementation of Locking A lock manager can be implemented as a separate process to which transactions send lock and unlock requests The lock manager replies to a lock request by sending a lock grant messages (or a message asking the transaction to roll back,in case of a deadlock) The requesting transaction waits until its request is answered The lock manager maintains a data-structure called a lock table to record granted locks and pending requests The lock table is usually implemented as an in-memory hash table indexed on the name of the data item being locked Database System Concepts-5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 16.14 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 16.14 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 Implementation of Locking A lock manager can be implemented as a separate process to which transactions send lock and unlock requests The lock manager replies to a lock request by sending a lock grant messages (or a message asking the transaction to roll back, in case of a deadlock) The requesting transaction waits until its request is answered The lock manager maintains a data-structure called a lock table to record granted locks and pending requests The lock table is usually implemented as an in-memory hash table indexed on the name of the data item being locked
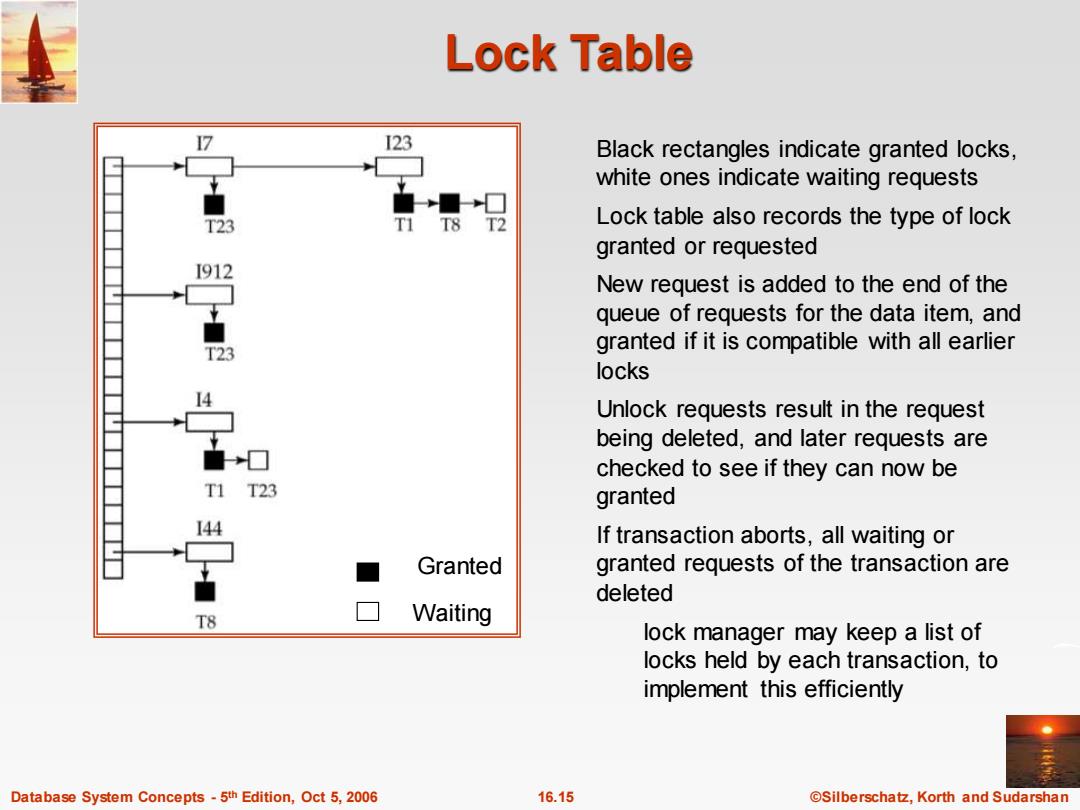
Lock Table I23 Black rectangles indicate granted locks, white ones indicate waiting requests T23 T8 T2 Lock table also records the type of lock granted or requested I912 New request is added to the end of the queue of requests for the data item,and T23 granted if it is compatible with all earlier locks Unlock requests result in the request being deleted,and later requests are checked to see if they can now be T1T23 granted 144 If transaction aborts,all waiting or ■ Granted granted requests of the transaction are deleted T8 Waiting lock manager may keep a list of locks held by each transaction,to implement this efficiently Database System Concepts-5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 16.15 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 16.15 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 Lock Table Black rectangles indicate granted locks, white ones indicate waiting requests Lock table also records the type of lock granted or requested New request is added to the end of the queue of requests for the data item, and granted if it is compatible with all earlier locks Unlock requests result in the request being deleted, and later requests are checked to see if they can now be granted If transaction aborts, all waiting or granted requests of the transaction are deleted lock manager may keep a list of locks held by each transaction, to implement this efficiently Granted Waiting
Graph-Based Protocols Graph-based protocols are an alternative to two-phase locking Impose a partial ordering->on the set D={d,d2,...,dh}of all data items. If d;->d;then any transaction accessing both d;and d;must access d;before accessing di. Implies that the set D may now be viewed as a directed acyclic graph,called a database graph. The tree-protocol is a simple kind of graph protocol. Database System Concepts-5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 16.16 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 16.16 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 Graph-Based Protocols Graph-based protocols are an alternative to two-phase locking Impose a partial ordering → on the set D = {d1 , d2 ,..., dh } of all data items. If di → dj then any transaction accessing both di and dj must access di before accessing dj . Implies that the set D may now be viewed as a directed acyclic graph, called a database graph. The tree-protocol is a simple kind of graph protocol