
NEUROLOGICAL PROGRESS Large-Scale Neurocognitive Networks and Distributed Processing for Attention, Language,and Memory M-Marsel Mesulam,MD tion and ment are subserved by inter high-eve com ing aard sim ultiple po e to this del co mplexb ed at than sp cal sit ioa.coatetand The relationship be een brain structure and complex play a de det .Mos ber of weak traints o that the system n rela oduct of the rapid computai ons required orentdlactivig enab Pprocessadditionlcog There ed at the ch,Pitts,a networks iences now allow ontain an int atnoedea processing,McCle an mediate al netw hecshnotoanlocdne etworks. rom Bullard and De ries,Divis ot Neu te p esmrDcnd m Copyright1990 by the American Neurological Association 597
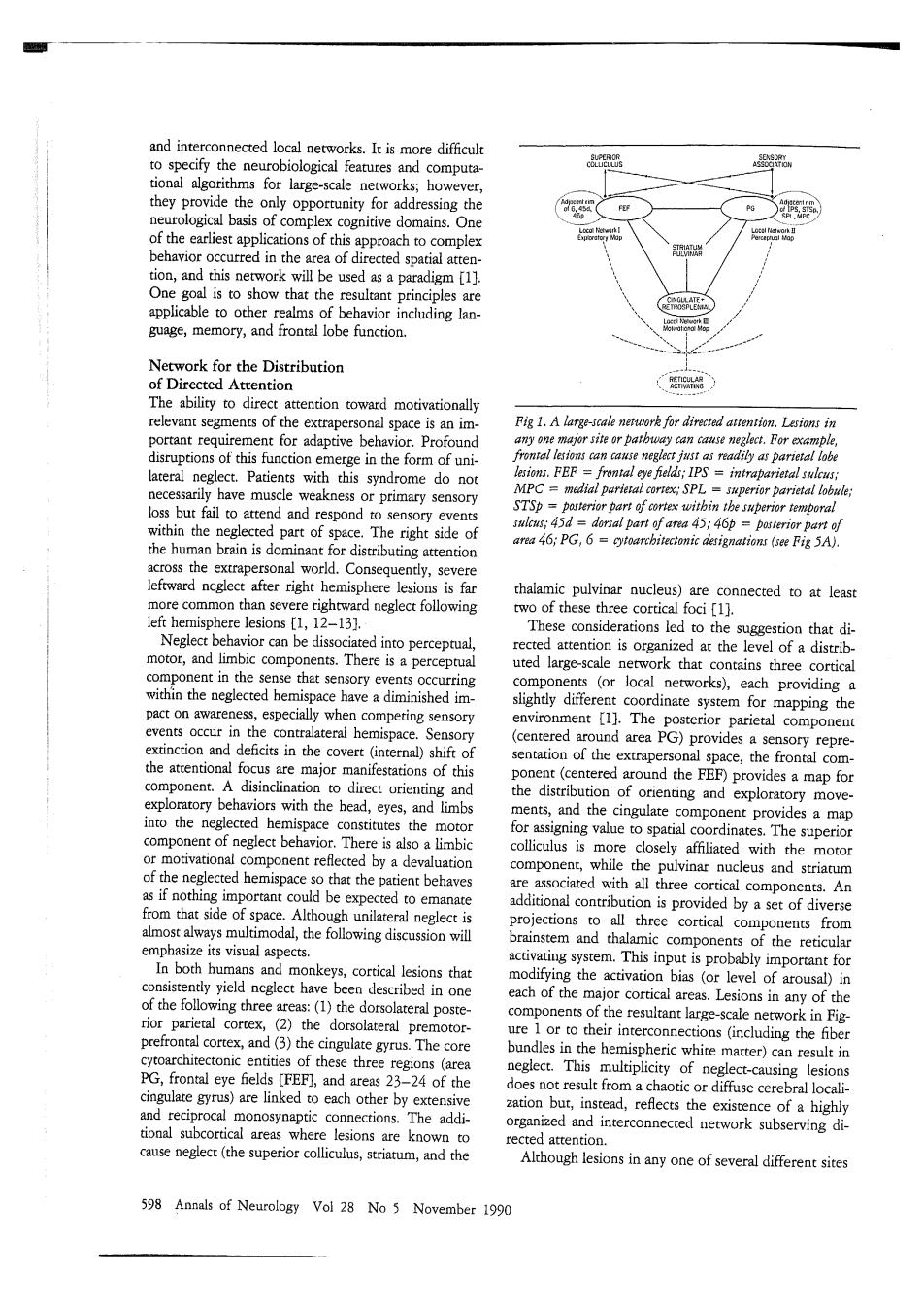
difficul howe is of comple cognitvedomains.g st ap the on,an will be used as a paradigm [1]. guage,memory,and frontal lobe function. Network for the Distribution relevant of thex Fig 1.A large-scale for adaptive be ior.Profound Patients with this syndrome do no MPC r primary sensory m e he ftward negle after right thalamic pulvinar nucleus)are connected to at least eft her Neglect ed into perceptual that di Th ued large-scale ork that c ontains three co the ,f ch providing environment.Thc osterior sentation of the extrape fo head,dm componcntofneglectbchag There is am d he ng value to dinate The of the negle th all three c A ortan projections acti of the re neglectwecorticallcs ns tha the activation bias (or level of Lesions in any of th 1)the teral t or to the inrerco cortex the natter)cai I result ir these th ingulate gyt are linked to each other by synaptic The add ized and inrerc (the superior esions inany one of several different sites 598 Annals of Neurology Vol 28 No 5 November 1990

of the damage urns{asinpri )bu is e ation and eye posi p of PG neglec a5 15a sions includes a c ected hem pace [14 of huma ubjects to prismat hat similar distinctions can [101.Shifts of neuro gical obse with eye pos ion or stimulus locarion.Cor keys have elucida of the ifts h t o in a way tha tra able the covert movement of ntion that area PG re sextensively pre s [5)have dem ation icnswihpostetiorpaietallesiog casca they cannot disengage the focus of proximal (upstream)sc inform attention for con sive shift provide to (and eventually to arise thr ough is impo PG m un d s the as.Accordi PG in the form of a co thus in oor sensory nation (3)en Such a distr ibute (an hiness of se L nantic imnar t of certain stimuli aded)infor ation in pq spatial coordinates on corresponding groups of PG ome of the ne PG increase firing able information has also been gathered on ce is made beh but not hen th ent h ng di consequ behav t objecs or to thei of the ote atedwithsimilar activity. hat normal the PG plexand tsk-reaed rather mal's ability determin the rela e Dosition of ex or co 21 des and may also infue the sho ic visa nation abou movements since damage to one d ye po n [10].An individual PG neuron olishes the 1261 The supor coliculus may be its retinotonic feld de on eye position,and a mportantfor fovearing the gen eral area of iner f that regio Nerolopical prosrress:Mesulam:Neurocognitive Networks 599

The and the 0 subserve orientation to "fa egio es substa ntial neural input from the sam ct to the erior parietal co 2 eg27 lhcontrasttoprimi motor cortex where Furthermore,the ntermediate (oculo motor)laver o rep body d on the PPin reas ap behavioral poir t of view,a s ory represc tation a exp arms crossed.reaction time nd ing ha dating per er sho compo ofuniareral ect are ing used (13.Thes examples my show that explo not absolute are organize accordin absence of one ent but the rela ng on the ather sire of the lesion three nponents in Figure ording to these obs the Fean PG have are for pe eural cor me the tar ofehacan grasp, ts are probab atten tasks nd subiective ar tional lande hiecFEF ng are olan the sraegy for navigating them.The sum of percet t of this rk.Lesio ot the syndro eafcontralarernal tional)quality of the Is im with m hat thi arg cale network posit emi vanon during state dd of F51 could ibution of visua ing of the ape It is re Areas such as the FEF and PG that he FEF ut the behavi hav nshrough or synchro ponent [18 bet sens and moto omy mat resp ectively by PGand FEP. 1 e gyrus but also mo th tion and p te [11.Complex p nodal prefrontal nd the TE-TH region [18.32.37 or fe pair o schema [301 whi rex is likely to additional cortical connect member of the pair.Th and the FE ann need not be identical and can vary 600 Annals of Neurology Vol 28 No 5 November 1990
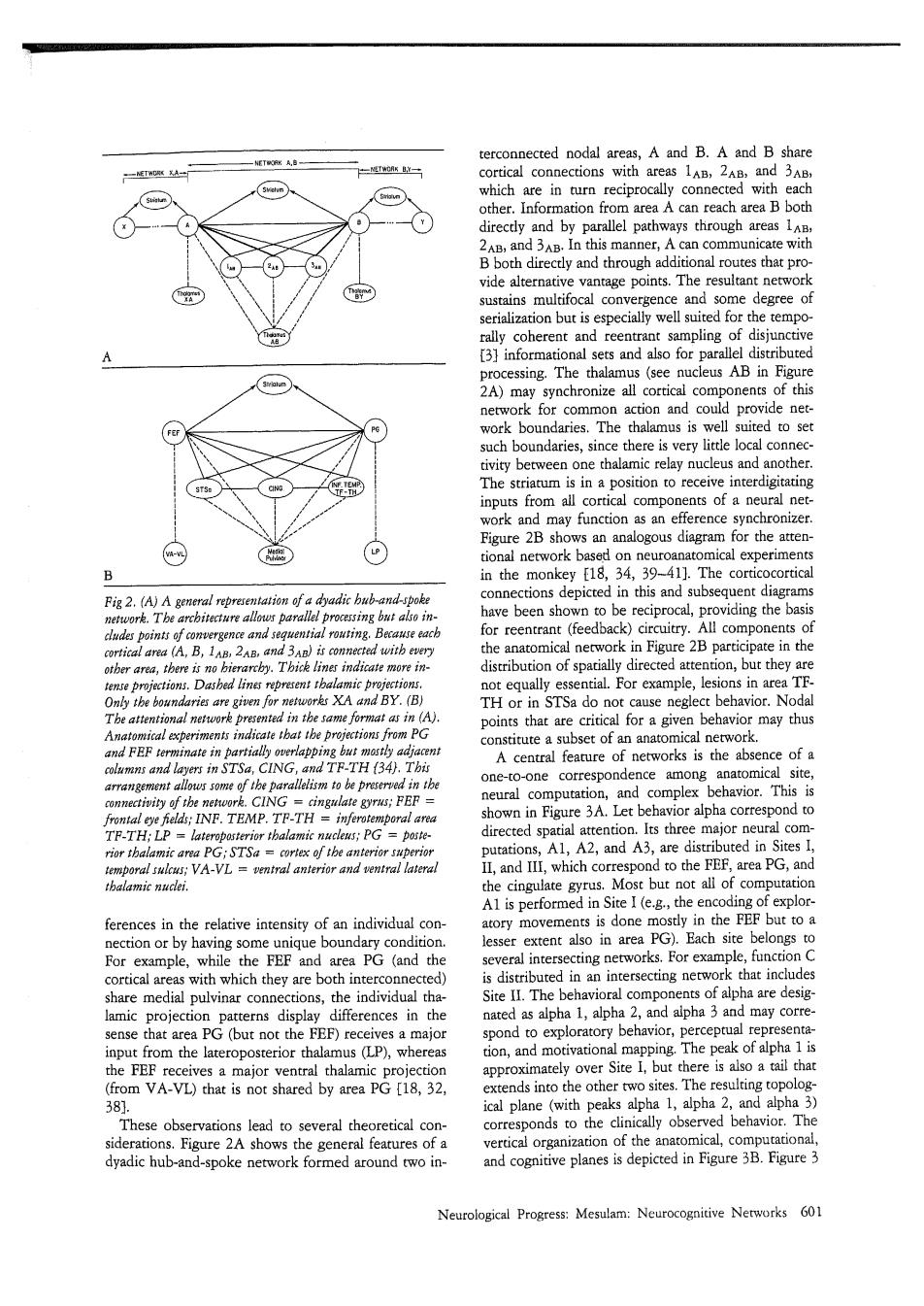
terconnected noda areas which are in turo other. is man 13]info chronize all d pro ride ne there is vity en one thalami y nucleus and 8 from all cortical comp ts of a ral ne 5 a for the a al network .O0 ical exp the mo d in The c diag Fiz 2.(A)A ger sho viding the 足d 2T distribuion of spa XA dBY.(B do no for ae tha r may thus FEF t (34). fearure of networks is the absence of o-one espondence TH:Lp:INE in Fisure3A Let be oralphacocrespondo PG= area PG.an ces in the relariv of an individual cor in the FEF but to a ction or by h ng s igu exter k PG that include e medial pulving tha Th not the FEF)recei om the lateroposterior thala on,an VA-VL)that is ot. rwoses.Thergliagto0p0eg al plane ure 2A show yadic hub-and-spoke etwork formed around wo in cognitive planes is depi Neurological Progress:Mesulam:Neurocognitive Networks 601