
●●● ●●●● S 3.1 Review of Random Processes ●●●● ●●●● ●●●● 随机过程回顾 ●●●● ●●●● §3.2 Thermal Noise热噪声 §3.3 Noise in Linear System线性系统中的噪声 §3.4 Basic Threshold Detection基本的门限检测 3.5 Noise Temperature and Noise Figure 噪声温度和噪声系数 3.6 Noise Figure of Passive Networks 无源网络的噪声系数 3.7 Dynamic Range and Intermodulation Distortion 动态范围和交调失真 7
§3.1 Review of Random Processes 随机过程回顾 §3.2 Thermal Noise 热噪声 §3.3 Noise in Linear System 线性系统中的噪声 §3.4 Basic Threshold Detection 基本的门限检测 §3.5 Noise Temperature and Noise Figure 噪声温度和噪声系数 §3.6 Noise Figure of Passive Networks 无源网络的噪声系数 §3.7 Dynamic Range and Intermodulation Distortion 动态范围和交调失真 7

●● 3.1 Review of Random Processes ●● ●●● ●●● 概率与随 ●●●● (I)Probability and Random Variables机变量 -∞<Xo<+∞,PX=X}=0;0≤PX≤X}≤1; (2)The Cumulative Distribution Function 累积分布函数 Fx(X)=PX≤x;P{X1≤X≤x2}=Fx(X2)-Fx(K1)i (3)The Probability Density Function概率密度函数 fx=dFx()/dx;px<X≤x,}=∫f(w)d∫f.(dx=l (4)Some Important Probability Density Functions Uniform distribution:(x)= ,for a≤x≤b均匀分布 b-a Gaussian distribution: f(x)= e-(x-mi12o,for -0≤X≤+0 Rayleigh distribution: V2πo2 高斯分布 r 瑞利分布 (x)=京e "for 0≤x≤+0 8
2 2 ( ) /2 2 1 ( )= , 2 x m x f x e for x 1 ( )= , b-a x f x for a x b §3.1 Review of Random Processes (1) Probability and Random Variables -∞<x 0<+ ∞ , P{X=x 0}=0; 0 ≤ P{X≤x 0} ≤1; (2)The Cumulative Distribution Function F X(x)=P{X ≤ x}; P{x1 ≤ X ≤x2 }=F X(x 2)-F X(x 1); (3)The Probability Density Function fX(x)=dF X(x)/dx; (4) Some Important Probability Density Functions Uniform distribution: Gaussian distribution: Rayleigh distribution: 2 1 x + 1 2 x P{x <X x }= ( ) ; ( ) 1 x x f x dx f x dx 2 2 /2 2 r ( )= , 0 r x f x e for x 8 概率与随 机变量 累积分布函数 概率密度函数 均匀分布 高斯分布 瑞利分布

●●● ●●●● ●●●●● (5)Expected Values ●●●● 期望值 ●●●● ●●●● =EX)=[xf(x)dx,EfeX)=cE(X).E(X+Y)=E(X)+E(Y) ●●●● Variance,o2=E{(x-x))=(x-x)f (x)dx 自相关及功率谱密度 (6)Autocorrelation and Power Spectral Density Deterministic Signal:R()=x(t)x(t+dt;R(0)2R(),R()=R() Random Signal:R()=E{x (t)x(t+)} Power Spetral Density:S(@)=R()ed--Fourier transform of R() R)=2a」s(eede ac时Rmer月-7-r20-&0-2 .(eo V2(t) Z 9
2 2 { } ( ) , { } { }, { } { } { } , {( )} ( ) ( ) x x x E X xf x dx E cX cE X E X Y E X E Y Variance E x x x x f x dx * * Deterministic Signal: ( ) ( ) ( ) ; (0) ( ), ( ) ( ) Random Signal: ( ) { ( ) ( )} R x t x t dt R R R R R E x t xt 2 2 Power Spetral Density: ( ) ( ) Fourier transform of ( ) 1 () ( ) ; 2 ( ) ( ( )) 1 (0) Received Power: ( ) 2 j j V j L V LL LL S Re d R R S ed V t EV t R P S ed ZZZZ (5)Expected Values (6)Autocorrelation and Power Spectral Density 9 期望值 自相关及功率谱密度

●●● ●●● §3.2 Thermal Noise ●●●● ●●●● ●●●● ●●●● 1Thermal noise is caused by the random motion of charge carriers.噪声由电荷的随机运动产生 2Other sources of noise include shot noise,flicker noise,plasma noise,,and quantum noise..噪声的其它来源 包括散弹噪声、闪烁噪声、等离子噪声和量子噪声 3Although these types of noise differ from thermal noise in terms of their origin,their characteristics are similar.尽管这些噪声的来源不同于热噪声,它们的特点相同。 10
§3.2 Thermal Noise ①Thermal noise is caused by the random motion of charge carriers. 噪声由电荷的随机运动产生 ②Other sources of noise include shot noise, flicker noise, plasma noise, and quantum noise.噪声的其它来源 包括散弹噪声、闪烁噪声、等离子噪声和量子噪声 ③Although these types of noise differ from thermal noise in terms of their origin, their characteristics are similar.尽管这些噪声的来源不同于热噪声,它们的特点相同。 10
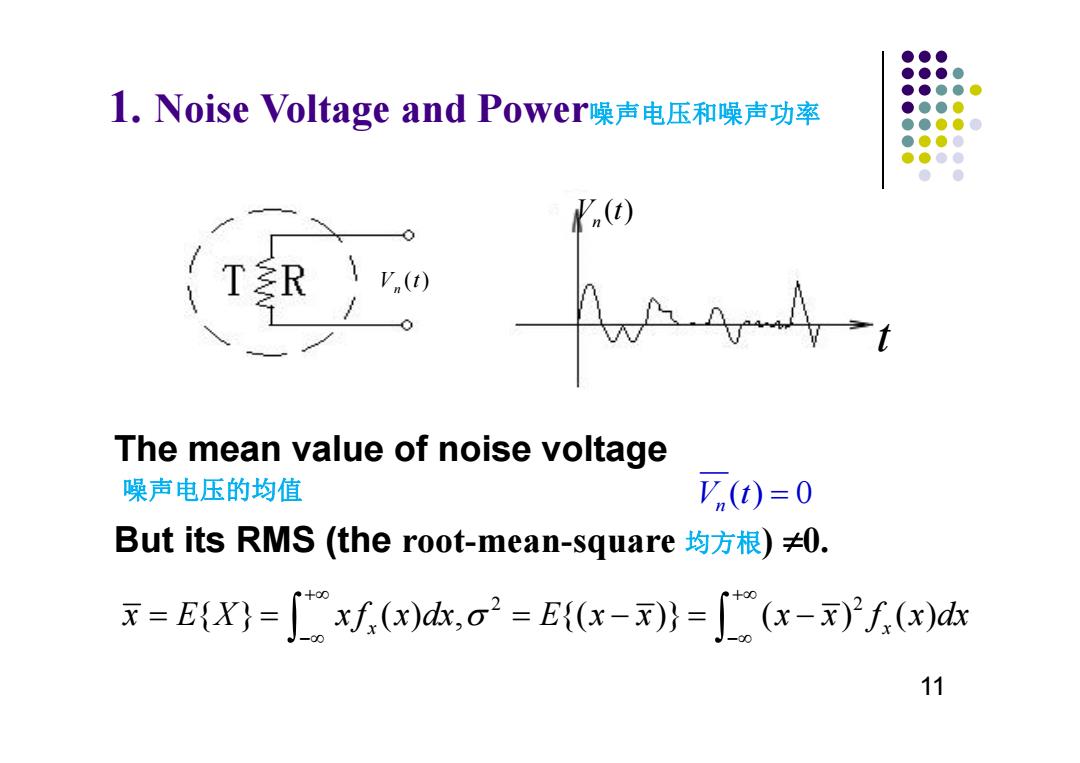
●●● ●●●● ●●●●● l.Noise Voltage and Poweri噪声电压和噪声功率 ●●●0 ●●●●0 ●●●0 ●●●● ●● The mean value of noise voltage 噪声电压的均值 ()=0 But its RMS(the root-mean-square均方根)≠0. =E)=xf(x)dx,o2=E((x-x))=(x-x)f(x)dx 11
1. Noise Voltage and Power噪声电压和噪声功率 The mean value of noise voltage 噪声电压的均值 () 0 V t n ( ) V t n ( ) V t n t 2 2 { } ( ) , {( )} ( ) ( ) x x x E X x f x dx E x x x x f x dx But its RMS (the root-mean-square 均方根) 0. 11