
第十章 粪便检查 the examination of feces/stool
第十章 粪便检查 the examination of feces/stool

KEY POINTS 1.Collection and disposal of stool specimen 2.Physics examination and clinical value of stool 3.Visible composition and clinical value of the microscope examination 4.Principle、methodology assessment and clinical value of occult blood test 5.Quality control of stool examination
KEY POINTS 1.Collection and disposal of stool specimen 2.Physics examination and clinical value of stool 3.Visible composition and clinical value of the microscope examination 4.Principle、methodology assessment and clinical value of occult blood test 5.Quality control of stool examination
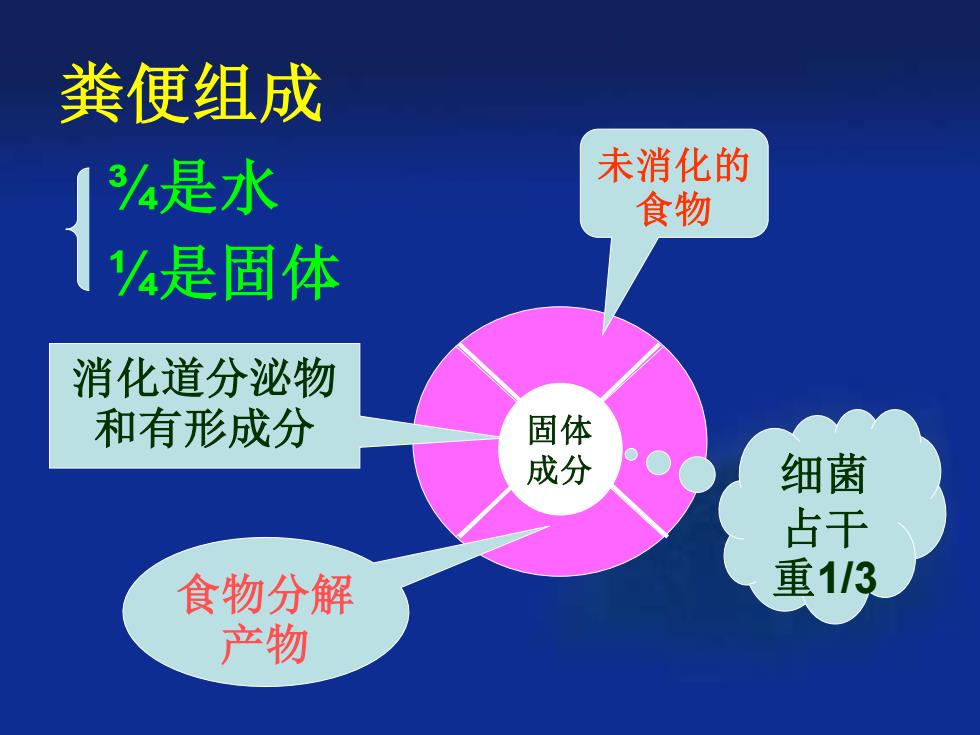
粪便组成 ¾是水 ¼是固体 未消化的 食物 消化道分泌物 和有形成分 食物分解 产物 细菌 占干 重1/3 固体 成分
粪便组成 ¾是水 ¼是固体 未消化的 食物 消化道分泌物 和有形成分 食物分解 产物 细菌 占干 重1/3 固体 成分

检查的主要目的 1.了解消化道以及消化器官是否有炎症、出血和 寄生虫感染等情况; 2.OB试验作为消化道肿瘤的过筛试验; 3.根据粪便的性状和组成,了解消化状况,借以 粗略判断胰腺外分泌功能; 4.检查粪便中有无致病菌以防治肠道传染病
检查的主要目的 1.了解消化道以及消化器官是否有炎症、出血和 寄生虫感染等情况; 2.OB试验作为消化道肿瘤的过筛试验; 3.根据粪便的性状和组成,了解消化状况,借以 粗略判断胰腺外分泌功能; 4.检查粪便中有无致病菌以防治肠道传染病

第一节 标本采集与处理 一、标本的采集 二、粪便标本的处理
第一节 标本采集与处理 一、标本的采集 二、粪便标本的处理