
Mass Spectrometry The molecular ion peak can fragment Due to the high energy of the radical/cation generated,this species can fragment CH3CH2· m/z72 m/z43 CH3· m/z57 Remember only the charged species will be detected (the radical species will not be affected by the magnetic field) The probability of obtaining a given fragment is due to the STABILITY of the cations produced
The molecular ion peak can fragment Due to the high energy of the radical/cation generated, this species can fragment Remember only the charged species will be detected (the radical species will not be affected by the magnetic field) The probability of obtaining a given fragment is due to the STABILITY of the cations produced Mass Spectrometry m/z 72 CH3CH2 m/z 43 CH3 m/z 57

Effect of Isotopes Remember that an isotope has the same number of protons and electrons, but a different number of neutrons Since neutrons and protons are the "heavy"parts of an atom, the extra number of neutrons will cause a greater mass In a mass spectrometer we can see the effect of this by peaks above the molecular ion peak (M,M+1,M+2,etc.) The ratio of these peaks is diagnostic for which atoms are present The natural abundance of isotopes is well known M M+1 M+2 X 100% C 98.9% 1.1% S 95% 0.8% 4.2% CI 75.5% 24.5% Br 50.5% 49.5% I 100%
Effect of Isotopes Remember that an isotope has the same number of protons and electrons, but a different number of neutrons Since neutrons and protons are the “heavy” parts of an atom, the extra number of neutrons will cause a greater mass In a mass spectrometer we can see the effect of this by peaks above the molecular ion peak (M, M+1, M+2, etc.) M M+1 M+2 H 100% C 98.9% 1.1% S 95% 0.8% 4.2% Cl 75.5% 24.5% Br 50.5% 49.5% I 100% The ratio of these peaks is diagnostic for which atoms are present The natural abundance of isotopes is well known

Effect of Isotopes Can distinguish atoms by the ratio of peaks above the molecular ion Especially useful to distinguish which halogen is present Br 人 m/z78 m/z122 m/z170 M/M+2=3 M/M+2=1 100 h3--4951 80 60 40 M/M+2卡1 20 0-tmmpmttrprtimm mmmmjmmphmttimmmmmmmpmmirtpmmmmr 10 20 30 40 50 60708090100110120 m/z
Can distinguish atoms by the ratio of peaks above the molecular ion Especially useful to distinguish which halogen is present Cl Br I m/z 78 M/M+2 = 3 ~ 3/1 m/z 122 M/M+2 = 1 M/M+2 = 1 m/z 170 Effect of Isotopes

Mass Spectrometry Nitrogen Nitrogen is also diagnostic in a mass spectrum due to the odd/even parity of the mass Consider small molecules and their corresponding mass CH m/z=16 NH m/z=17 The molecular ion peak for a molecule with one nitrogen is always odd, all other common atoms in an organic compound yield an even mass
Nitrogen Nitrogen is also diagnostic in a mass spectrum due to the odd/even parity of the mass Consider small molecules and their corresponding mass CH4 m/z = 16 NH3 m/z = 17 The molecular ion peak for a molecule with one nitrogen is always odd, all other common atoms in an organic compound yield an even mass Mass Spectrometry
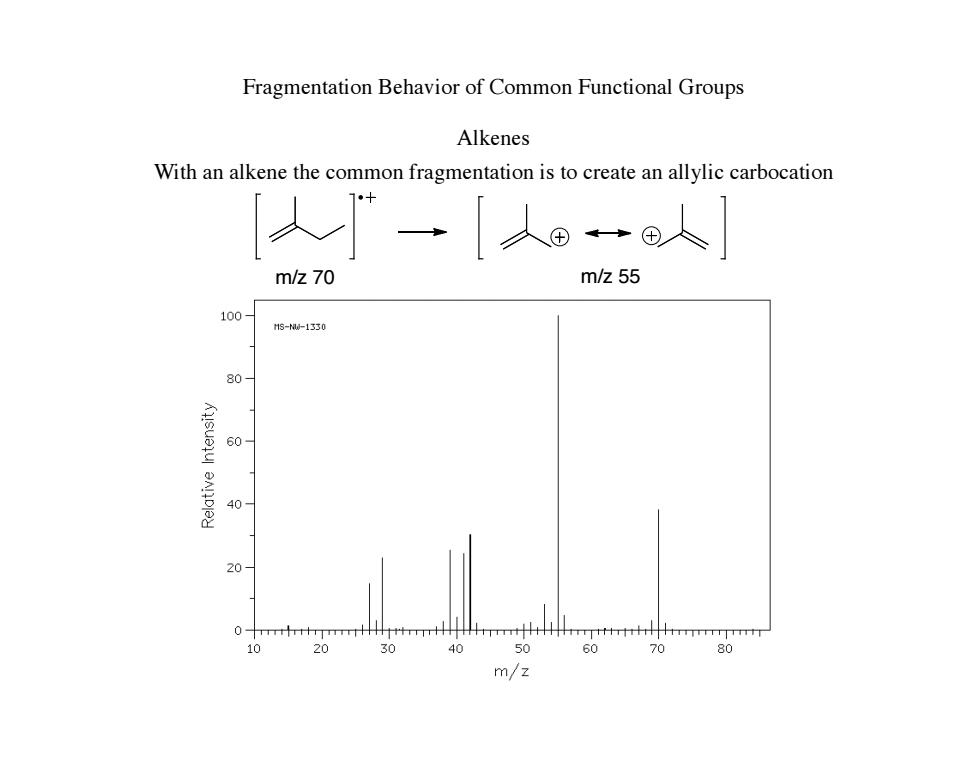
Fragmentation Behavior of Common Functional Groups Alkenes With an alkene the common fragmentation is to create an allylic carbocation 人 ”→人®人 m/z70 m/z55 100 13--1330 80 60 40 10 30 60 70 80 m/z
Fragmentation Behavior of Common Functional Groups Alkenes With an alkene the common fragmentation is to create an allylic carbocation m/z 70 m/z 55