
2013-2-27 Two-Phase Liquid-Vapor Mixture When the system is at the saturated liquid state additional heat transfer at fixed pressure results in the formation of vapor without change in temperature but with a considerable increase in specific volume as shown by movement of the blue dot. With additional heating at fixed pressure,more vapor is formed and specific volume increases further as shown by additional movement of the blue do At these states,the system now consists of a two-phas liquid-vapor mixture. Two-Phase Liquid-Vapor Mixture When a mixture of liquid and vapor exists in equilibrium,the liquid phase is a saturated liquid and the vapor phase is a saturated vapor. For a two-phase liquid-vapor mixture,the ratio of the mass of vapor present to the total mass of the mixture is its quality,x. mvapor The value of miquid+mvapor 86 At saturated liquid states,x= 0 12
2013-2-27 12 Two-Phase Liquid-Vapor Mixture ►When the system is at the saturated liquid state, additional heat transfer at fixed pressure results in the formation of vapor without change in temperature but with a considerable increase in specific volume as shown by movement of the blue dot. ►With additional heating at fixed pressure, more vapor is formed and specific volume increases further as shown by additional movement of the blue dot. ● f ● ►At these states, the system now consists of a two-phase liquid-vapor mixture. 3-23 Two-Phase Liquid-Vapor Mixture ►When a mixture of liquid and vapor exists in equilibrium, the liquid phase is a saturated liquid and the vapor phase is a saturated vapor. ►For a two-phase liquid-vapor mixture, the ratio of the mass of vapor present to the total mass of the mixture is its quality, x. ● liquid vapor vapor m m m x + = ►The value of quality ranges from 0 to 1. ►At saturated liquid states, x = 0

2013-2-27 Saturated Vapor If the system is heated further until the last bit of liquid has vaporized it is brought to the saturated vapor state. This state is represented by g(highlighted by the blue dot). At saturated vapor states,x =1. 0212p 3-25 Superheated Vapor When the system is at the saturated vapor state, further heating at fixed pressure results in increases in both temperature and specific volume. This state is represented by s(highlighted by the blue dot). Vapor states such as this,where temperature is higher than the saturation temperature corresponding to the pressure at the state,are called superheated vapor states. 13
2013-2-27 13 Saturated Vapor ►If the system is heated further until the last bit of liquid has vaporized it is brought to the saturated vapor state. ►This state is represented by g (highlighted by the blue dot). ►At saturated vapor states, x = 1. ● g 3-25 Superheated Vapor ►When the system is at the saturated vapor state, further heating at fixed pressure results in increases in both temperature and specific volume. ►This state is represented by s (highlighted by the blue dot). ►Vapor states such as this, where temperature is higher than the saturation temperature corresponding to the pressure at the state, are called superheated vapor states. ● s 3-26
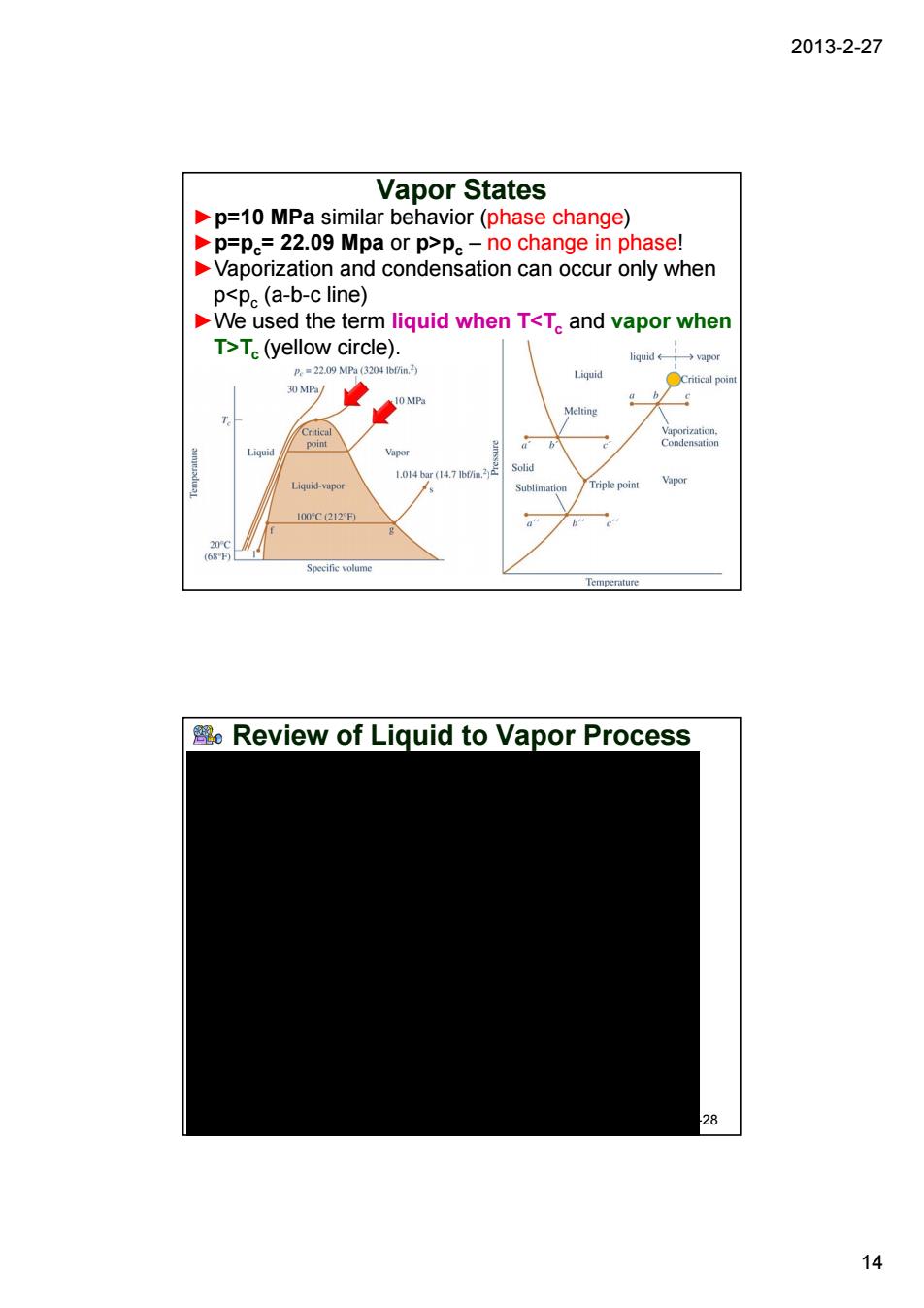
2013-2-27 Vapor States p=10 MPa similar behavior(phase change) p=p=22.09 Mpa or p>pe-no change in phase! Vaporization and condensation can occur only when p<p。(a-b-c line) We used the term liquid when T<T.and vapor when T>T(yellow circle). →apo O MP Review of Liquid to Vapor Process <8 14
2013-2-27 14 Vapor States ►p=10 MPa similar behavior (phase change) ►p=pc= 22.09 Mpa or p>pc – no change in phase! ►Vaporization and condensation can occur only when p<pc (a-b-c line) ►We used the term liquid when T<Tc and vapor when T>Tc (yellow circle). Review of Liquid to Vapor Process 2-28