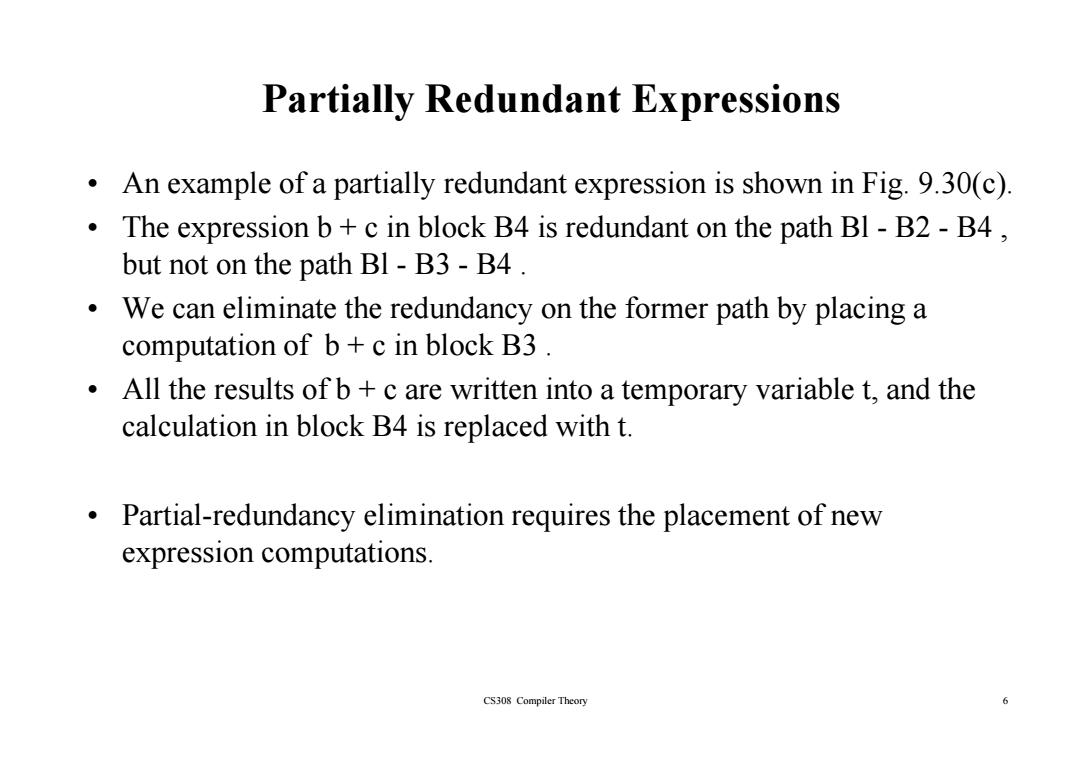
Partially Redundant Expressions An example of a partially redundant expression is shown in Fig.9.30(c). The expression b+c in block B4 is redundant on the path Bl-B2-B4, but not on the path Bl-B3-B4. We can eliminate the redundancy on the former path by placing a computation of b+c in block B3 All the results of b+c are written into a temporary variable t,and the calculation in block B4 is replaced with t. Partial-redundancy elimination requires the placement of new expression computations. CS308 Compiler Theory 6
Partially Redundant Expressions • An example of a partially redundant expression is shown in Fig. 9.30(c). • The expression b + c in block B4 is redundant on the path Bl - B2 - B4 , but not on the path Bl - B3 - B4 . • We can eliminate the redundancy on the former path by placing a computation of b + c in block B3 . • All th lt f b + itt i t t i bl t d th All the results o f b + c are written i n to a temporary var i able t, an d the calculation in block B4 is replaced with t. • Partial-redundancy elimination requires the placement of new expression computations expression computations. CS308 Compiler Theory 6
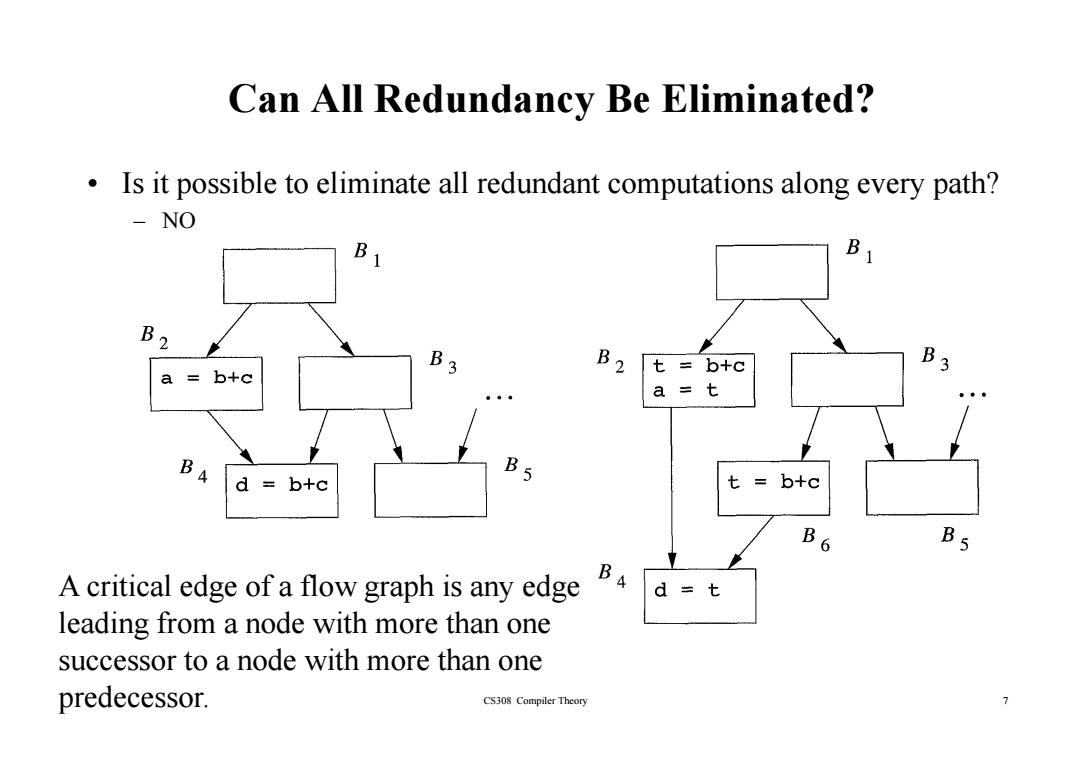
Can All Redundancy Be Eliminated? Is it possible to eliminate all redundant computations along every path? -NO B B2 B3 B2 =b+c B3 a =b+c d =b+c t =b+c B6 B5 A critical edge of a flow graph is any edge d =t leading from a node with more than one successor to a node with more than one predecessor. CS308 Compiler Theory 7
Can All Redundancy Be Eliminated? • Is it possible to eliminate all redundant computations along every path? – NO A critical edge of a flow graph is any edge leading from a node with more than one CS308 Compiler Theory 7 successor to a node with more than one predecessor