
SYSTEM CALLS o Programming interface to the services provided by the os o Typically written in a high-level language(C or C++) o Mostly accessed by programs via a high-level Application Program Interface (API)rather than direct system call use o Three most common APIs are Win32 API for Windows, POSIX API for POSIX-based systems (including virtually all versions of UNIX,Linux,and Mac OS X), and Java aPI for the Java virtual machine (JVM) o Why use APIs rather than system calls?(p45.) (Note that the system-call names used throughout this text are generic)
SYSTEM CALLS Programming interface to the services provided by the OS Typically written in a high-level language (C or C++) Mostly accessed by programs via a high-level Application Program Interface (API) rather than direct system call use Three most common APIs are Win32 API for Windows, POSIX API for POSIX-based systems (including virtually all versions of UNIX, Linux, and Mac OS X), and Java API for the Java virtual machine (JVM) Why use APIs rather than system calls?(p45.) (Note that the system-call names used throughout this text are generic)
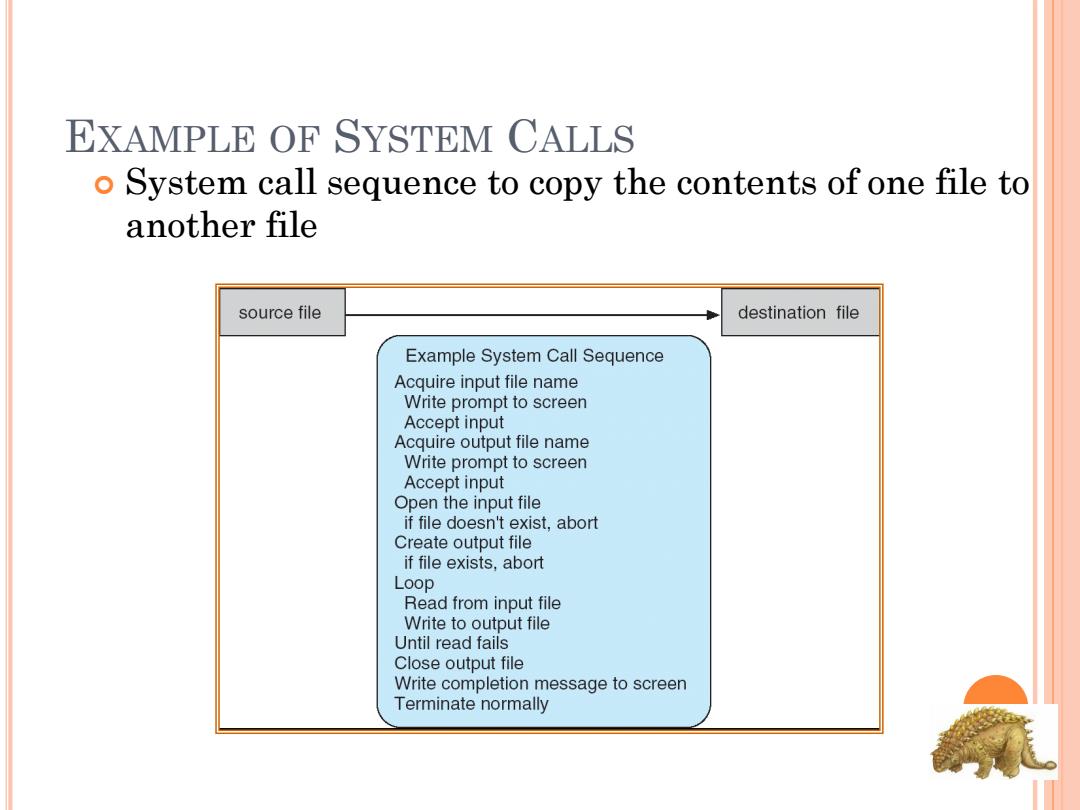
EXAMPLE OF SYSTEM CALLS o System call sequence to copy the contents of one file to another file source file destination file Example System Call Sequence Acquire input file name Write prompt to screen Accept input Acquire output file name Write prompt to screen Accept input Open the input file if file doesn't exist,abort Create output file if file exists,abort Loop Read from input file Write to output file Until read fails Close output file Write completion message to screen Terminate normally
EXAMPLE OF SYSTEM CALLS System call sequence to copy the contents of one file to another file
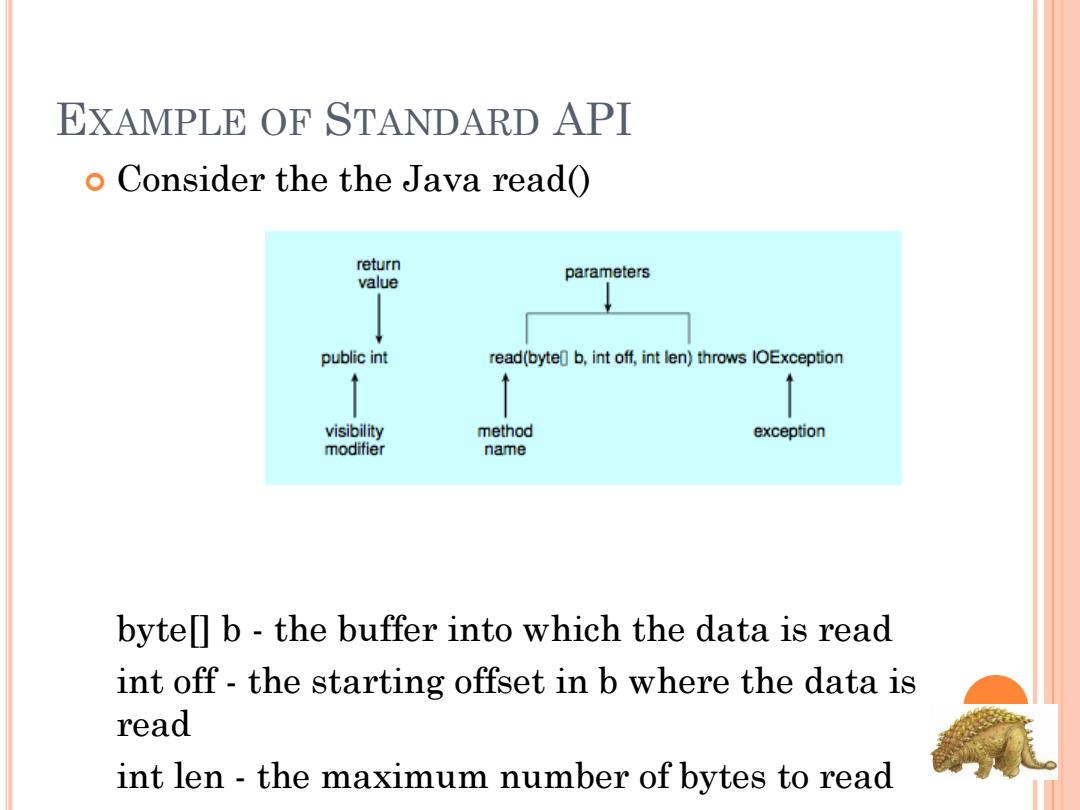
EXAMPLE OF STANDARD API o Consider the the Java read( return value parameters public int read(byte b,int off,int len)throws IOException visibility method exception modifier name bytel b-the buffer into which the data is read int off-the starting offset in b where the data is read int len-the maximum number of bytes to read
EXAMPLE OF STANDARD API Consider the the Java read() byte[] b - the buffer into which the data is read int off - the starting offset in b where the data is read int len - the maximum number of bytes to read

SYSTEM CALL IMPLEMENTATION o Typically,a number associated with each system call System-call interface maintains a table indexed according to these numbers The system call interface invokes intended system call in OS kernel and returns status of the system call and any return values o The caller need know nothing about how the system call is implemented Just needs to obey aPI and understand what OS will do as a result call Most details of OS interface hidden from programmer by API o Managed by run-time support library(set of functions built into libraries included with compiler)
SYSTEM CALL IMPLEMENTATION Typically, a number associated with each system call System-call interface maintains a table indexed according to these numbers The system call interface invokes intended system call in OS kernel and returns status of the system call and any return values The caller need know nothing about how the system call is implemented Just needs to obey API and understand what OS will do as a result call Most details of OS interface hidden from programmer by API Managed by run-time support library (set of functions built into libraries included with compiler)
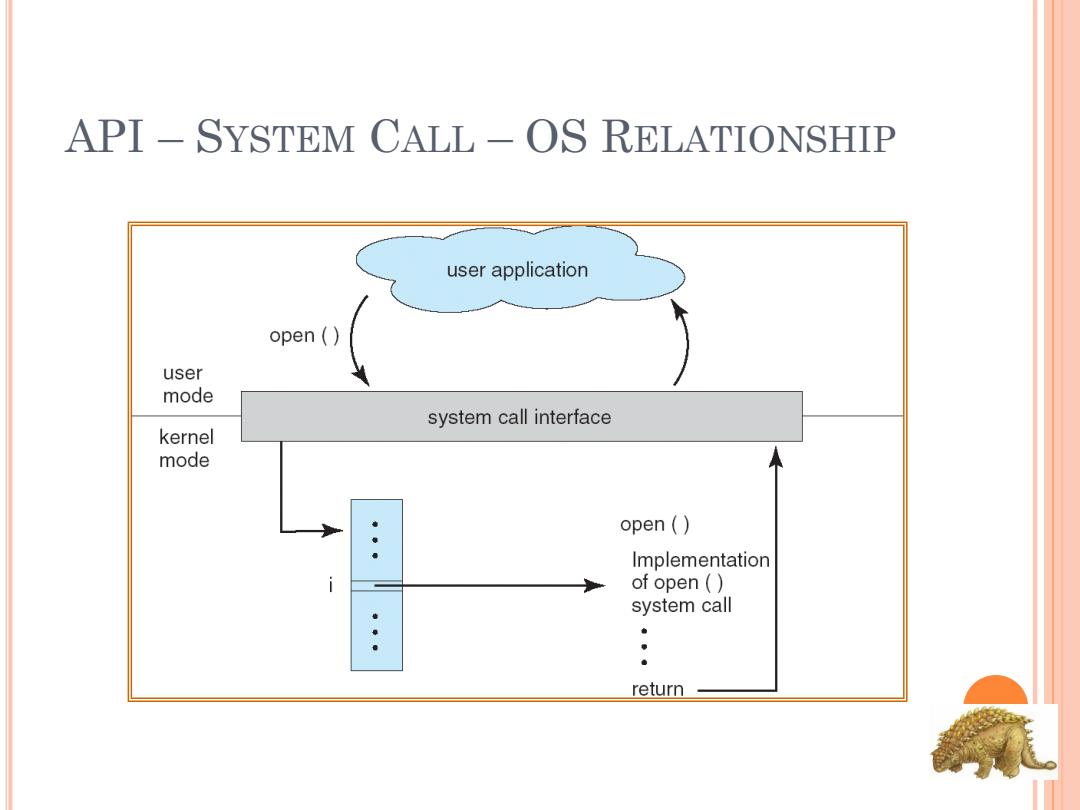
API SYSTEM CALL -OS RELATIONSHIP user application open ( user mode system call interface kernel mode open ( Implementation of open() system call 。 return
API – SYSTEM CALL – OS RELATIONSHIP