
Introduction 3. Packages are often defined by their intended destination ⚫ Consumer package: A package that will ultimately reach the consumer as a unit of sale from a merchandising outlet. ⚫ Industrial package: A package for delivering goods from manufacturer to manufacturer. Industrial packaging usually, but not always, contains goods or materials for further processing
Introduction 3. Packages are often defined by their intended destination ⚫ Consumer package: A package that will ultimately reach the consumer as a unit of sale from a merchandising outlet. ⚫ Industrial package: A package for delivering goods from manufacturer to manufacturer. Industrial packaging usually, but not always, contains goods or materials for further processing
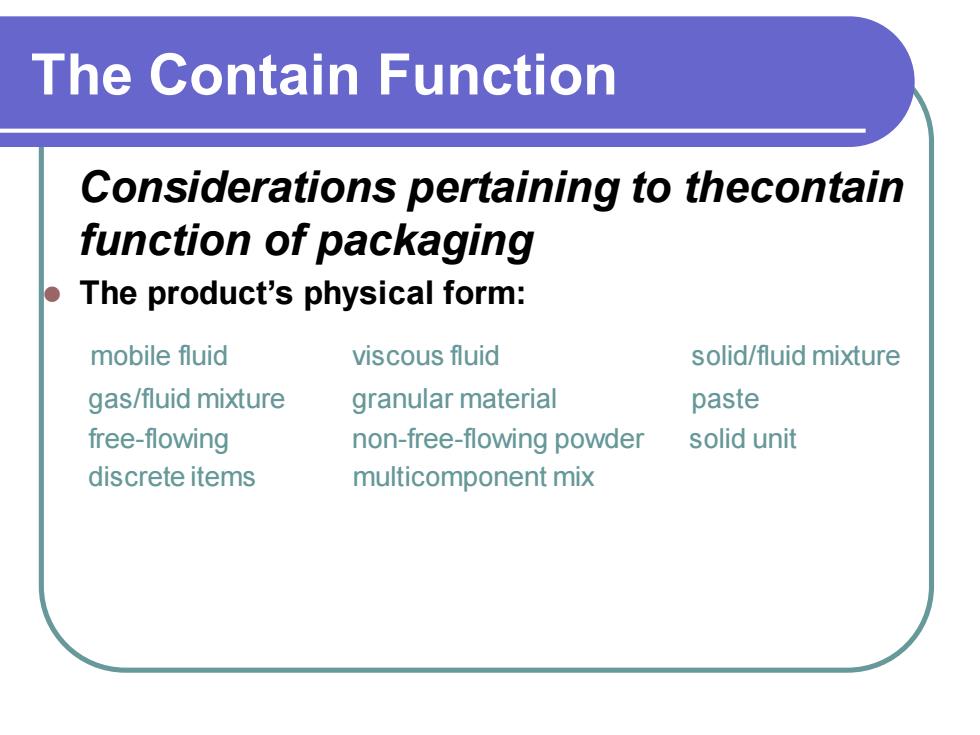
The Contain Function Considerations pertaining to thecontain function of packaging ⚫ The product’s physical form: mobile fluid viscous fluid solid/fluid mixture gas/fluid mixture granular material paste free-flowing non-free-flowing powder solid unit discrete items multicomponent mix
The Contain Function Considerations pertaining to thecontain function of packaging ⚫ The product’s physical form: mobile fluid viscous fluid solid/fluid mixture gas/fluid mixture granular material paste free-flowing non-free-flowing powder solid unit discrete items multicomponent mix
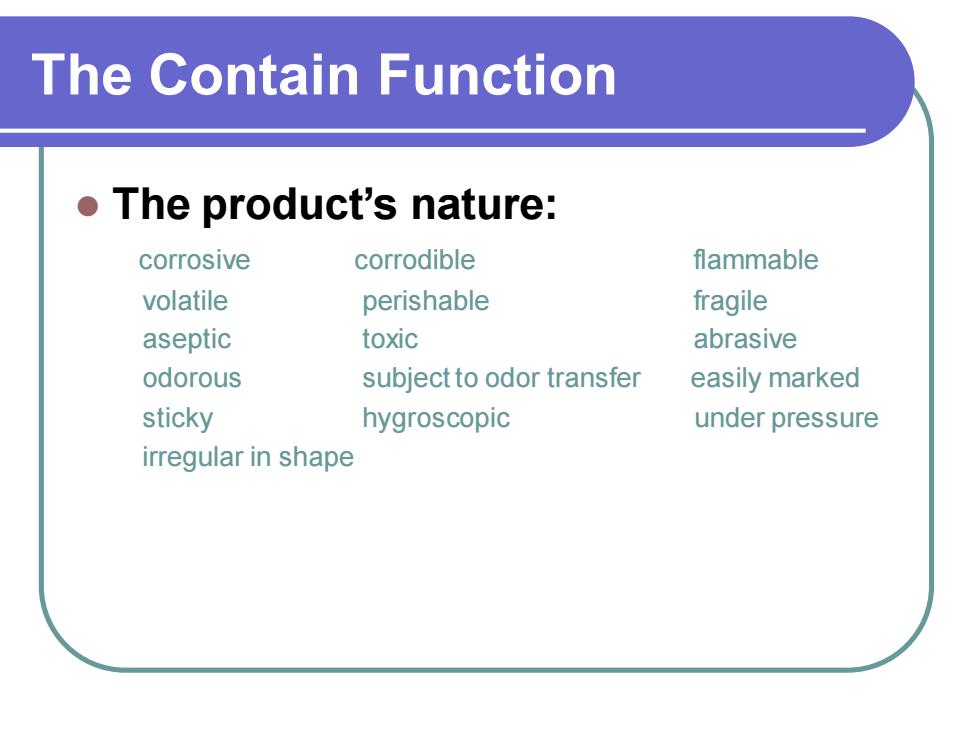
The Contain Function ⚫ The product’s nature: corrosive corrodible flammable volatile perishable fragile aseptic toxic abrasive odorous subject to odor transfer easily marked sticky hygroscopic under pressure irregular in shape
The Contain Function ⚫ The product’s nature: corrosive corrodible flammable volatile perishable fragile aseptic toxic abrasive odorous subject to odor transfer easily marked sticky hygroscopic under pressure irregular in shape

The Protect/Preserve Function 1. Considerations related to the protect/preserve function ⚫ “Protect” refers to the prevention of physical damage. Specifics on what will cause loss of value (damage) must be known. ⚫ “Preserve” refers to stopping or inhibiting chemical and biological change and to the extension of food shelf life beyond the product’s natural life or the maintenance of sterility in food or medical products
The Protect/Preserve Function 1. Considerations related to the protect/preserve function ⚫ “Protect” refers to the prevention of physical damage. Specifics on what will cause loss of value (damage) must be known. ⚫ “Preserve” refers to stopping or inhibiting chemical and biological change and to the extension of food shelf life beyond the product’s natural life or the maintenance of sterility in food or medical products

The Protect/Preserve Function 2. Examples of protective packaging problems Table 2.1 Examples of protective packaging problems and concerns Condition Quantification or DesignRequirement Vibration Determine resonant frequencies Mechanical shock Determine fragility factor (drop height) Abrasion Eliminate or isolate relative movement Deformation Determine safe compressive load Temperature Determine critical values Relative humidity Determine critical values Water Design liquid barrier Tampering Design appropriate systems
The Protect/Preserve Function 2. Examples of protective packaging problems Table 2.1 Examples of protective packaging problems and concerns Condition Quantification or DesignRequirement Vibration Determine resonant frequencies Mechanical shock Determine fragility factor (drop height) Abrasion Eliminate or isolate relative movement Deformation Determine safe compressive load Temperature Determine critical values Relative humidity Determine critical values Water Design liquid barrier Tampering Design appropriate systems