
Lesson 6 Glass Containers 第6课 玻璃容器 ⚫ Glass Types and General Properties ⚫ Bottle Manufacture ⚫ Bottle Design Features
Lesson 6 Glass Containers 第6课 玻璃容器 ⚫ Glass Types and General Properties ⚫ Bottle Manufacture ⚫ Bottle Design Features
一. Glass Types and General Properties ⚫ Definition and characters- an inorganic substance fused at high temperatures and cooled quickly ⚫ About the principle component -silica (quartz), ⚫ The ingredients of the components and different formulations. ⚫ Other mineral compounds be used to achieve improved properties: decolorizers – to clear; colorants– change the appearance. ⚫ Other glass types used for special packaging purposes. lead compounds, boron compounds, borosilicate glasses. ⚫ The problems of different formulations include soda-lime and regular container glass are mixed when recycling
一. Glass Types and General Properties ⚫ Definition and characters- an inorganic substance fused at high temperatures and cooled quickly ⚫ About the principle component -silica (quartz), ⚫ The ingredients of the components and different formulations. ⚫ Other mineral compounds be used to achieve improved properties: decolorizers – to clear; colorants– change the appearance. ⚫ Other glass types used for special packaging purposes. lead compounds, boron compounds, borosilicate glasses. ⚫ The problems of different formulations include soda-lime and regular container glass are mixed when recycling
一. Glass Types and General Properties Advantages as a packaging material: ⚫ inert to most chemicals ⚫ perfect foods container. ⚫ impermeability ⚫ clarity ⚫ perceived image ⚫ rigidity ⚫ stable at high temperatures Disadvantages : breakability; high weight; high energy costs
一. Glass Types and General Properties Advantages as a packaging material: ⚫ inert to most chemicals ⚫ perfect foods container. ⚫ impermeability ⚫ clarity ⚫ perceived image ⚫ rigidity ⚫ stable at high temperatures Disadvantages : breakability; high weight; high energy costs

二. Bottle Manufacture 1. Blowing the Bottle or Jar ⚫ Process: "blow-and-blow”; "press-and-blow" ⚫ two molds: blank mold forms the neck and the initial shape blow mold produce the final shape ⚫ A blank mold comes in a number of sections: finish section cavity section (made in two halves to allow parison removal) a guide or funnel for inserting the gob a seal for the gob opening once the gob is settled in the mold blowing tubes through the gob and neck openings
二. Bottle Manufacture 1. Blowing the Bottle or Jar ⚫ Process: "blow-and-blow”; "press-and-blow" ⚫ two molds: blank mold forms the neck and the initial shape blow mold produce the final shape ⚫ A blank mold comes in a number of sections: finish section cavity section (made in two halves to allow parison removal) a guide or funnel for inserting the gob a seal for the gob opening once the gob is settled in the mold blowing tubes through the gob and neck openings
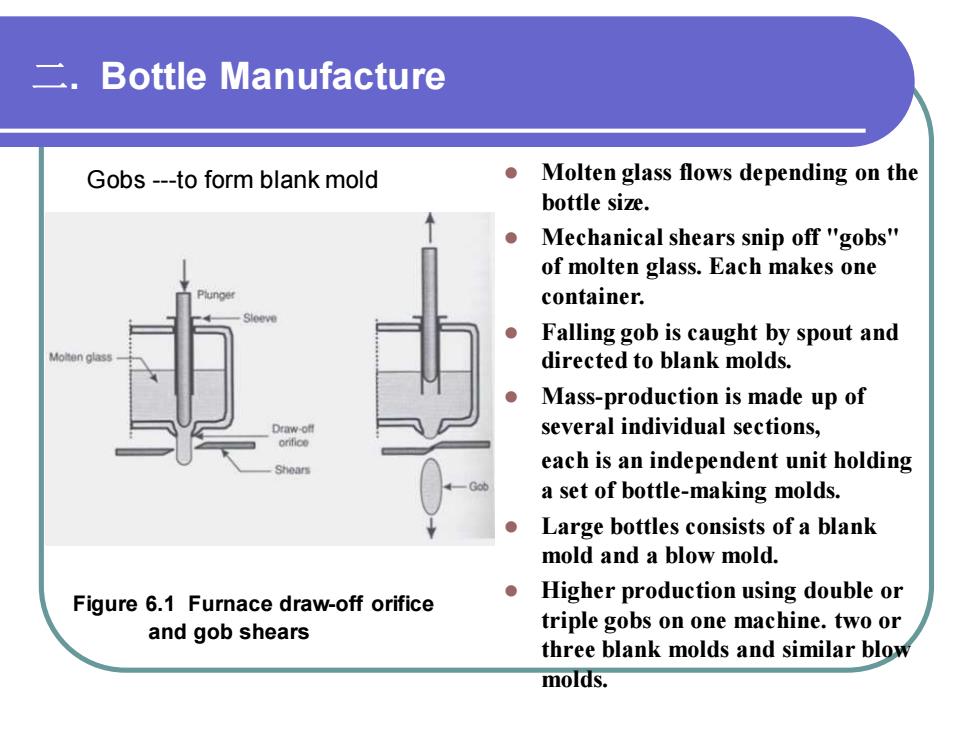
二. Bottle Manufacture Figure 6.1 Furnace draw-off orifice and gob shears ⚫ Molten glass flows depending on the bottle size. ⚫ Mechanical shears snip off "gobs" of molten glass. Each makes one container. ⚫ Falling gob is caught by spout and directed to blank molds. ⚫ Mass-production is made up of several individual sections, each is an independent unit holding a set of bottle-making molds. ⚫ Large bottles consists of a blank mold and a blow mold. ⚫ Higher production using double or triple gobs on one machine. two or three blank molds and similar blow molds. Gobs -to form blank mold
二. Bottle Manufacture Figure 6.1 Furnace draw-off orifice and gob shears ⚫ Molten glass flows depending on the bottle size. ⚫ Mechanical shears snip off "gobs" of molten glass. Each makes one container. ⚫ Falling gob is caught by spout and directed to blank molds. ⚫ Mass-production is made up of several individual sections, each is an independent unit holding a set of bottle-making molds. ⚫ Large bottles consists of a blank mold and a blow mold. ⚫ Higher production using double or triple gobs on one machine. two or three blank molds and similar blow molds. Gobs -to form blank mold