Main Properties of Clonal Selection (Burnet,1978) Elimination of self antigens Proliferation and differentiation on contact of mature lymphocytes with antigen Restriction of one pattern to one differentiated cell and retention of that pattern by clonal descendants; 张Generation of new random genetic changes, subsequently expressed as diverse antibody patterns by a form of accelerated somatic mutation
Main Properties of Clonal Selection (Burnet, 1978) Elimination of self antigens Proliferation and differentiation on contact of mature lymphocytes with antigen Restriction of one pattern to one differentiated cell and retention of that pattern by clonal descendants; Generation of new random genetic changes, subsequently expressed as diverse antibody patterns by a form of accelerated somatic mutation
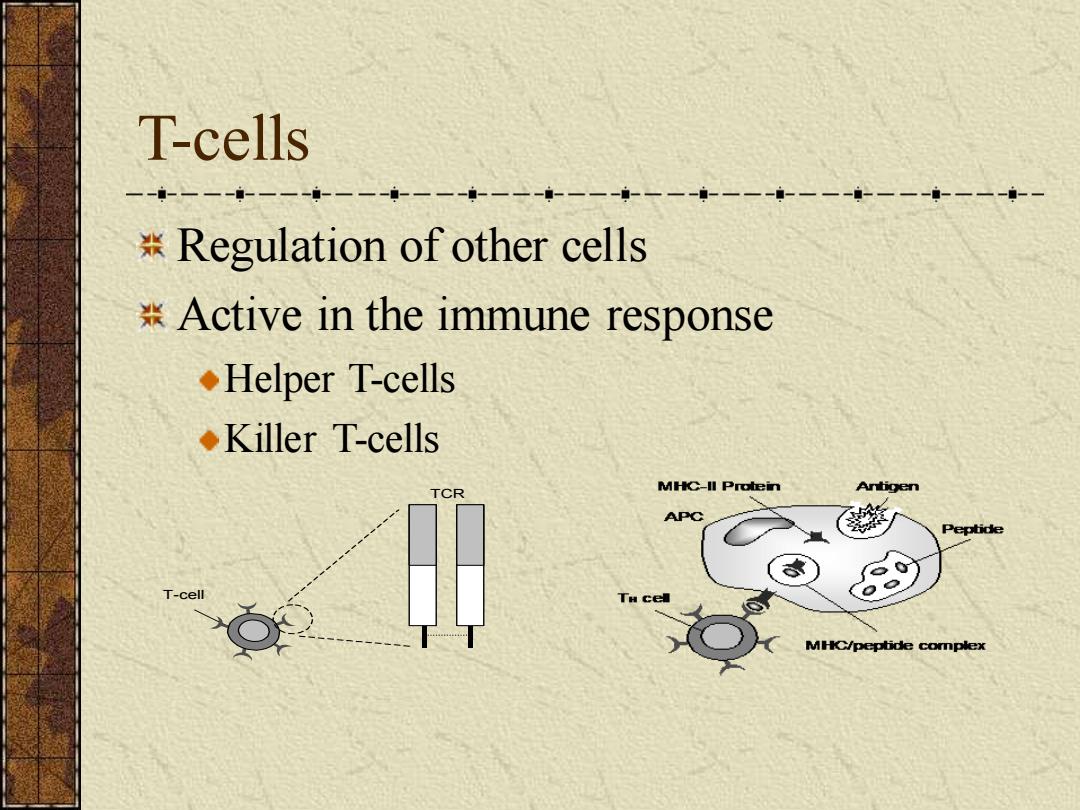
T-cells -------一---一一--一一--一一--一一---一 一--一一--一--一一-- Regulation of other cells *Active in the immune response ◆Helper T-cells ◆Killer T-cells TCR MHC-lI Protein APC Peptide T-cell MHC/peptide complex
T-cells Regulation of other cells Active in the immune response Helper T-cells Killer T-cells T-cell TCR
Reinforcement Learning and Immune Memory -0-一一--一一-0-一一--一一--一一 --一一-一一-- Repeated exposure to an antigen throughout a lifetime Primary,secondary immune responses Remembers encounters No need to start from scratch ◆Memory cells 张Associative memory
Reinforcement Learning and Immune Memory Repeated exposure to an antigen throughout a lifetime Primary, secondary immune responses Remembers encounters No need to start from scratch Memory cells Associative memory
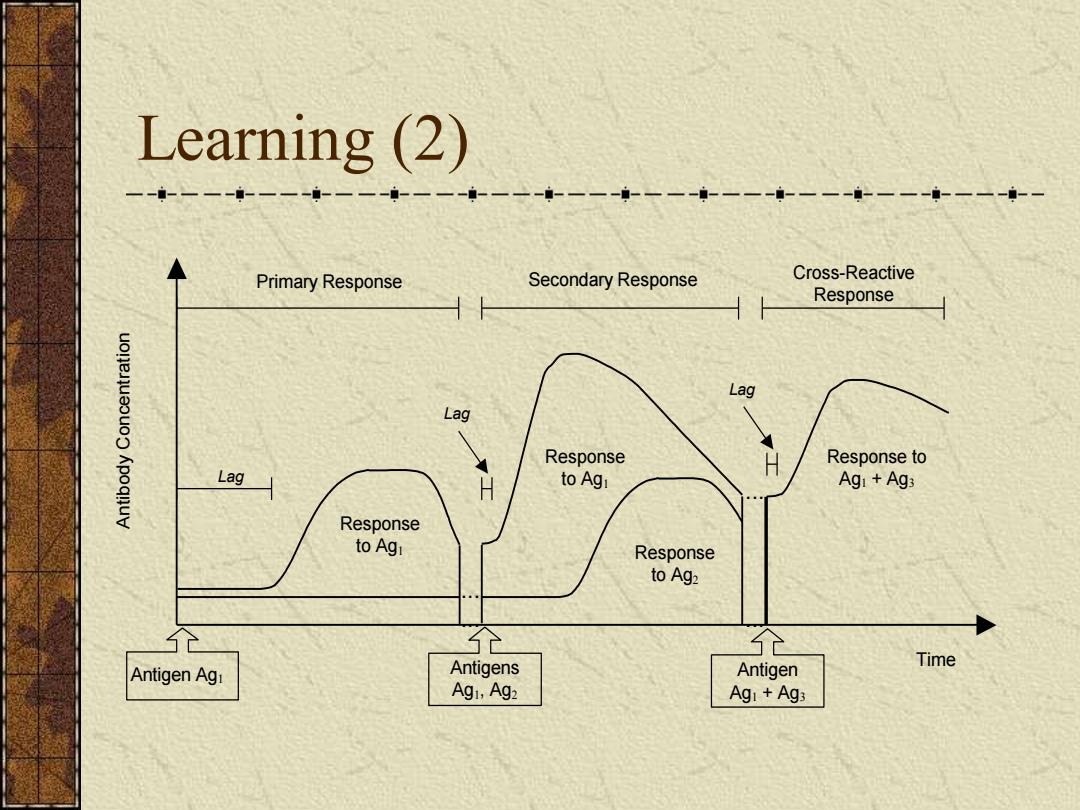
Learning (2) 一一--一一--一一--一一--- Primary Response Secondary Response Cross-Reactive Response Lag Lag Response Response to Lag to Agi Agi +Ag3 Response to Agi Response to Ag2 仓 Time Antigen Ag Antigens Antigen Agi,Ag2 Agi Ags
Learning (2) Antigen Ag1 Antigens Ag1, Ag2 Primary Response Secondary Response Lag Response to Ag1 Antibody Concentration Time Lag Response to Ag2 Response to Ag1 ... ... Cross-Reactive Response ... ... Antigen Ag1 + Ag3 Response to Ag1 + Ag3 Lag
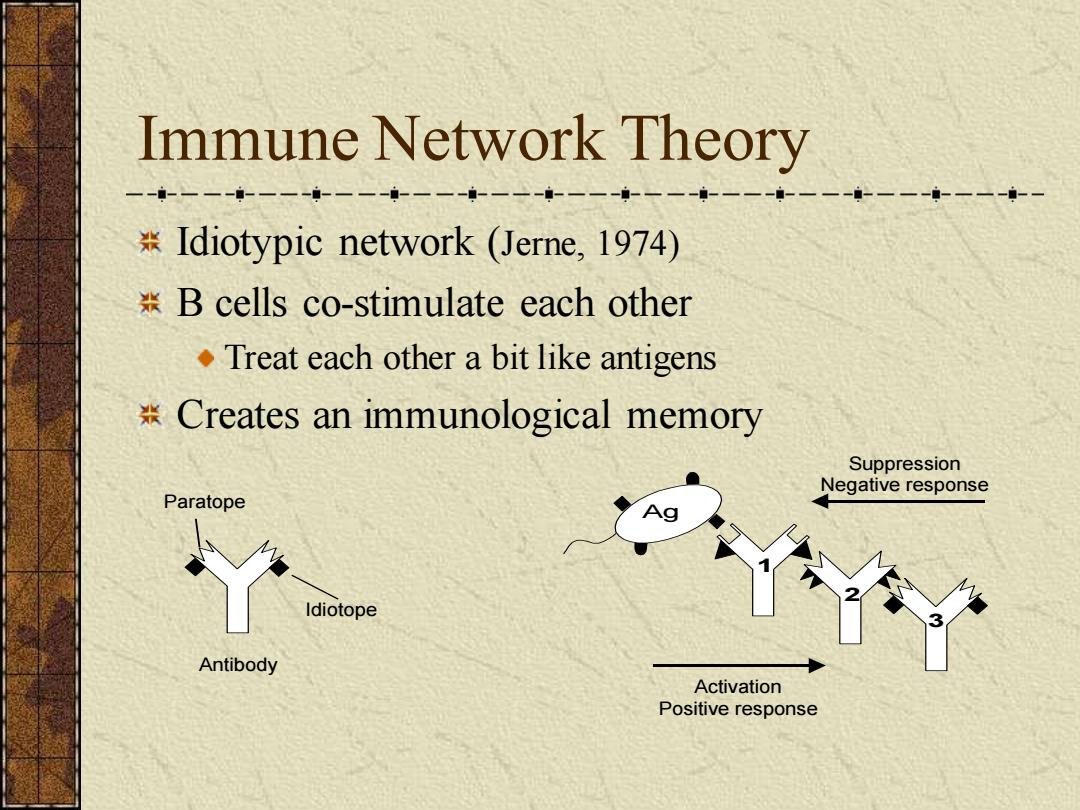
Immune Network Theory --i-一一--一一--一一--一一---一--一一----- Idiotypic network (Jerne,1974) B cells co-stimulate each other .Treat each other a bit like antigens Creates an immunological memory Suppression Negative response Paratope Idiotope Antibody Activation Positive response
Immune Network Theory Idiotypic network (Jerne, 1974) B cells co-stimulate each other Treat each other a bit like antigens Creates an immunological memory 1 2 3 Ag Activation Positive response Suppression Negative response Antibody Paratope Idiotope