Definitions of Protein Structure Primary structure-amino acid sequence Secondary structure-local conformation of peptide backbone Tertiary structure-interaction of different secondary structures on same polypeptide Quaternary structure-interaction of different polypeptides in structure that has more than one protein component
Definitions of Protein Structure Primary structure – amino acid sequence Secondary structure–local conformation of peptide backbone Tertiary structure– interaction of different secondary structures on same polypeptide Quaternary structure– interaction of different polypeptides in structure that has more than one protein component
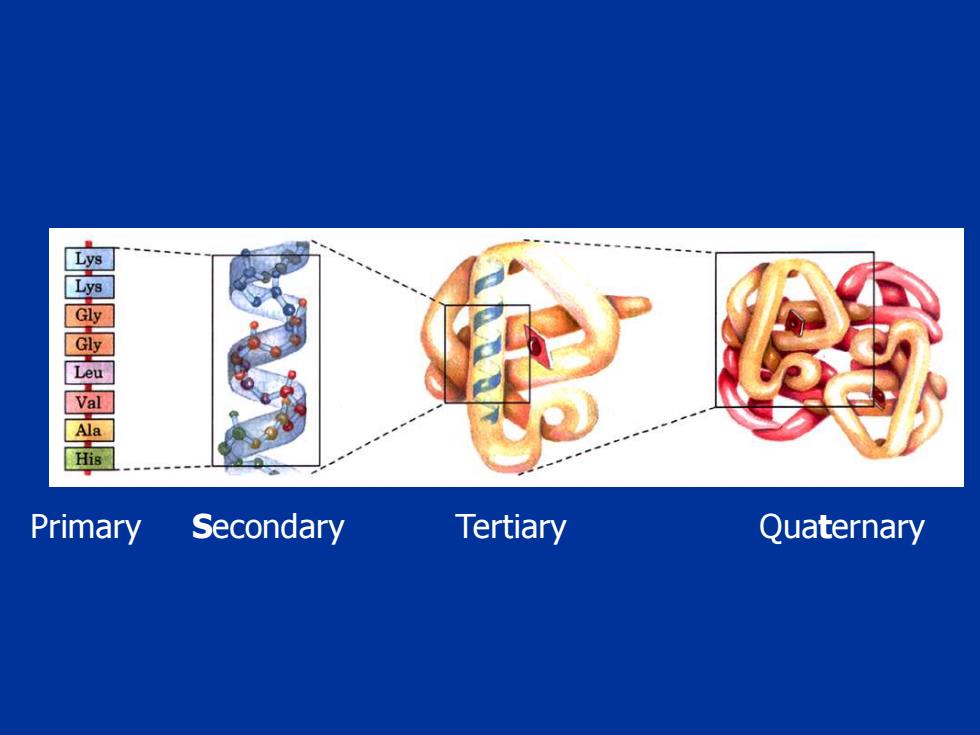
窗 His Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary
Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary

3.1.Forces Influencing Protein Structure Hydrogen Bonds Hydrophobic Interactions Electrostatic Interactions Van der Waals Interaction
3.1 • Forces Influencing Protein Structure Hydrogen Bonds Hydrophobic Interactions Electrostatic Interactions Van der Waals Interaction

Non-bonding Forces Influencing Protein Structures Amino acids of a protein are joined by covalent bonding interactions.The polypeptide is folded in three dimension by non-bonding interactions.These interactions can easily be disrupted by extreme pH,temperature,denaturants,reducing reagents.We will discuss the nature of these types of forces H-bond interactions(12-30 kJ/mol) Hydrophobic Interactions(<40 kJ/mol) Electrostatic Interactions(20 kJ/mol) Van Der Waals Interactions(0.4-4 kJ/mol) The total inter-atomic force acting between two atoms is the sum of all the forces they exert on each other
Non-bonding Forces Influencing Protein Structures Amino acids of a protein are joined by covalent bonding interactions. The polypeptide is folded in three dimension by non-bonding interactions. These interactions can easily be disrupted by extreme pH, temperature, denaturants, reducing reagents. We will discuss the nature of these types of forces H-bond interactions (12-30 kJ/mol) Hydrophobic Interactions (<40 kJ/mol) Electrostatic Interactions (20 kJ/mol) Van Der Waals Interactions (0.4-4 kJ/mol) The total inter-atomic force acting between two atoms is the sum of all the forces they exert on each other
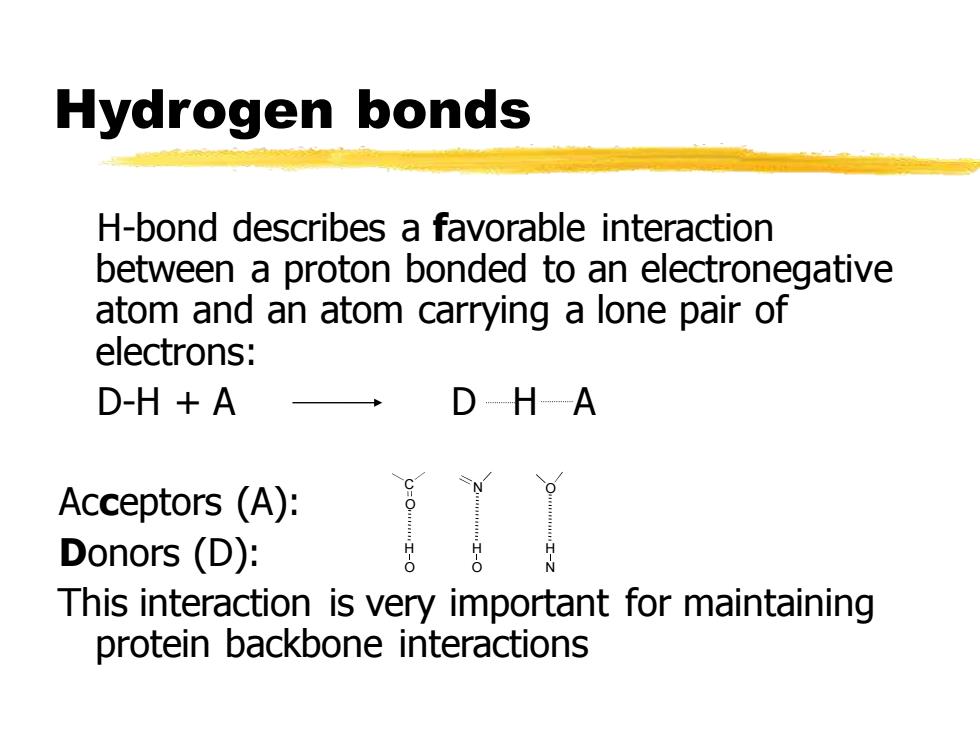
Hydrogen bonds H-bond describes a favorable interaction between a proton bonded to an electronegative atom and an atom carrying a lone pair of electrons: D-H +A D-HA Acceptors (A): Donors (D): This interaction is very important for maintaining protein backbone interactions
H-bond describes a favorable interaction between a proton bonded to an electronegative atom and an atom carrying a lone pair of electrons: D-H + A D H A Acceptors (A): Donors (D): This interaction is very important for maintaining protein backbone interactions Hydrogen bonds C N O O H O H O H N