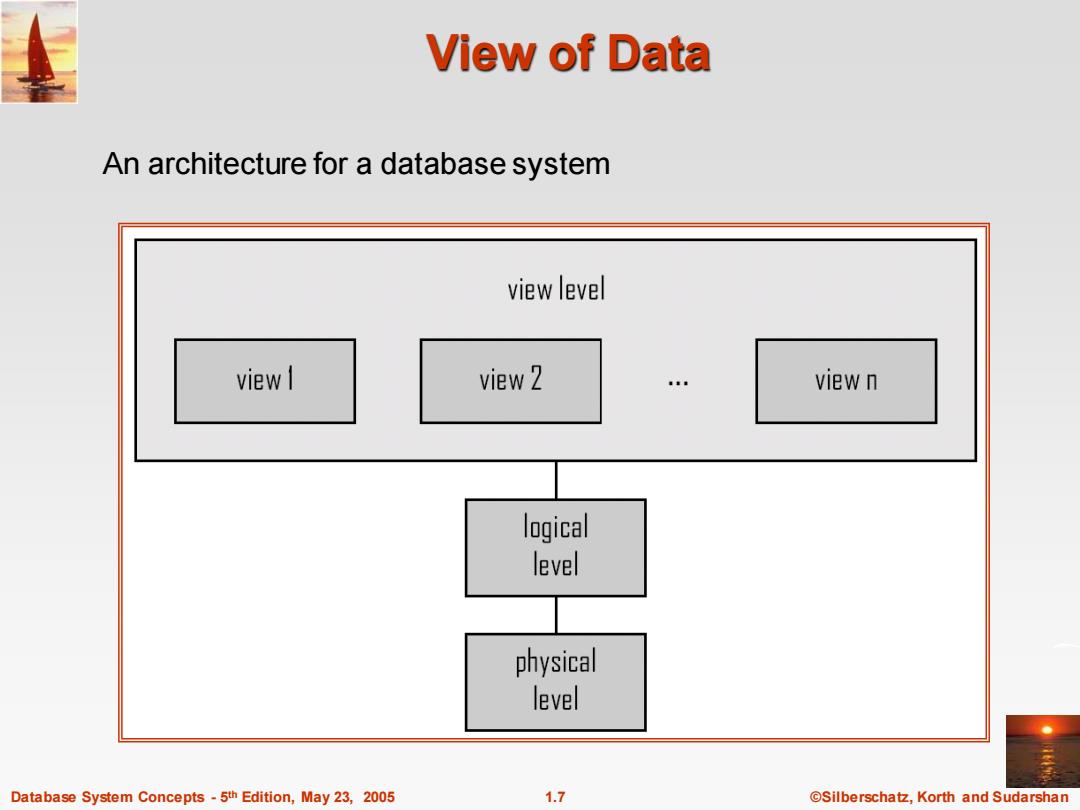
View of Data An architecture for a database system view level view 1 view 2 view n logical level physical level Database System Concepts-5th Edition,May 23,2005 1.7 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 1.7 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, May 23, 2005 View of Data An architecture for a database system
Instances and Schemas Similar to types and variables in programming languages Schema-the logical structure of the database Example:The database consists of information about a set of customers and accounts and the relationship between them) Analogous to type information of a variable in a program Physical schema:database design at the physical level Logical schema:database design at the logical level Instance-the actual content of the database at a particular point in time Analogous to the value of a variable Physical Data Independence-the ability to modify the physical schema without changing the logical schema Applications depend on the logical schema In general,the interfaces between the various levels and components should be well defined so that changes in some parts do not seriously influence others Database System Concepts-5th Edition,May 23,2005 1.8 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 1.8 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, May 23, 2005 Instances and Schemas Similar to types and variables in programming languages Schema – the logical structure of the database Example: The database consists of information about a set of customers and accounts and the relationship between them) Analogous to type information of a variable in a program Physical schema: database design at the physical level Logical schema: database design at the logical level Instance – the actual content of the database at a particular point in time Analogous to the value of a variable Physical Data Independence – the ability to modify the physical schema without changing the logical schema Applications depend on the logical schema In general, the interfaces between the various levels and components should be well defined so that changes in some parts do not seriously influence others
Data Models A collection of tools for describing Data Data relationships Data semantics Data constraints Relational model Entity-Relationship data model(mainly for database design) Object-based data models(Object-oriented and Object-relational) Semistructured data model (XML) Other older models: Network model Hierarchical model Database System Concepts-5th Edition,May 23,2005 1.9 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 1.9 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, May 23, 2005 Data Models A collection of tools for describing Data Data relationships Data semantics Data constraints Relational model Entity-Relationship data model (mainly for database design) Object-based data models (Object-oriented and Object-relational) Semistructured data model (XML) Other older models: Network model Hierarchical model
Data Manipulation Language (DML) Language for accessing and manipulating the data organized by the appropriate data model DML also known as query language Two classes of languages Procedural-user specifies what data is required and how to get those data Declarative (nonprocedural)-user specifies what data is required without specifying how to get those data SQL is the most widely used query language Database System Concepts-5th Edition,May 23,2005 1.10 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 1.10 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, May 23, 2005 Data Manipulation Language (DML) Language for accessing and manipulating the data organized by the appropriate data model DML also known as query language Two classes of languages Procedural – user specifies what data is required and how to get those data Declarative (nonprocedural) – user specifies what data is required without specifying how to get those data SQL is the most widely used query language
Data Definition Language(DDL) Specification notation for defining the database schema Example: create table account account-number char(10), balance integer) DDL compiler generates a set of tables stored in a data dictionary Data dictionary contains metadata(i.e.,data about data) Database schema Data storage and definition language Specifies the storage structure and access methods used Integrity constraints Domain constraints Referential integrity(references constraint in SQL) Assertions Authorization Database System Concepts-5th Edition,May 23,2005 1.11 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 1.11 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, May 23, 2005 Data Definition Language (DDL) Specification notation for defining the database schema Example: create table account ( account-number char(10), balance integer) DDL compiler generates a set of tables stored in a data dictionary Data dictionary contains metadata (i.e., data about data) Database schema Data storage and definition language Specifies the storage structure and access methods used Integrity constraints Domain constraints Referential integrity (references constraint in SQL) Assertions Authorization