
Database Schema Database schema--is the logical structure of the database. ■ Database instance--is a snapshot of the data in the database at a given instant in time. Example: ·schema: instructor(ID,name,dept name,salary) ·Instance: ID name dept name salary 22222 Einstein Physics 95000 12121 Wu Finance 90000 32343 El Said History 60000 45565 Katz Comp.Sci. 75000 98345 Kim Elec.Eng. 80000 76766 Crick Biology 72000 10101 Srinivasan Comp.Sci. 65000 58583 Califieri History 62000 83821 Brandt Comp.Sci. 92000 15151 Mozart Music 40000 33456 Gold Physics 87000 76543 Singh Finance 80000 Database System Concepts-7th Edition 2.7 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 2.7 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Database Schema ▪ Database schema -- is the logical structure of the database. ▪ Database instance -- is a snapshot of the data in the database at a given instant in time. ▪ Example: • schema: instructor (ID, name, dept_name, salary) • Instance:

Keys ■LetKcR K is a superkey of R if values for K are sufficient to identify a unique tuple of each possible relation r(R) Example:{ID}and {ID,name}are both superkeys of instructor. ■ Superkey K is a candidate key if K is minimal Example:{ID)is a candidate key for Instructor One of the candidate keys is selected to be the primary key. ·Vhich one? Foreign key constraint:Value in one relation must appear in another Referencing relation ·Referenced relation Example:dept name in instructor is a foreign key from instructor referencing department Database System Concepts-7th Edition 2.8 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 2.8 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Keys ▪ Let K R ▪ K is a superkey of R if values for K are sufficient to identify a unique tuple of each possible relation r(R) • Example: {ID} and {ID,name} are both superkeys of instructor. ▪ Superkey K is a candidate key if K is minimal Example: {ID} is a candidate key for Instructor ▪ One of the candidate keys is selected to be the primary key. • Which one? ▪ Foreign key constraint: Value in one relation must appear in another • Referencing relation • Referenced relation • Example: dept_name in instructor is a foreign key from instructor referencing department
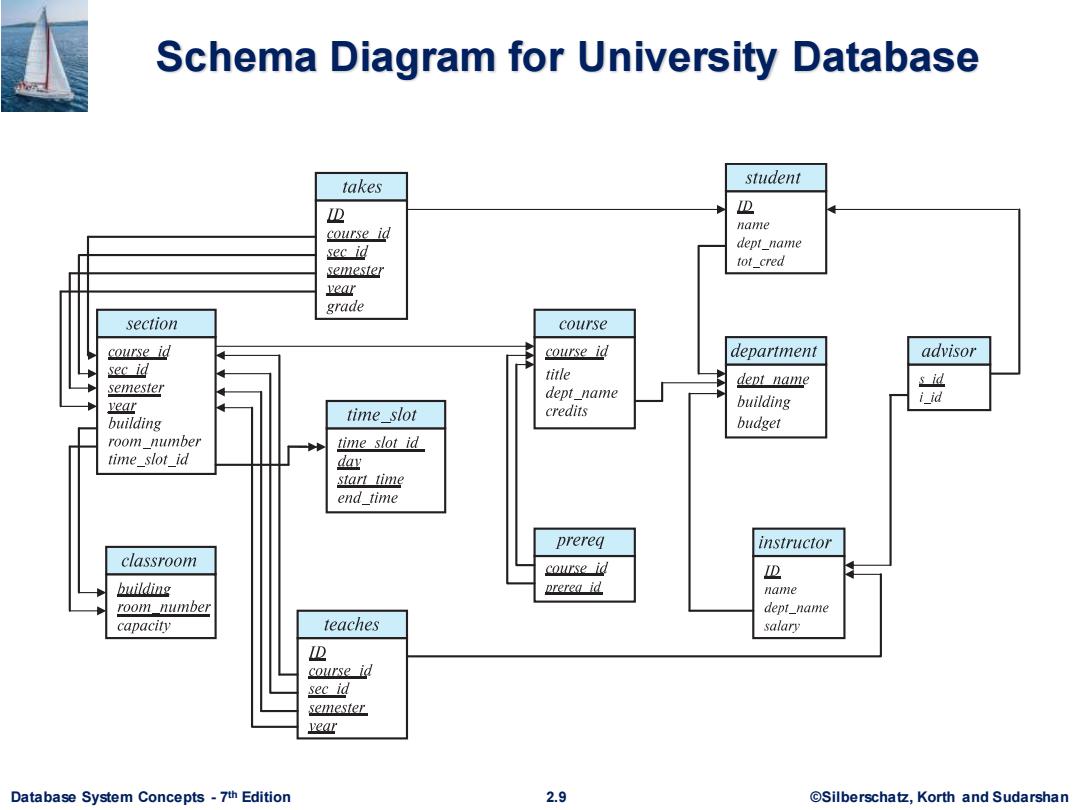
Schema Diagram for University Database takes student I D name course id sec id dept name semester tot_cred vear grade section course course id course id department advisor sec id title dept name s id semester dept_name building iid vear credits building time slot budget room number time slot id time slot id dav start time end time prereg instructor classroom course id D building prereg id name room number dept_name capacity teaches salary D course id sec id semester vear Database System Concepts-7th Edition 2.9 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 2.9 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Schema Diagram for University Database

Relational Query Languages Procedural versus non-procedural,or declarative ■“Pure”languages: ·Relational algebra Tuple relational calculus Domain relational calculus The above 3 pure languages are equivalent in computing power We will concentrate in this chapter on relational algebra Not Turing-machine equivalent Consists of 6 basic operations Database System Concepts-7th Edition 2.10 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 2.10 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Relational Query Languages ▪ Procedural versus non-procedural, or declarative ▪ “Pure” languages: • Relational algebra • Tuple relational calculus • Domain relational calculus ▪ The above 3 pure languages are equivalent in computing power ▪ We will concentrate in this chapter on relational algebra • Not Turing-machine equivalent • Consists of 6 basic operations

Relational Algebra A procedural language consisting of a set of operations that take one or two relations as input and produce a new relation as their result ■Six basic operators ·select:o project:Π 。union:U ·set difference:- 。 Cartesian product:x 。rename:p Database System Concepts-7th Edition 2.11 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 2.11 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Relational Algebra ▪ A procedural language consisting of a set of operations that take one or two relations as input and produce a new relation as their result. ▪ Six basic operators • select: • project: • union: • set difference: – • Cartesian product: x • rename: