
5.2 Classification of shear connectors ductility -the most important material property ductile connectors延性连接件-those having sufficient deformation capacity,in slip,to justify the assumption of perfectly plastic behaviour for the shear connection. For slip capacity su EC 4 estimates that a value greater than 6 mm allows shear connectors to be considered as ductile. rigid shear connectors刚性(非延性)连接件,i.e. non-ductile-as those which fracture when the ultimate load PR of the connector is reached without any significant slip;in this case,the subsequent shear resistance falls suddenly to zero
5.2 Classification of shear connectors • ductility -the most important material property • ductile connectors 延性连接件- those having sufficient deformation capacity, in slip, to justify the assumption of perfectly plastic behaviour for the shear connection. • For slip capacity su , EC 4 estimates that a value greater than 6 mm allows shear connectors to be considered as ductile. • rigid shear connectors刚性(非延性)连接件, i.e. non-ductile- as those which fracture when the ultimate load PR of the connector is reached without any significant slip; in this case, the subsequent shear resistance falls suddenly to zero

Real behaviour Real behaviour R Ideal behaviour Schematic behaviour (a)Ductile shear connector (b)Non-ductile connector Ductile and non-ductile shear connectors 延性和非延性连接件力-滑移曲线
Ductile and non-ductile shear connectors 延性和非延性连接件力-滑移曲线

Ductile and non-ductile connectors Slip capacity of headed stud connectors increases with the diameter of the shank; Slip enables longitudinal shear to be redistributed between the connectors in a critical length,before any of them fail; The definitions of'ductile'connectors is interpreted that the connector has sufficient slip capacity to enable the shear force redistribution at the ultimate state; Ductile connectors may be spaced uniformly along the critical length,whereas,for non-ductile connectors,the spacing must be based on elastic analysis for longitudinal shear
Ductile and non-ductile connectors • Slip capacity of headed stud connectors increases with the diameter of the shank; • Slip enables longitudinal shear to be redistributed between the connectors in a critical length, before any of them fail; • The definitions of ‘ductile’ connectors is interpreted that the connector has sufficient slip capacity to enable the shear force redistribution at the ultimate state; • Ductile connectors may be spaced uniformly along the critical length, whereas, for non-ductile connectors, the spacing must be based on elastic analysis for longitudinal shear
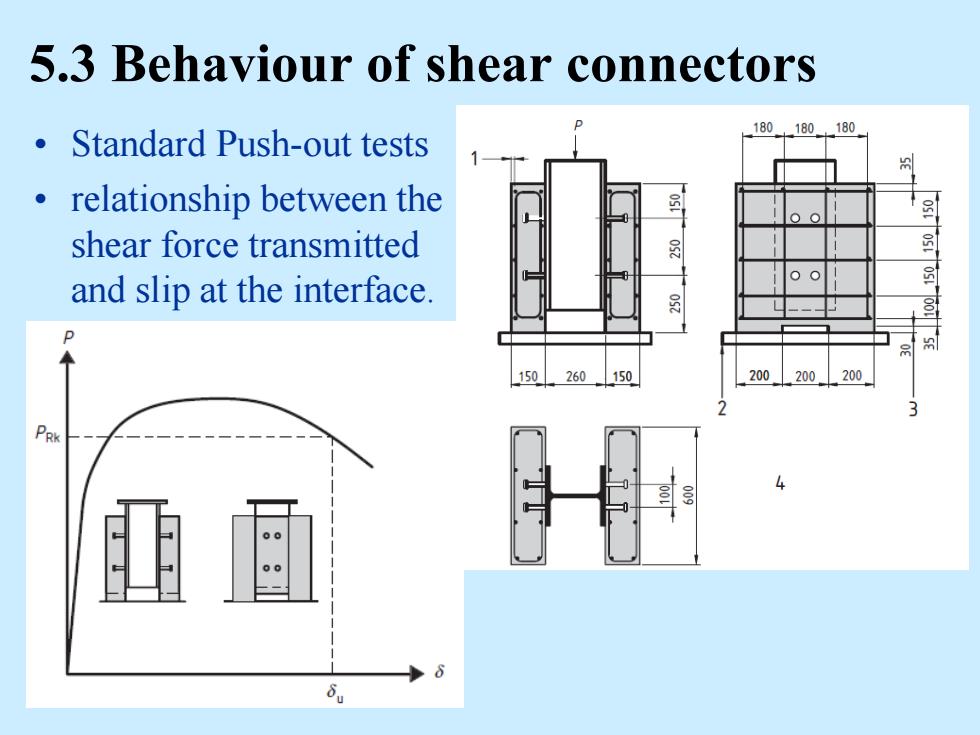
5.3 Behaviour of shear connectors 180180.180 Standard Push-out tests relationship between the shear force transmitted 5 and slip at the interface. 10 260 150 200 200 200
5.3 Behaviour of shear connectors • Standard Push-out tests • relationship between the shear force transmitted and slip at the interface

(a) (b) (b) Load (kN/stud) 150 100. Push-out tests 50 and load slip 。468101214sp(mm) curves
Push-out tests and load slip curves