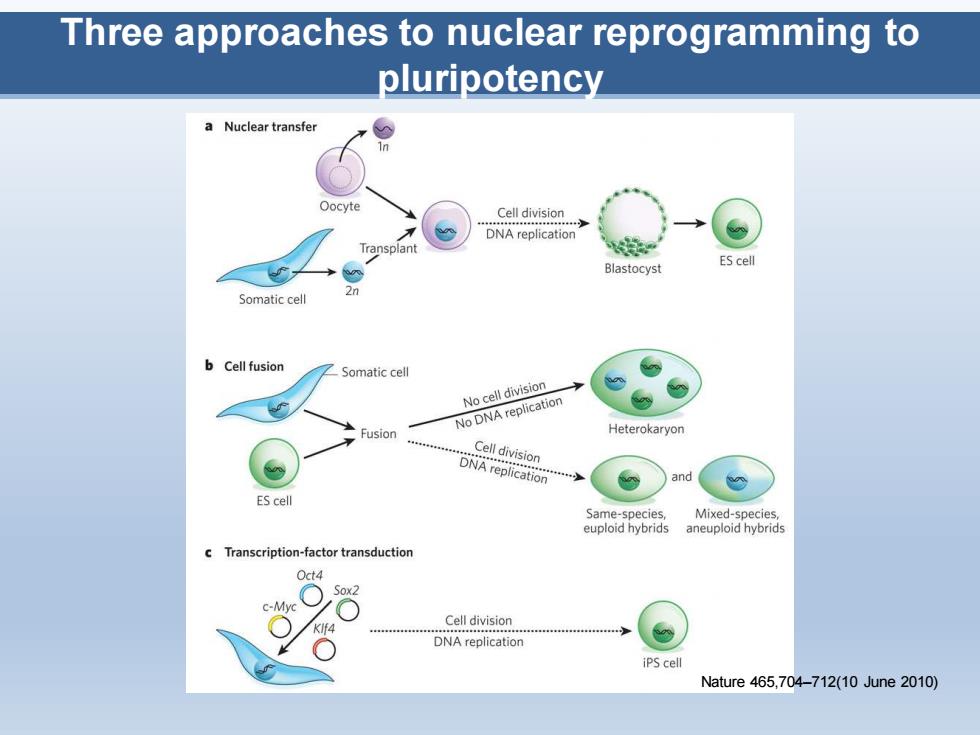
Three approaches to nuclear reprogramming to pluripotency a Nuclear transfer Oocyte Cell division DNA replication Transplant Blastocyst ES cell Somatic cell 2n b Cell fusion Somatic cell No cell division No DNA replication Fusion Heterokaryon Cell division DNA replication and ES cell Same-species, Mixed-species euploid hybrids aneuploid hybrids c Transcription-factor transduction Oct4 Cell division DNA replication iPS cell Nature465,704-712(10June2010)
Three approaches to nuclear reprogramming to pluripotency Nature 465,704–712(10 June 2010)
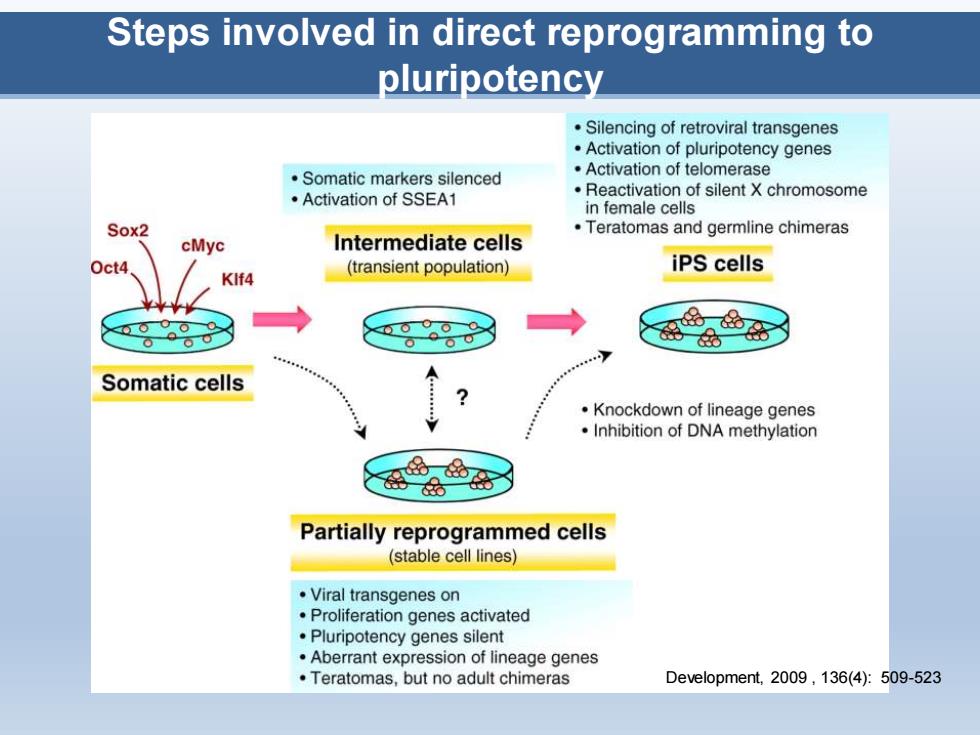
Steps involved in direct reprogramming to pluripotency Silencing of retroviral transgenes Activation of pluripotency genes Somatic markers silenced Activation of telomerase ·Activation of SSEA1 Reactivation of silent X chromosome in female cells Sox2 Teratomas and germline chimeras cMyc Intermediate cells Oct4 (transient population) iPS cells KIf4 7 Somatic cells Knockdown of lineage genes Inhibition of DNA methylation Partially reprogrammed cells (stable cell lines) Viral transgenes on Proliferation genes activated Pluripotency genes silent Aberrant expression of lineage genes Teratomas,but no adult chimeras Development,.2009,136(4):509-523
Steps involved in direct reprogramming to pluripotency Development, 2009 , 136(4): 509-523

人胚胎干细胞定向诱导分化 05050 5 20m 0 07 1421283542 49 56 B 时间ld
人胚胎干细胞定向诱导分化
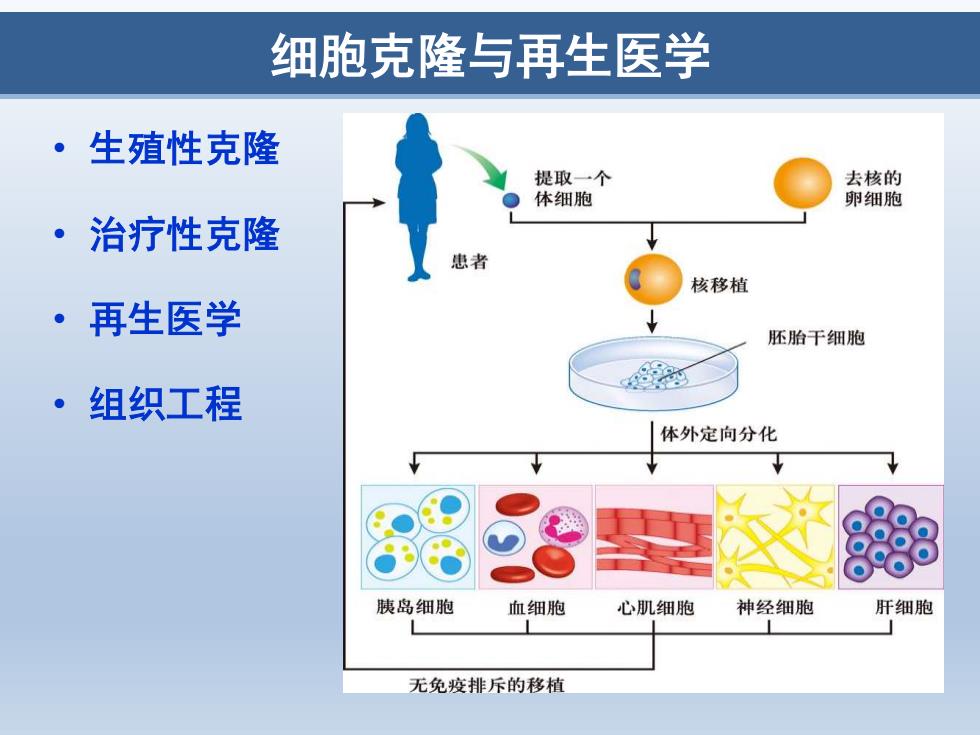
细胞克隆与再生医学 ·生殖性克隆 提取一个 去核的 体细胞 卵细胞 治疗性克隆 患者 核移植 ·再生医学 胚胎干细胞 4型 ·组织工程 体外定向分化 胰岛细胞 血细胞 心肌细胞 神经细胞 肝细胞 无免疫排斥的移植
细胞克隆与再生医学 • 生殖性克隆 • 治疗性克隆 • 再生医学 • 组织工程
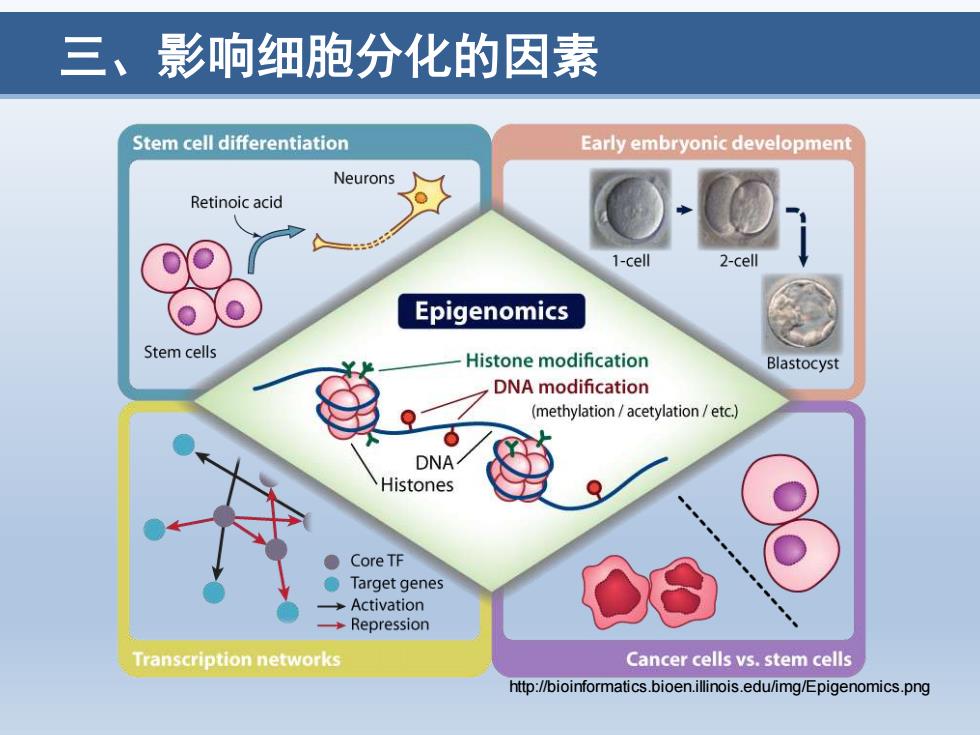
三、影响细胞分化的因素 Stem cell differentiation Early embryonic development Neurons Retinoic acid cell Epigenomics Stem cells Histone modification Blastocyst DNA modification (methylation/acetylation/etc.) DNA Histones ● Core TF ● Target genes →Activation →Repression Transcription networks Cancer cells vs.stem cells http://bioinformatics.bioen.illinois.edu/img/Epigenomics.png
三、影响细胞分化的因素 http://bioinformatics.bioen.illinois.edu/img/Epigenomics.png