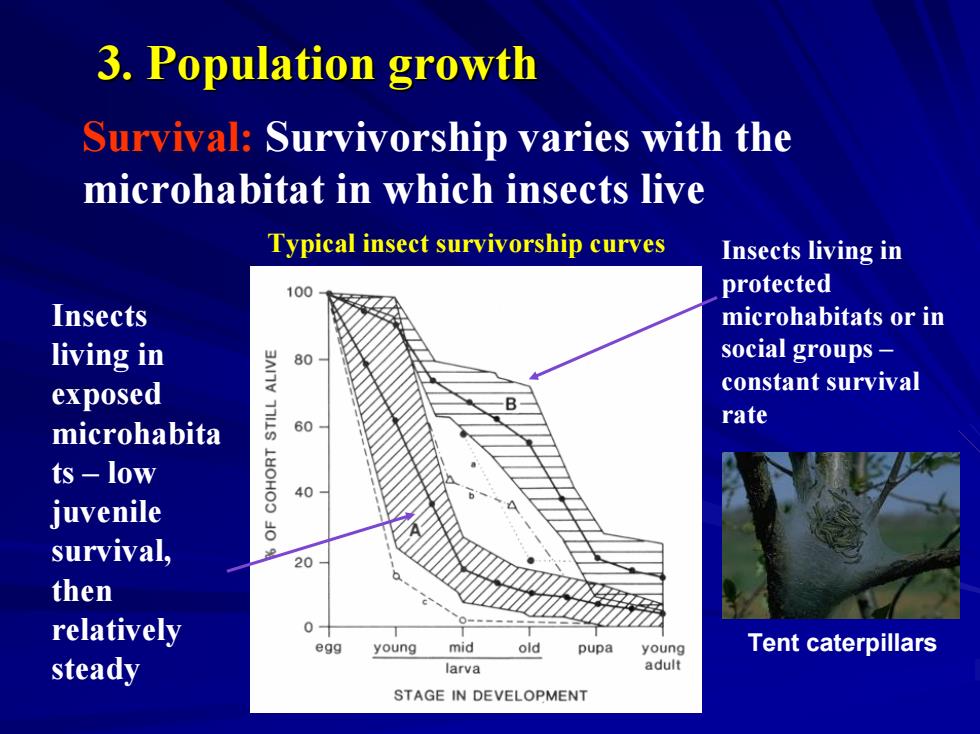
3.Population growth Survival:Survivorship varies with the microhabitat in which insects live Typical insect survivorship curves Insects living in 100 protected Insects microhabitats or in living in 80 social groups exposed constant survival microhabita 60 rate ts-low 40 juvenile survival, 20 then relatively 0- egg young mid old pupa young Tent caterpillars steady larva adult STAGE IN DEVELOPMENT
Survival: Survivorship varies with the microhabitat in which insects live Insects living in protected microhabitats or in social groups – constant survival rate Insects living in exposed microhabita ts – low juvenile survival, then relatively steady Tent caterpillars Typical insect survivorship curves 3. Population growth 3. Population growth
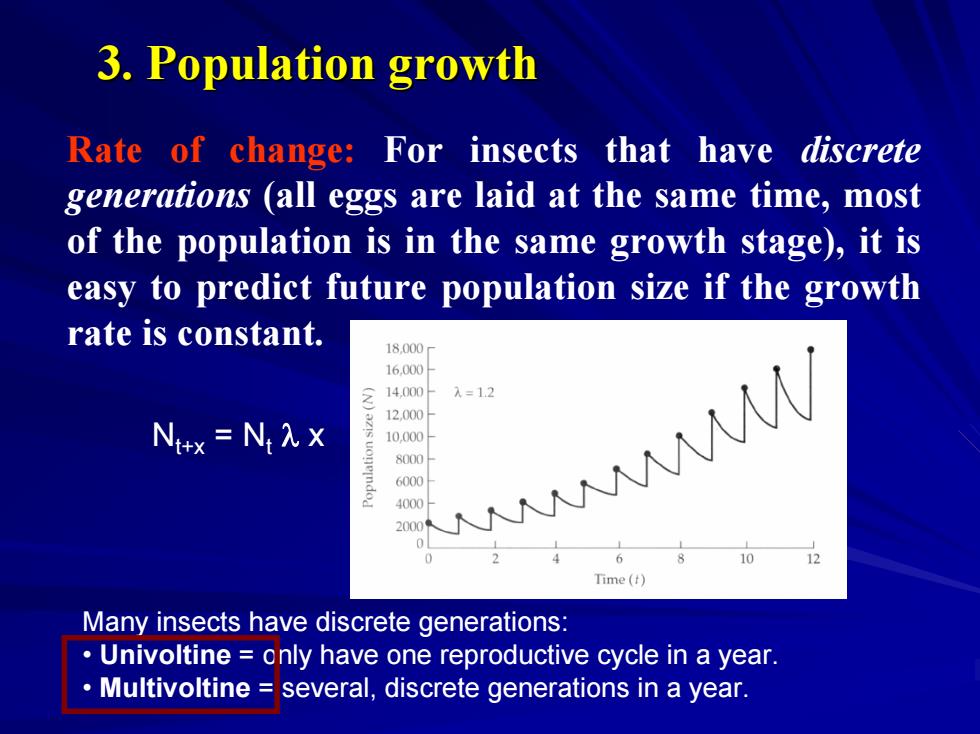
3.Population growth Rate of change:For insects that have discrete generations (all eggs are laid at the same time,most of the population is in the same growth stage),it is easy to predict future population size if the growth rate is constant. 18.000 16.000 214,000 入=12 12,000 N+x=N入X 10.000 8000 6000 4000 20004 / 0 2 Time ( Many insects have discrete generations: Univoltine only have one reproductive cycle in a year. Multivoltine several,discrete generations in a year
Many insects have discrete generations: • Univoltine = only have one reproductive cycle in a year. • Multivoltine = several, discrete generations in a year. Rate of change: For insects that have discrete generations (all eggs are laid at the same time, most of the population is in the same growth stage), it is easy to predict future population size if the growth rate is constant. Nt+x = Nt λ x 3. Population growth 3. Population growth
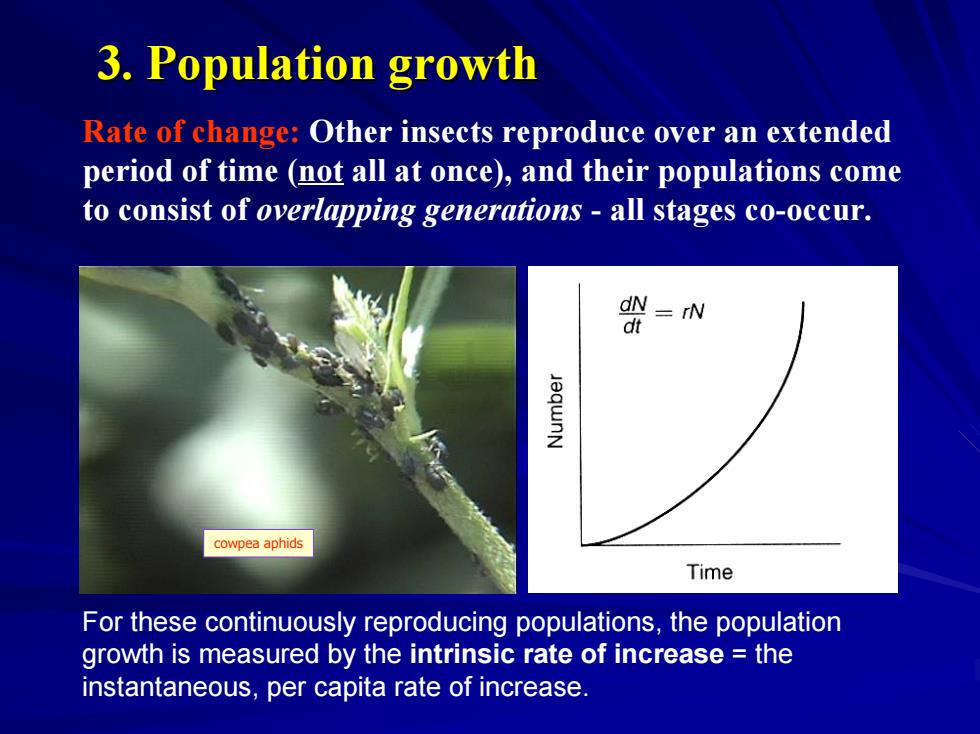
3.Population growth Rate of change:Other insects reproduce over an extended period of time (not all at once),and their populations come to consist of overlapping generations all stages co-occur. dN =rN d cowpea aphids Time For these continuously reproducing populations,the population growth is measured by the intrinsic rate of increase the instantaneous,per capita rate of increase
Rate of change: Other insects reproduce over an extended period of time (not all at once), and their populations come to consist of overlapping generations - all stages co-occur. For these continuously reproducing populations, the population growth is measured by the intrinsic rate of increase = the instantaneous, per capita rate of increase. cowpea aphids 3. Population growth 3. Population growth
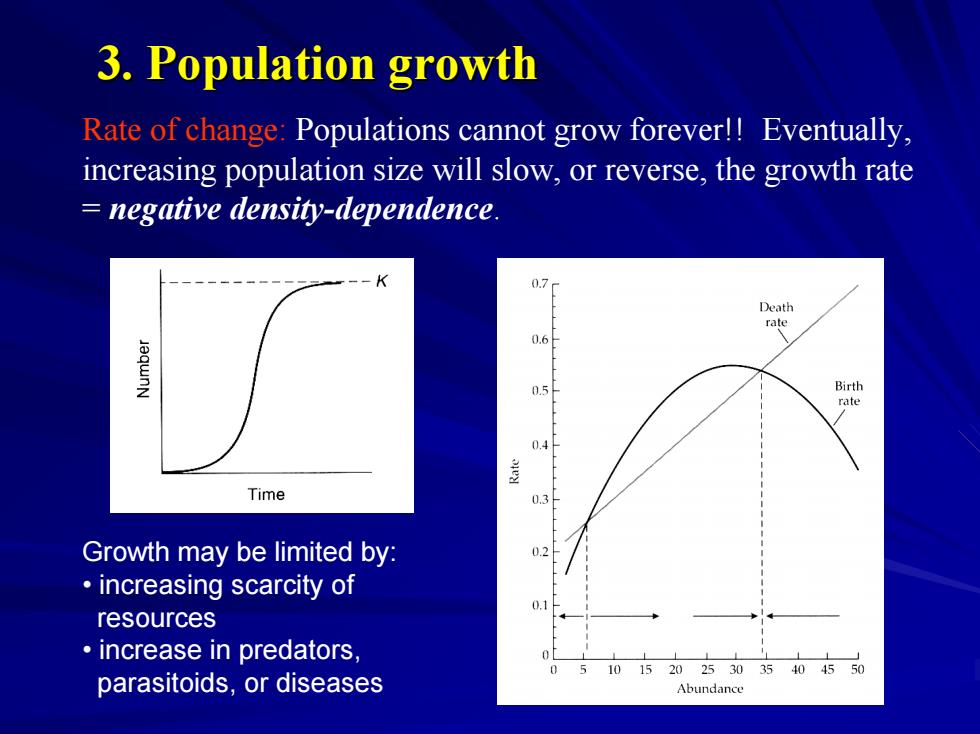
3.Population growth Rate of change:Populations cannot grow forever!!Eventually, increasing population size will slow,or reverse,the growth rate negative density-dependence. K 0.7 Death rate 05 Birth ate 0.4 Time 03 Growth may be limited by: increasing scarcity of resources increase in predators, parasitoids,or diseases 5101520253035404550 Abundance
Rate of change: Populations cannot grow forever!! Eventually, increasing population size will slow, or reverse, the growth rate = negative density-dependence. Growth may be limited by: • increasing scarcity of resources • increase in predators, parasitoids, or diseases 3. Population growth 3. Population growth

4.Competition The common use of resources can lead to competition negative effects on individuals due to interactions within a trophic level. Competition between 0.4r Species B members of the same 0.3 Niche overlap species intraspecific competition.Competition 0- Species A between different species 0.I interspecific competition,depends on niche overlap 2 345678 Resource Set
The common use of resources can lead to competition = negative effects on individuals due to interactions within a trophic level. Niche overlap 4. Competition 4. Competition Competition between members of the same species = intraspecific competition. Competition between different species = interspecific competition, depends on niche overlap