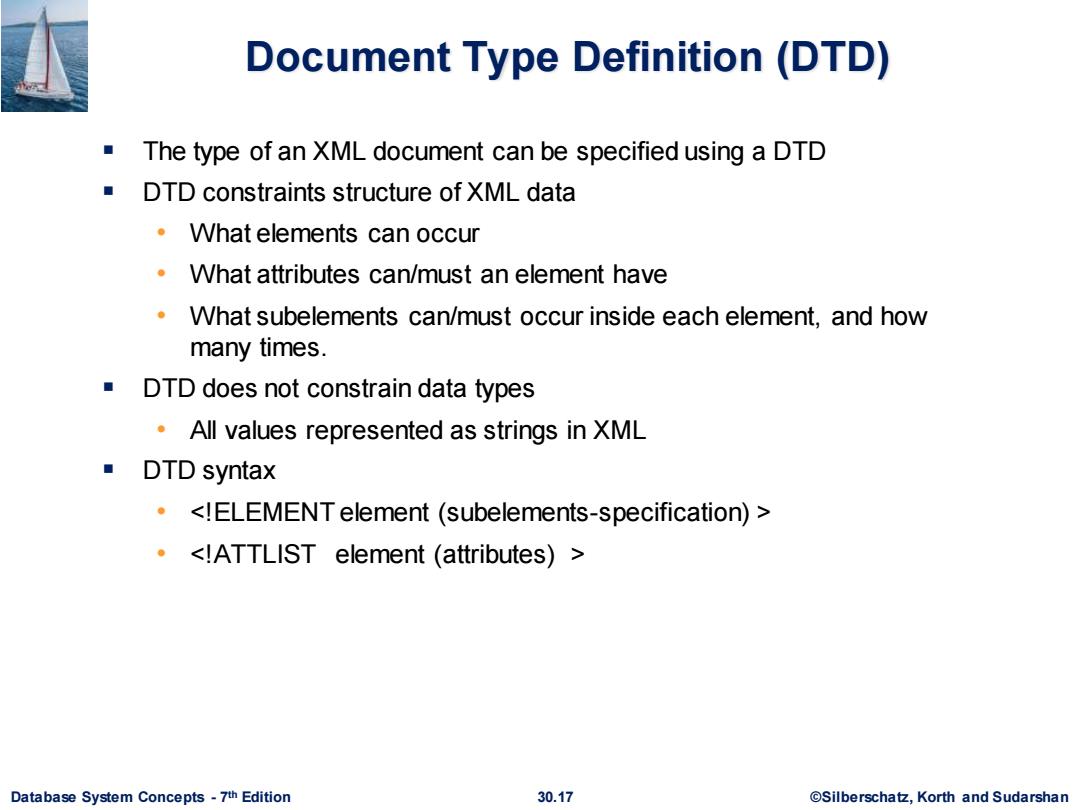
Document Type Definition(DTD) The type of an XML document can be specified using a DTD DTD constraints structure of XML data What elements can occur What attributes can/must an element have What subelements can/must occur inside each element,and how many times. DTD does not constrain data types All values represented as strings in XML ■DTD syntax .<!ELEMENT element (subelements-specification)> .<!ATTLIST element (attributes)> Database System Concepts-7th Edition 30.17 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 30.17 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Document Type Definition (DTD) ▪ The type of an XML document can be specified using a DTD ▪ DTD constraints structure of XML data • What elements can occur • What attributes can/must an element have • What subelements can/must occur inside each element, and how many times. ▪ DTD does not constrain data types • All values represented as strings in XML ▪ DTD syntax • <!ELEMENT element (subelements-specification) > • <!ATTLIST element (attributes) >
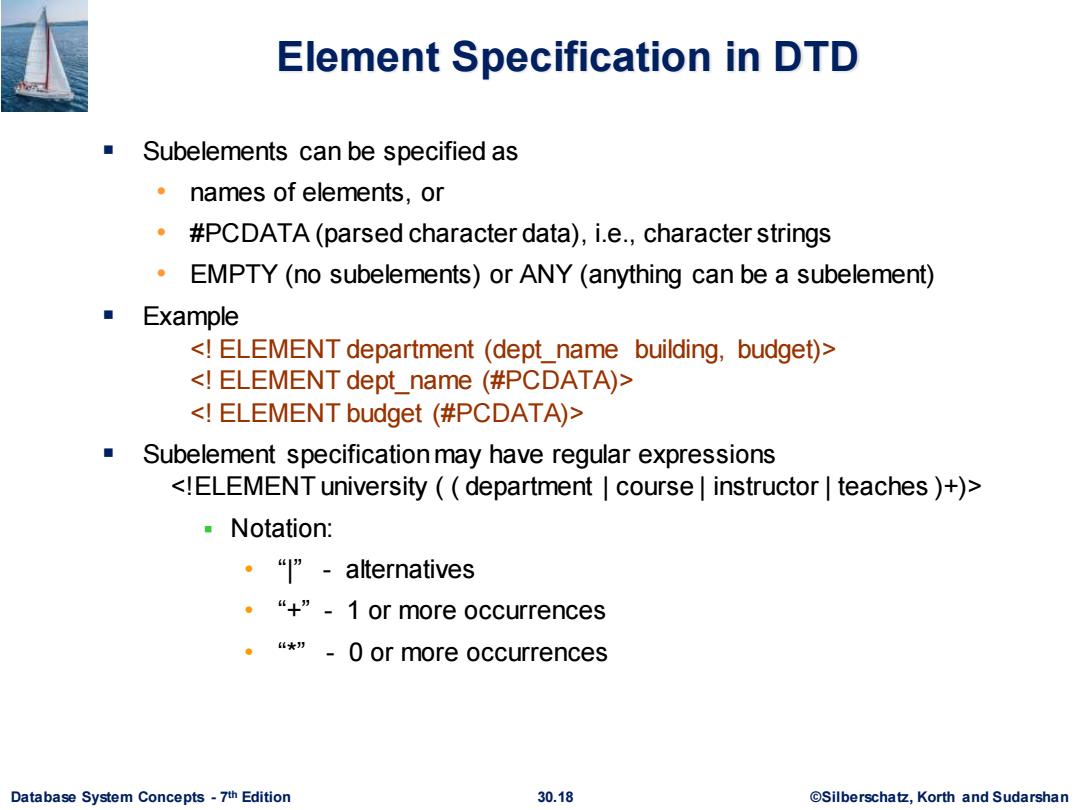
Element Specification in DTD Subelements can be specified as ·names of elements,or .#PCDATA(parsed character data),i.e.,character strings EMPTY(no subelements)or ANY (anything can be a subelement) ■ Example <ELEMENT department (dept_name building,budget)> <ELEMENT dept name (#PCDATA)> <ELEMENT budget (#PCDATA)> ■ Subelement specification may have regular expressions <!ELEMENT university (department course instructor teaches )+) ▣Notation: ·“"-alternatives ,“+”-1 or more occurrences 。“*”-0 or more occurrences Database System Concepts-7th Edition 30.18 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 30.18 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Element Specification in DTD ▪ Subelements can be specified as • names of elements, or • #PCDATA (parsed character data), i.e., character strings • EMPTY (no subelements) or ANY (anything can be a subelement) ▪ Example <! ELEMENT department (dept_name building, budget)> <! ELEMENT dept_name (#PCDATA)> <! ELEMENT budget (#PCDATA)> ▪ Subelement specification may have regular expressions <!ELEMENT university ( ( department | course | instructor | teaches )+)> ▪ Notation: • “|” - alternatives • “+” - 1 or more occurrences • “*” - 0 or more occurrences

University DTD <!DOCTYPE university <!ELEMENT university ((department courselinstructor|teaches)+)> <!ELEMENT department(dept name,building,budget)> <!ELEMENT course(course id,title,dept name,credits)> <!ELEMENT instructor(IID,name,dept name,salary)> <!ELEMENTteaches(IID,course id)> <!ELEMENT dept name(#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT building(#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT budget(#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT course id (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT title (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT credits(#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT IID(#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT name(#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT salary(#PCDATA)> P Database System Concepts-7th Edition 30.19 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 30.19 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition University DTD <!DOCTYPE university [ <!ELEMENT university ( (department|course|instructor|teaches)+)> <!ELEMENT department ( dept name, building, budget)> <!ELEMENT course ( course id, title, dept name, credits)> <!ELEMENT instructor (IID, name, dept name, salary)> <!ELEMENT teaches (IID, course id)> <!ELEMENT dept name( #PCDATA )> <!ELEMENT building( #PCDATA )> <!ELEMENT budget( #PCDATA )> <!ELEMENT course id ( #PCDATA )> <!ELEMENT title ( #PCDATA )> <!ELEMENT credits( #PCDATA )> <!ELEMENT IID( #PCDATA )> <!ELEMENT name( #PCDATA )> <!ELEMENT salary( #PCDATA )> ]>