
Teaching Plan for International Economic Law By Zhang Lina School of Law Hainan University October 2010
Teaching Plan for International Economic Law By Zhang Lina School of Law Hainan University October 2010

Content Part One General Introduction to International Economic Law Chapter One General Introduction to International Economic Law Chapter Two International Economic Organizations Chapter Tree Transnational Corporation Part Two Legal System of International Trade Chapter Four Gener ion to Legal System of International Trade Chapter Five Law of International Sale of Goods Chapter Six Transportation and Insurance Concerning International Sale of Goods Chapter Seven Legal System of Government Control on International Trade Part Three Legal System of International Technology Transfer Chapter Eight General Inroduction to Legal System of International Technology Transfer (Trade) Chapter Nine International Licensing Contract Chapter Ten Legal Regulation to International Technology Transfer Part Four Legal System of International Direct Investment Chapter Elev ren Gener】 alDirect Investment Chapter Thirteen Domestic Laws Concerning Transnational Investment Chapter Fourteen International Treaties Concerning Transnational Investment Part Five International Legal System of Monetary and Financing Chapter Sixteen Inter al Monetary System Chapter Seventeen International Legal System of Financing Chapter Eighteen Legal Control for Transnational Bank Part Six Legal System of International Taxation Chapter nineteen general Introduction to legal system of International taxation Chapter Twenty Taxation Juri isdiction Chapter Twenty-one International Double and Overlapping Taxation Chapter Twenty-two International Avoidance and Evasion of Taxation Part Seven Legal System of International Economic Dispute Settlement Chapter Twenty-Three consultation Conciliation.Arbitration and Action Chapter Twenty-four Disputes Settlement in WTO System Chapter Twenty-five Settlement of the Investment Disputes Between State and National of Other State
2 Content Part One General Introduction to International Economic Law Chapter One General Introduction to International Economic Law Chapter Two International Economic Organizations Chapter Tree Transnational Corporation Part Two Legal System of International Trade Chapter Four General Introduction to Legal System of International Trade Chapter Five Law of International Sale of Goods Chapter Six Transportation and Insurance Concerning International Sale of Goods Chapter Seven Legal System of Government Control on International Trade Part Three Legal System of International Technology Transfer Chapter Eight General Introduction to Legal System of International Technology Transfer (Trade) Chapter Nine International Licensing Contract Chapter Ten Legal Regulation to International Technology Transfer Part Four Legal System of International Direct Investment Chapter Eleven General Introduction to Legal System of International Direct Investment Chapter Twelve Legal Forms of International Investment Chapter Thirteen Domestic Laws Concerning Transnational Investment Chapter Fourteen International Treaties Concerning Transnational Investment Part Five International Legal System of Monetary and Financing Chapter Fifteen General Introduction Chapter Sixteen International Monetary System Chapter Seventeen International Legal System of Financing Chapter Eighteen Legal Control for Transnational Bank Part Six Legal System of International Taxation Chapter Nineteen General Introduction to Legal System of International Taxation Chapter Twenty Taxation Jurisdiction Chapter Twenty-one International Double and Overlapping Taxation Chapter Twenty-two International Avoidance and Evasion of Taxation Part Seven Legal System of International Economic Dispute Settlement Chapter Twenty-Three Consultation,Conciliation, Arbitration and Action Chapter Twenty-four Disputes Settlement in WTO System Chapter Twenty-five Settlement of the Investment Disputes Between State and National of Other State
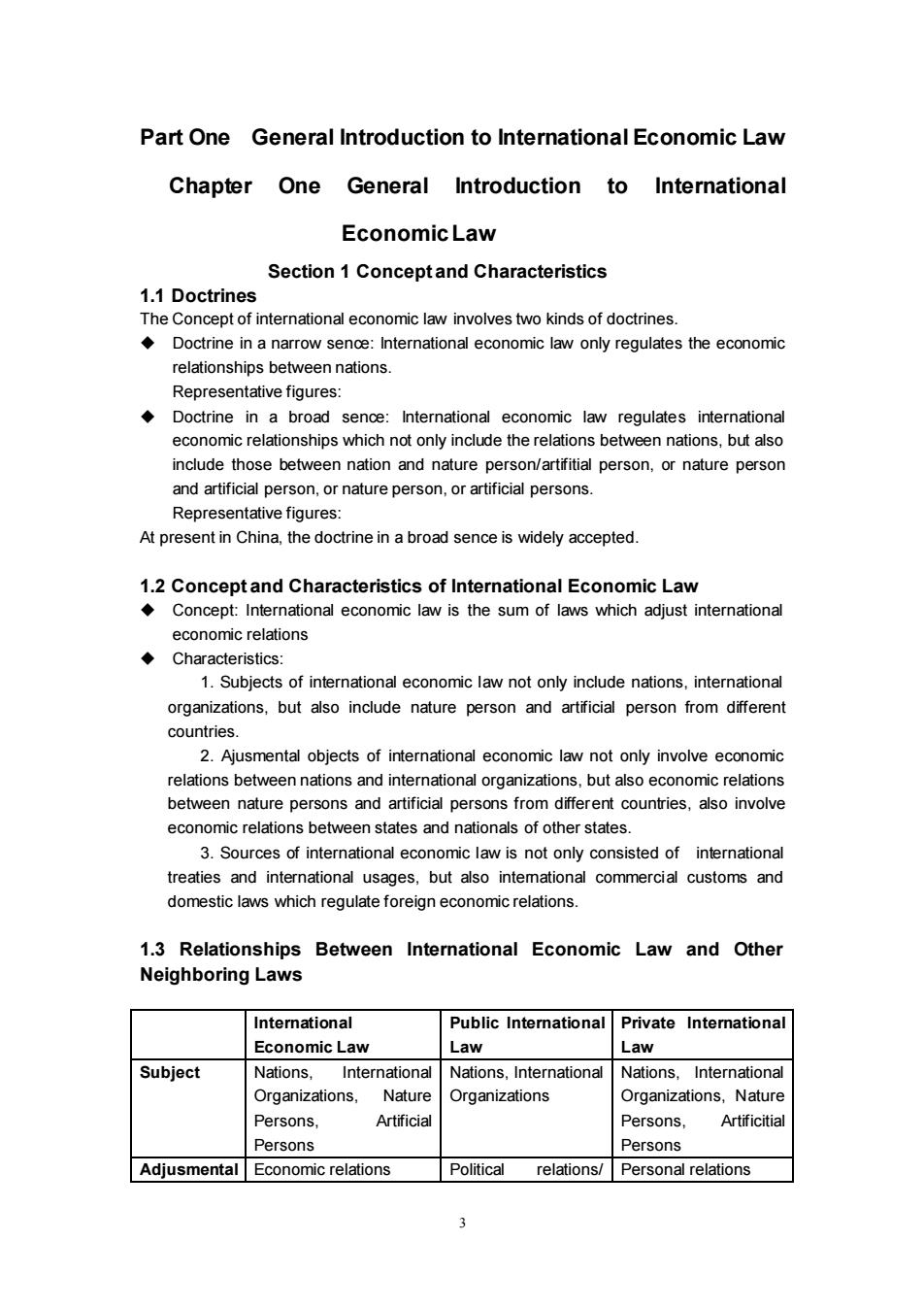
Part One General Introduction to International Economic Law Chapter One General Introduction to International Economic Law Section 1 Conceptand Characteristics 1.1 Doctrines The Concept of international economic law involves two kinds of doctrines Doctrine in a narrow sence:International economic law only regulates the economic relationships between nations. Representative figures: ◆ Doctrine in a broad sence Inte economic relationships which not only include the relations between nations,but als include those between nation and nature person/artifitial person,or nature person and artificial person,or nature person,or artificial persons. Representative figures: At present in China,the doctrine in a broad sence is widely accepted. 1.2 Concept and Characteristics of International Economic Law Concept:International economic law is the sum of laws which adjust international economic relations ◆Characteristics: 1.Subjects of international eco omic law not ony include nations,interationl organizations.but also include nature person and artificial person from different countries. 2.Ajusmental objects of international economic law not only involve economic relations between nations and international organizations.but also economic relations between nature persons and artificial persons from different countries.also involve economic relat ns between states and natic hals of other states 3.Sources of international economic law is not only consisted of international treaties and international usages,but also intemational commercial customs and domestic laws which requlate foreign economic relations. 1.3 Relationships Between International Economic Law and Other Neighboring Laws International Public International Private Intemational Economic Law I aw Law Subject Nations ational ations,International tions. International Organizations, Nature Organizations,Nature Persons. Artificia Persons. Artificitia Persons Persons Adjusmental Economic relations Political relations/Personal relations
3 Part One General Introduction to International Economic Law Chapter One General Introduction to International Economic Law Section 1 Concept and Characteristics 1.1 Doctrines The Concept of international economic law involves two kinds of doctrines. ◆ Doctrine in a narrow sence: International economic law only regulates the economic relationships between nations. Representative figures: ◆ Doctrine in a broad sence: International economic law regulates international economic relationships which not only include the relations between nations, but also include those between nation and nature person/artifitial person, or nature person and artificial person, or nature person, or artificial persons. Representative figures: At present in China, the doctrine in a broad sence is widely accepted. 1.2 Concept and Characteristics of International Economic Law ◆ Concept: International economic law is the sum of laws which adjust international economic relations ◆ Characteristics: 1. Subjects of international economic law not only include nations, international organizations, but also include nature person and artificial person from different countries. 2. Ajusmental objects of international economic law not only involve economic relations between nations and international organizations, but also economic relations between nature persons and artificial persons from different countries, also involve economic relations between states and nationals of other states. 3. Sources of international economic law is not only consisted of international treaties and international usages, but also international commercial customs and domestic laws which regulate foreign economic relations. 1.3 Relationships Between International Economic Law and Other Neighboring Laws International Economic Law Public International Law Private International Law Subject Nations, International Organizations, Nature Persons, Artificial Persons Nations, International Organizations Nations, International Organizations, Nature Persons, Artificitial Persons Adjusmental Economic relations Political relations/ Personal relations
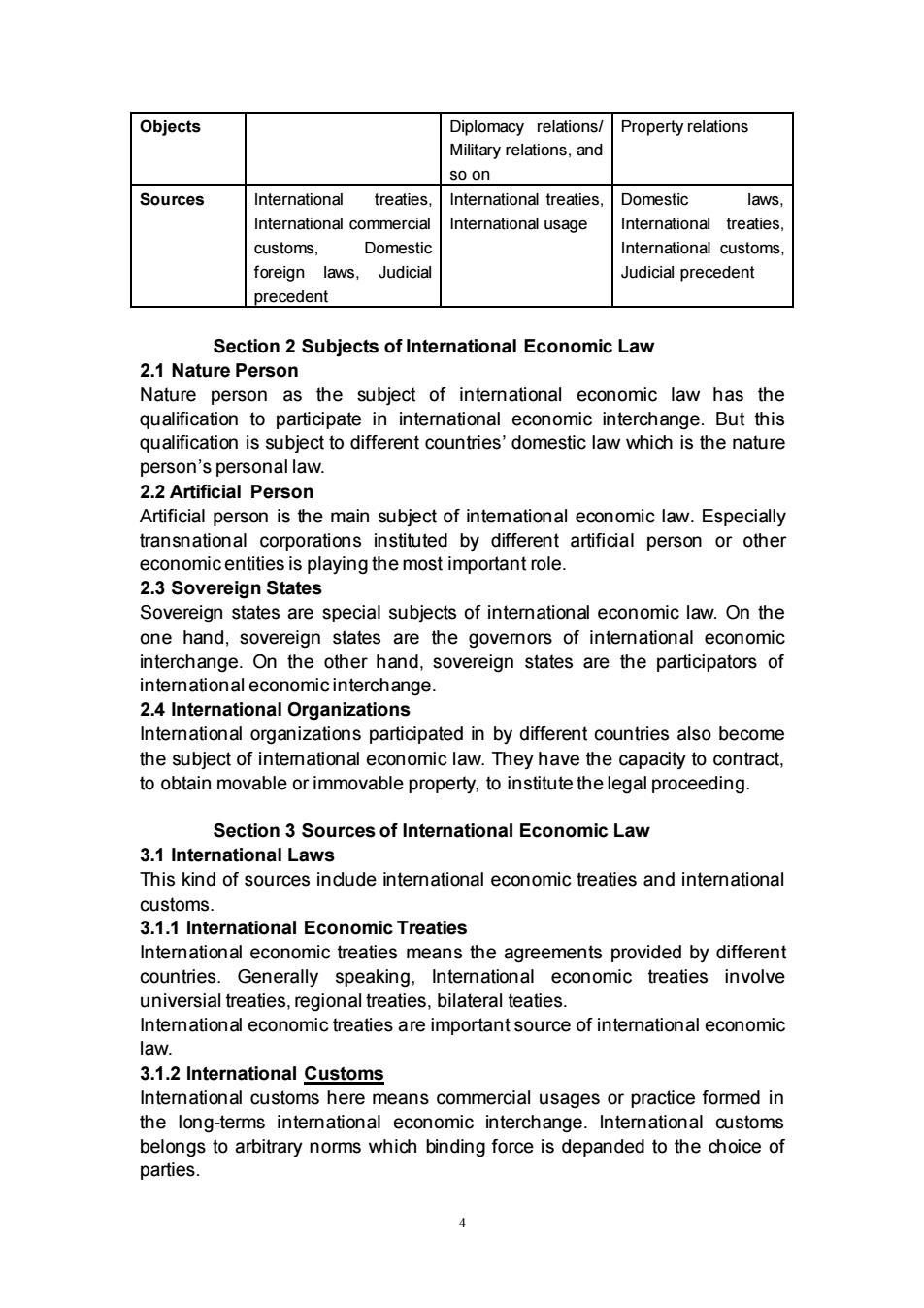
Objects Diplomacy relations/Property relations Military relations.n so on Sources International treaties. International treaties. Domestic laws International commercial International usage I International treaties customs, Domesti International customs foreign laws udicial precedent precedent Section 2 Subjects of International Economic Law 2.1 Nature Person Nature person as the subject of intemnational economic law has the qualification to participate in interational economic interchange.But this qualification is subject to different countries'domestic law which is the nature person's personallaw 22 Artificial Person Artificial per on is the main subject of intemational economic law.Especially transnational corporations instituted by different artificial person or other economic entities is playing the most important role. 2.3 Sovereign States Sovereign states are special subjects of intemational economic law.On the one hand, ereign state are the govemors of intemational economi interchange.On the other hand,sovereign states are the participators of intemational economic interchange. 2.4 International Organizations Intemational organizations participated in by different countries also become the subject of intemational economic law.They have the capacity to contract. to obtain movable or immovable property,to institute the legal proceeding. Section 3 Sources of International Economic Law 3.1 International Laws This kind of sources incude intemational economic treaties and intemational Intemational economic treaties means the agreements provided by different countries.Generally speaking,Intemational economic treaties involve universial treaties.regional treaties.bilateral teaties. mic treaties are important source of intemational economic 3.1.2 International Customs Intemnational customs here means commercial usages or practice formed in the long-terms international economic interchange.Intemational customs belongs to arbitrary norms which binding force is depanded to the choice of parties
4 Objects Diplomacy relations/ Military relations, and so on Property relations Sources International treaties, International commercial customs, Domestic foreign laws, Judicial precedent International treaties, International usage Domestic laws, International treaties, International customs, Judicial precedent Section 2 Subjects of International Economic Law 2.1 Nature Person Nature person as the subject of international economic law has the qualification to participate in international economic interchange. But this qualification is subject to different countries’ domestic law which is the nature person’s personal law. 2.2 Artificial Person Artificial person is the main subject of international economic law. Especially transnational corporations instituted by different artificial person or other economic entities is playing the most important role. 2.3 Sovereign States Sovereign states are special subjects of international economic law. On the one hand, sovereign states are the governors of international economic interchange. On the other hand, sovereign states are the participators of international economic interchange. 2.4 International Organizations International organizations participated in by different countries also become the subject of international economic law. They have the capacity to contract, to obtain movable or immovable property, to institute the legal proceeding. Section 3 Sources of International Economic Law 3.1 International Laws This kind of sources include international economic treaties and international customs. 3.1.1 International Economic Treaties International economic treaties means the agreements provided by different countries. Generally speaking, International economic treaties involve universial treaties, regional treaties, bilateral teaties. International economic treaties are important source of international economic law. 3.1.2 International Customs International customs here means commercial usages or practice formed in the long-terms international economic interchange. International customs belongs to arbitrary norms which binding force is depanded to the choice of parties

3.2 Domestic Laws As the source of intemational economic law,the domestic laws means those whichregulate foreign economic relations.Those domestic laws which only regulate domestic relations are not the source of intemational economic law. 3.3 Other Sources 3.3.1 Judicial precedent In common-law countries,judicial precedents may be regarded as the source of interantional conomic law. But in continental countries,judicia precedents are not the source of intemational economic law 3.3.2 Doctrines Doctrines could effect intemational economic law but are not the source of intemational economiclaw. Section 4 Er ergence and Development of International Economic Law 4.1 Before the 19th century 4.2 From the 19th century to WarII 4.3 After WarⅡ Section 5 Basic Principles of International Economic Law 5.1 Principle of Economic Sovereign 5.2 Principle of Equity(Equality)and Mutual Benefit 5.3 Principle of International Cooperation 5.4 Pacta sunt servanda(Agreements of the Parties must be observed)
5 3.2 Domestic Laws As the source of international economic law, the domestic laws means those which regulate foreign economic relations. Those domestic laws which only regulate domestic relations are not the source of international economic law. 3.3 Other Sources 3.3.1 Judicial precedent In common-law countries, judicial precedents may be regarded as the source of interantional economic law. But in continental law countries, judicial precedents are not the source of international economic law. 3.3.2 Doctrines Doctrines could effect international economic law but are not the source of international economic law. Section 4 Emergence and Development of International Economic Law 4.1 Before the 19th century 4.2 From the 19th century to WarⅡ 4.3 After WarⅡ Section 5 Basic Principles of International Economic Law 5.1 Principle of Economic Sovereign 5.2 Principle of Equity(Equality) and Mutual Benefit 5.3 Principle of International Cooperation 5.4 Pacta sunt servanda (Agreements of the Parties must be observed)