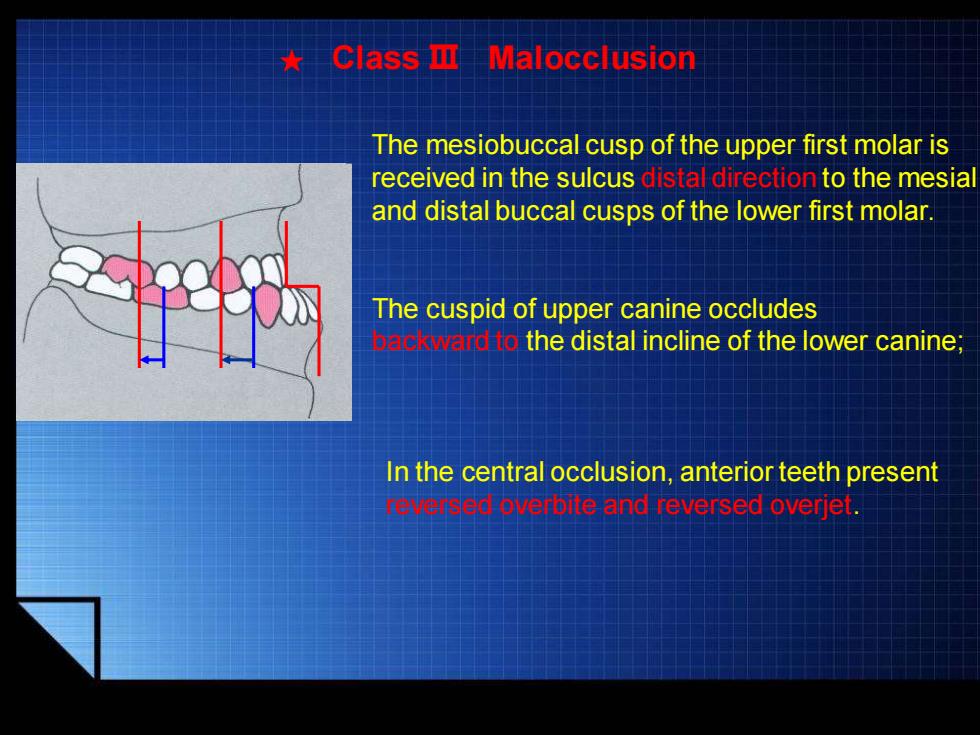
★Class m Malocclusion The mesiobuccal cusp of the upper first molar is received in the sulcus distal direction to the mesial and distal buccal cusps of the lower first molar. The cuspid of upper canine occludes ard to the distal incline of the lower canine; In the central occlusion,anterior teeth present ed bverbite and reversed overjet
The mesiobuccal cusp of the upper first molar is received in the sulcus distal direction to the mesial and distal buccal cusps of the lower first molar. The cuspid of upper canine occludes backward to the distal incline of the lower canine; ★ Class Ⅲ Malocclusion In the central occlusion, anterior teeth present reversed overbite and reversed overjet
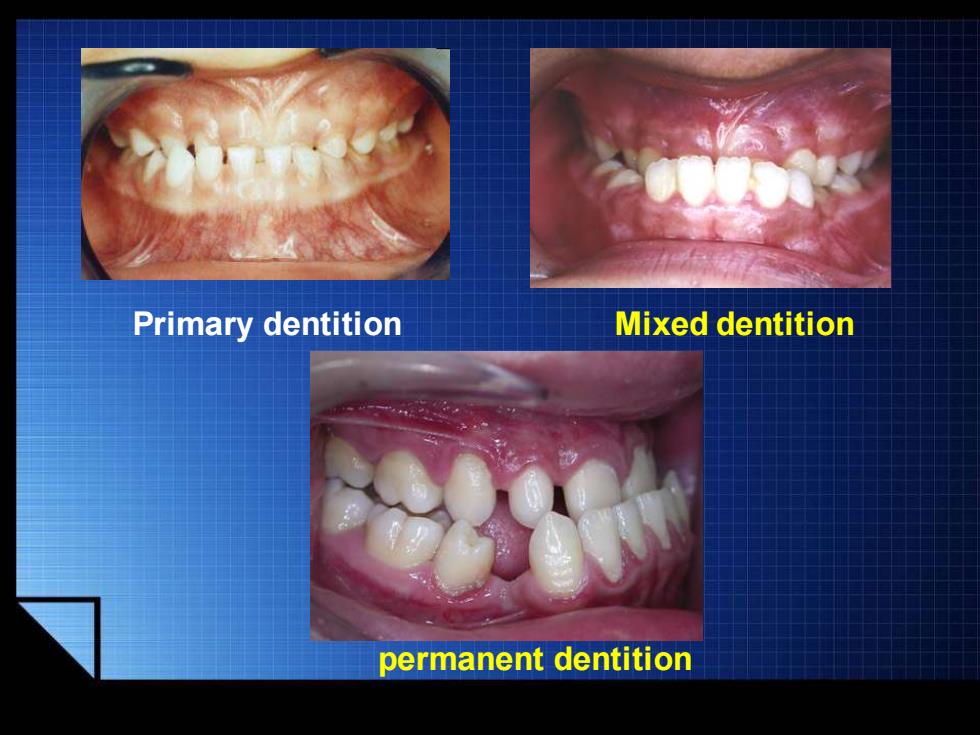
Primary dentition Mixed dentition permanent dentition
Primary dentition Mixed dentition permanent dentition

Part 2 Etiology (familiar)
Part 2 Etiology (familiar)

Etiology ANIMATION FACTORY 1.Inheritance *Litton SF et al:A genetic study of Class Ill malocclusion,Am J Orthod 58:565577,1970. *Harris JE,Kowalski CJ,Watnick SS:Genetic factors in the shape of the craniofacial complex,Angle Orthod 43:109-111,1973. McGuigan DG:The Hapsburgs,London,1966,WH Allen. *Rakosi T,Schilli W:Class Ill anomalies:a coordinated approach to skeletal,dental,and soft tissue problems,J Oral Surg 39:860-870,1981
Etiology 1. Inheritance ☆Litton SF et al: A genetic study of Class III malocclusion,Am J Orthod 58:565 577, 1970. ☆ Harris JE, Kowalski CJ, Watnick SS: Genetic factors in the shape of the craniofacial complex, Angle Orthod 43:109-111,1973. ☆ McGuigan DG: The Hapsburgs, London, 1966, WH Allen. ☆ Rakosi T, Schilli W: Class III anomalies: a coordinated approach to skeletal, dental, and soft tissue problems, J Oral Surg 39:860-870, 1981
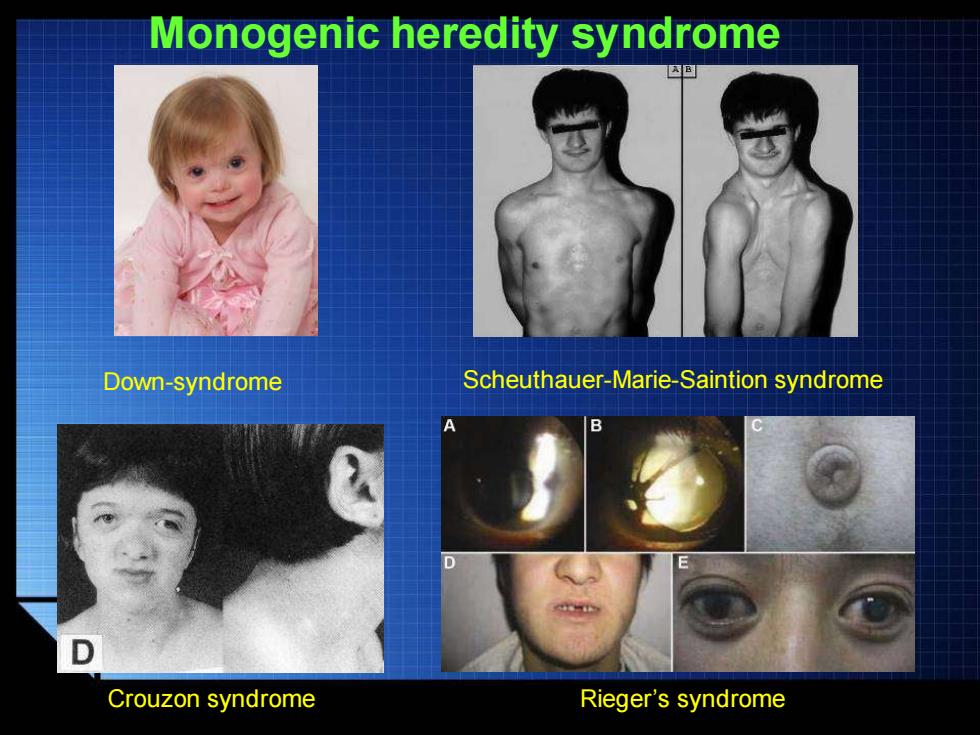
Monogenic heredity syndrome A B Down-syndrome Scheuthauer-Marie-Saintion syndrome Crouzon syndrome Rieger's syndrome
Monogenic heredity syndrome Down-syndrome Scheuthauer-Marie-Saintion syndrome Crouzon syndrome Rieger’s syndrome