
第一节 药物分子的跨膜转运 Drug Transport 第二章 人风只生公版松
第一节 第二章 Drug Transport Drug Transport 药物分子的跨膜转运
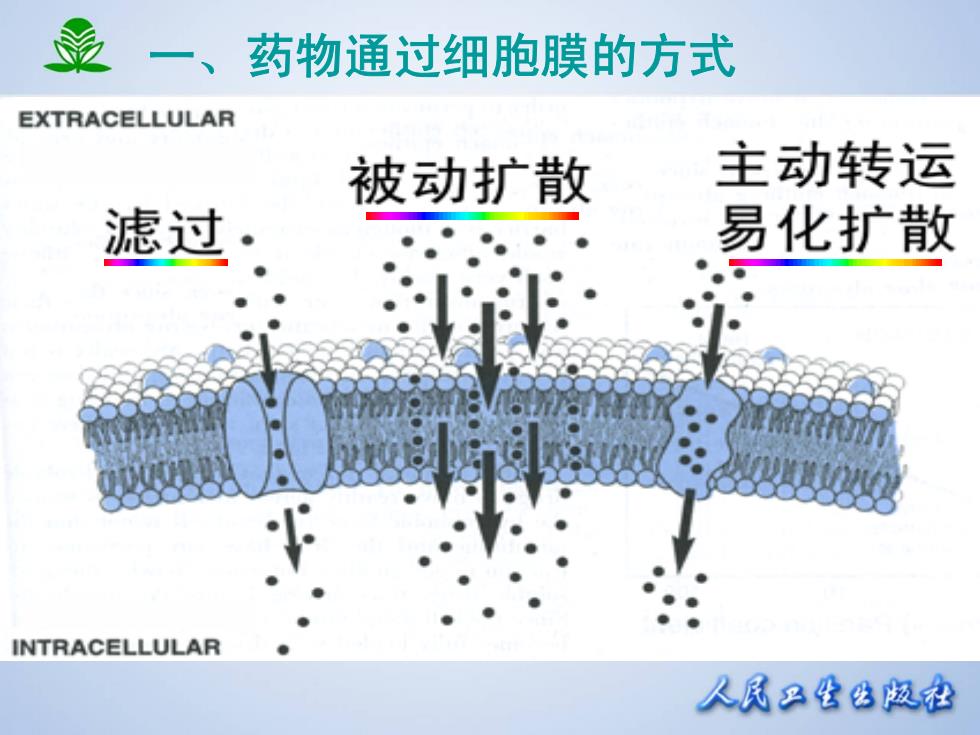
一、 药物通过细胞膜的方式 EXTRACELLULAR 被动扩散 主动转运 滤过 易化扩散 INTRACELLULAR 人凤只生公版松
一、药物通过细胞膜的方式

Passive transport(downhill transport) Active transport (uphill transport) Electrochemical potential Eloctrochemical polential High gradient of the substrate Low High gradient of the s边strate Passive diffusion ©.Symport Secondary active transport ○Antiport Facilitated diffusion ATP Primary active transport ADP Figure 2-4.Classification of membrane transport mechanisms.Light blue circles depict the substrate.Size of the circles is proportional to the concentration of the substrate.Arrows show the direction of flux.Black squares represent the ion that supplies the driving force for transport(size is proportional to the concentration of the ion).Dark blue ovals depict transport proteins. 人凤只生公版松
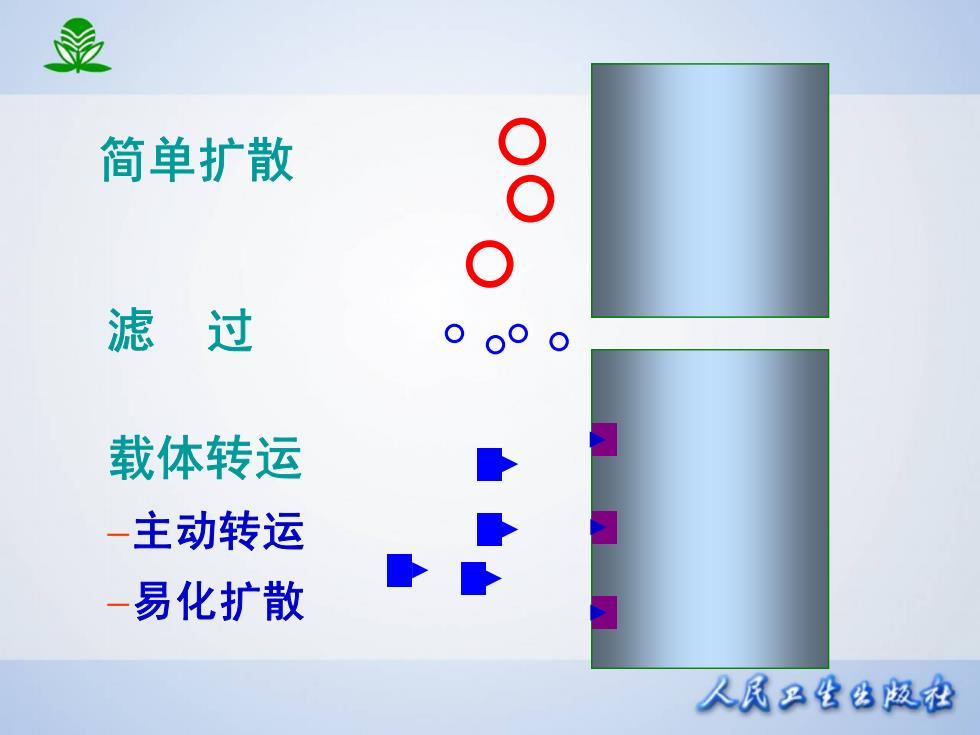
显 简单扩散 8 滤过 载体转运 -主动转运 -易化扩散 人凤只生公版松
简单扩散 滤 过 载体转运 主动转运 易化扩散

能 1.简单扩散(Simple diffusion,,Passive diffusion) 脂溶性物质直接溶于膜的类脂相而通过 特点: 转运速度与脂溶度(lipid solubility)成正比 。顺浓度差,不耗能。 转运速度与浓度差成正比 +转运速度与药物解离度(pKa)有关 人凤只生公版出
1.简单扩散(Simple diffusion, Passive diffusion) 脂溶性物质直接溶于膜的类脂相而通过 特 点: 转运速度与脂溶度(lipid solubility lipid solubility)成正比 顺浓度差,不耗能。 转运速度与浓度差成正比 转运速度与药物解离度 (pKa) 有关