
精子发生的分子机制 朱复希
精子发生的分子机制 朱复希
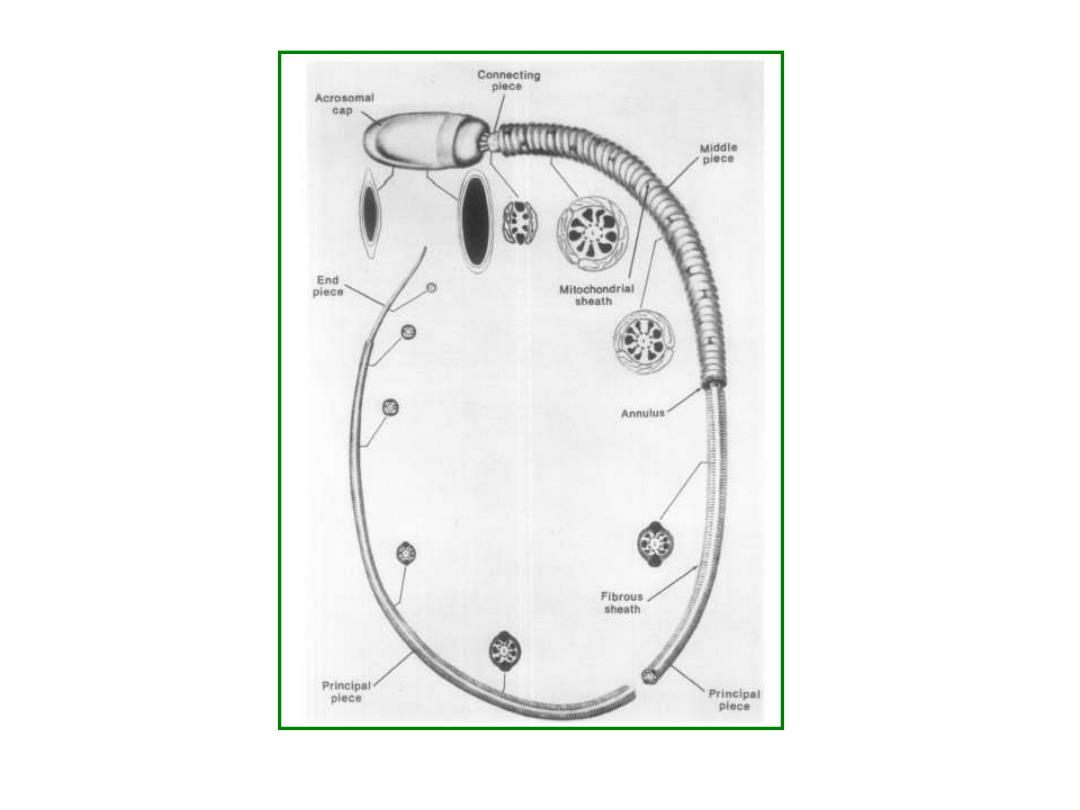
Connecting piece Acrosomal cap Middle plece End piece Mitochondrial sbeath g 0 Annulus 西 Fibrous sheath Princloal plece
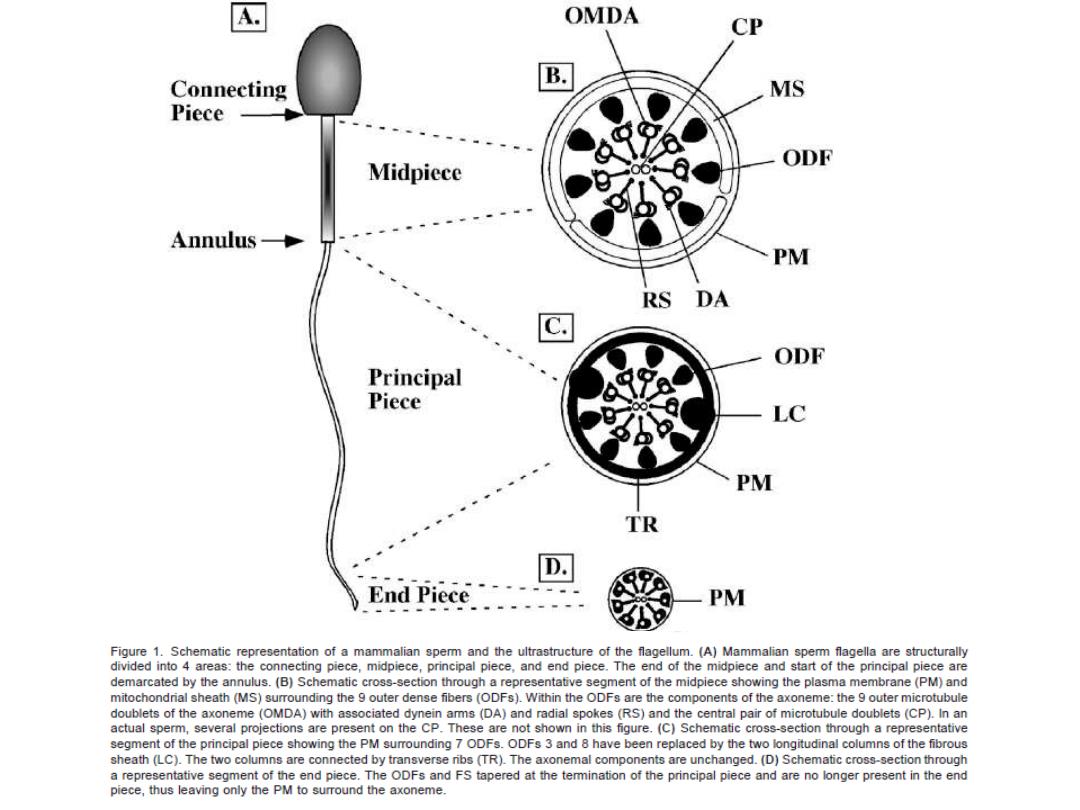
A OMDA CP Connecting B MS Piece ODF Midpiece Annulus- PM RS DA ODF Principal Piece LC PM TR D. End Piece PM Figure 1.Schematic representation of a mammalian sperm and the ultrastructure of the flagellum.(A)Mammalian sperm flagella are structurally divided into 4 areas:the connecting piece,midpiece,principal piece.and end piece.The end of the midpiece and start of the principal piece are demarcated by the annulus.(B)Schematic cross-section through a representative segment of the midpiece showing the plasma membrane(PM)and mitochondrial sheath(MS)surrounding the 9 outer dense fibers (ODFs).Within the ODFs are the components of the axoneme:the 9 outer microtubule doublets of the axoneme (OMDA)with associated dynein arms(DA)and radial spokes (RS)and the central pair of microtubule doublets(CP).In an actual sperm,several projections are present on the CP.These are not shown in this figure.(C)Schematic cross-section through a representative segment of the principal piece showing the PM surrounding 7 ODFs.ODFs 3 and 8 have been replaced by the two longitudinal columns of the fibrous sheath(LC).The two columns are connected by transverse ribs (TR).The axonemal components are unchanged.(D)Schematic cross-section through a representative segment of the end piece.The ODFs and FS tapered at the temmination of the principal piece and are no longer present in the end piece,thus leaving only the PM to surround the axoneme
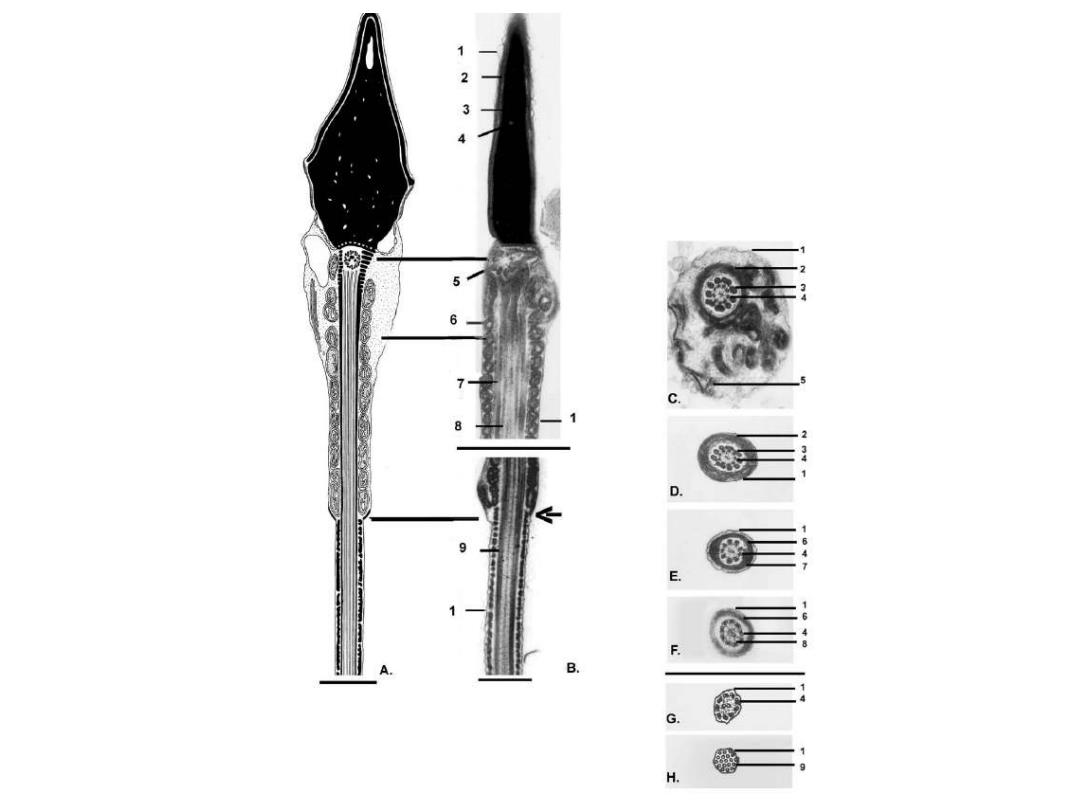
3 A 6 34 D. E 三 B. G. H
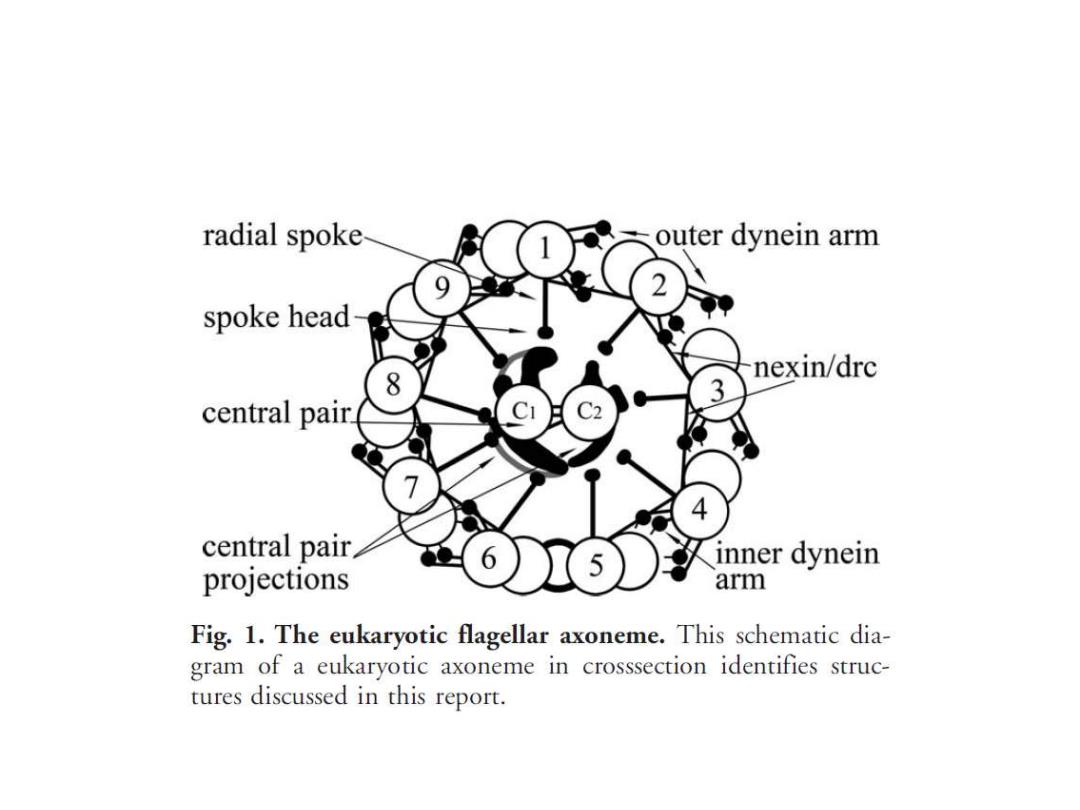
radial spoke outer dynein arm spoke head 8 nexin/drc 3 central pair. central pair inner dynein projections arm Fig.1.The eukaryotic flagellar axoneme.This schematic dia- gram of a eukaryotic axoneme in crosssection identifies struc- tures discussed in this report