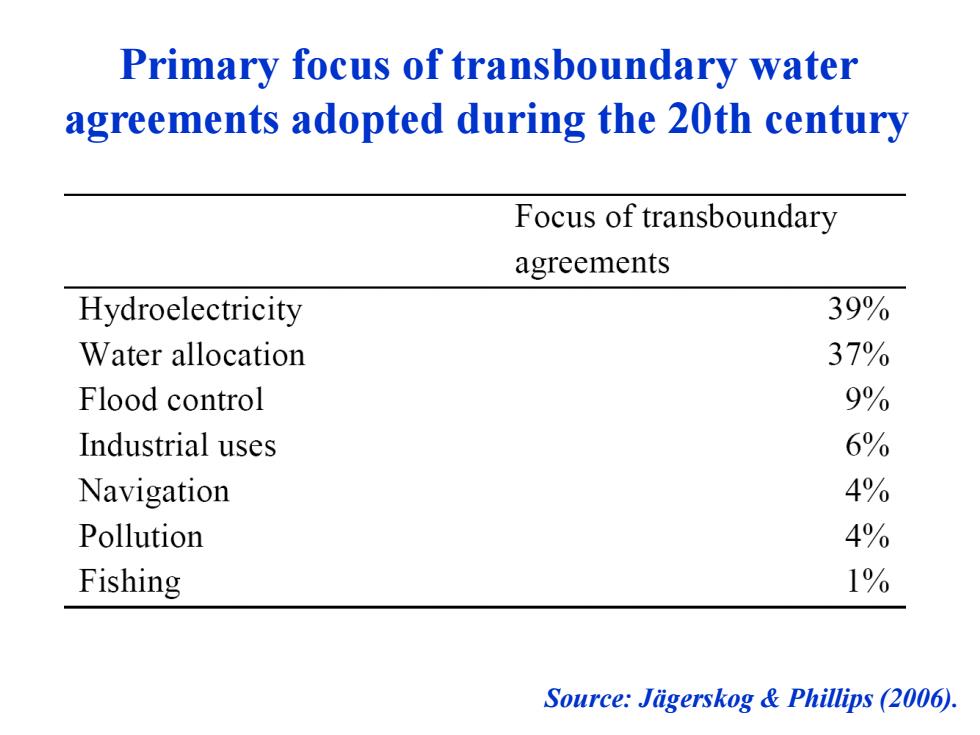
Primary focus of transboundary water agreements adopted during the 20th century Focus of transboundary agreements Hydroelectricity 39% Water allocation 37% Flood control 9% Industrial uses 6% Navigation 4% Pollution 4% Fishing 1% Source:Jigerskog Phillips(2006)
Primary focus of transboundary water agreements adopted during the 20th century Source: Jägerskog & Phillips (2006)
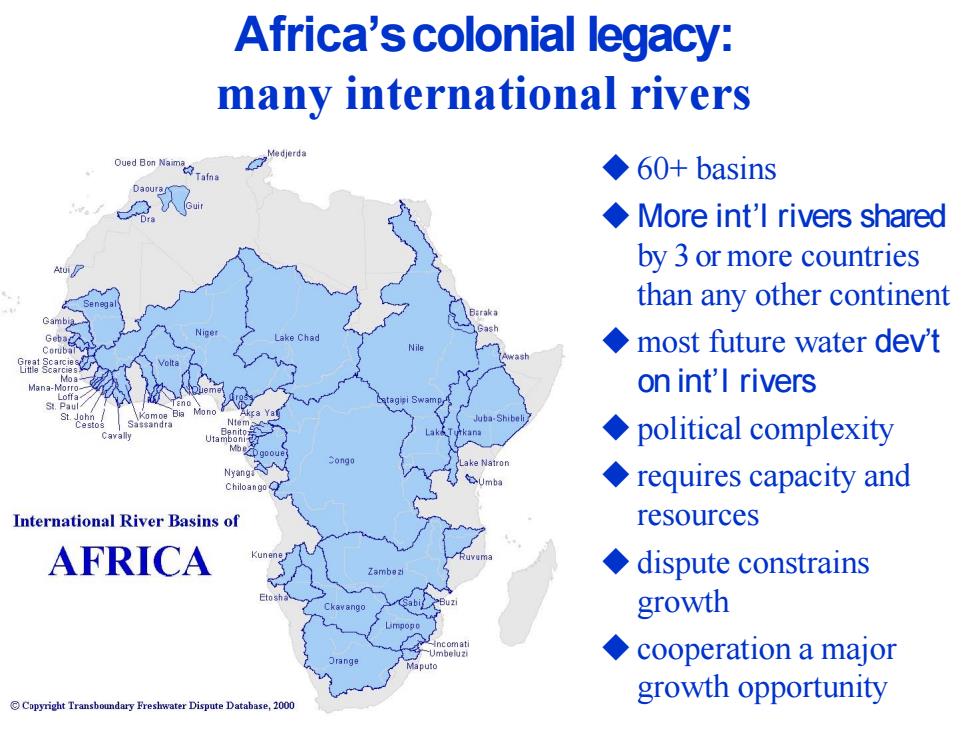
Africa's colonial legacy: many international rivers ◆60+basins More int'l rivers shared by 3 or more countries than any other continent Lake Cha most future water dev't Mana-M on int'I rivers St Pa Juba-Shibeli political complexity ake Natron Umba requires capacity and International River Basins of resources AFRICA ◆dispute constrains growth ◆cooperation a major growth opportunity Copyright Transboundary Freshwater Dispute Database,2000
Africa’scolonial legacy: many international rivers ◆60+ basins ◆More int’l rivers shared by 3 or more countries than any other continent ◆most future water dev’t on int’l rivers ◆political complexity ◆requires capacity and resources ◆dispute constrains growth ◆cooperation a major growth opportunity
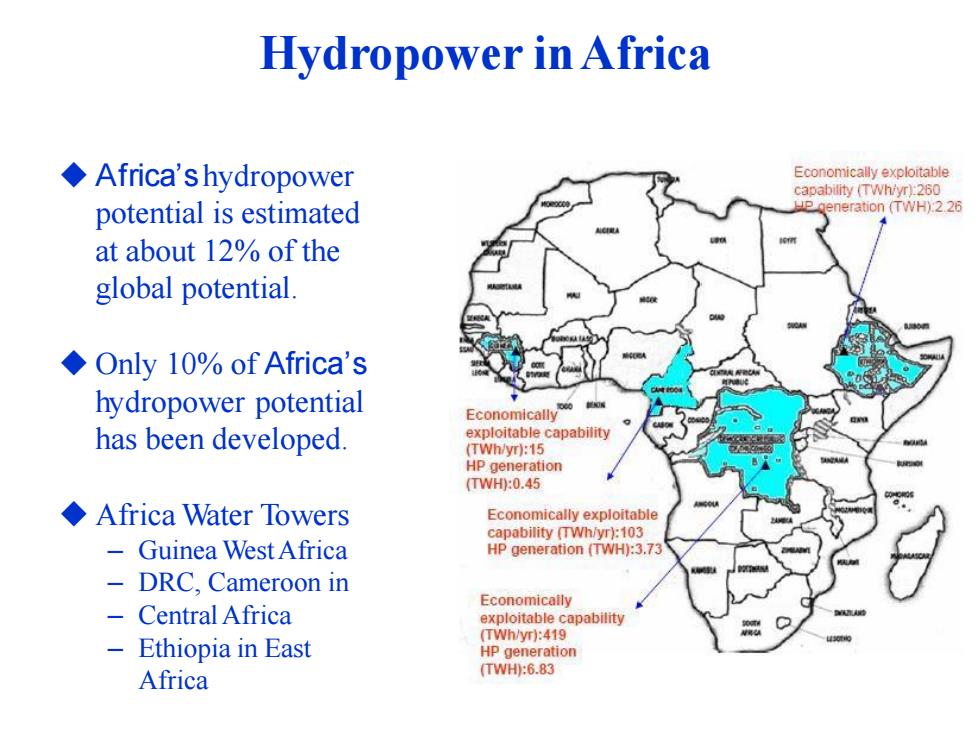
Hydropower in Africa ◆Africa's hydropower Economically exploitable capability (TWh/yr):260 potential is estimated Hegeneration (TWH):2.26 at about 12%of the global potential. ◆Only 10%of Africa's hydropower potential Economically has been developed. exploitable capability (TWh/yr):15 HP generation (TWH:0.45 ◆Africa Water Towers Economically exploitable capability (TWh/yr):103 Guinea West Africa HP generation (TWH):3.73 DRC,Cameroon in Economically Central Africa exploitable capability (TWh/yr):419 Ethiopia in East HP generation Africa (TWH:6.83
Hydropower inAfrica ◆ Africa’shydropower potential is estimated at about 12% of the global potential. ◆ Only 10% of Africa’s hydropower potential has been developed. ◆ Africa Water Towers – Guinea WestAfrica – DRC, Cameroon in – CentralAfrica – Ethiopia in East Africa
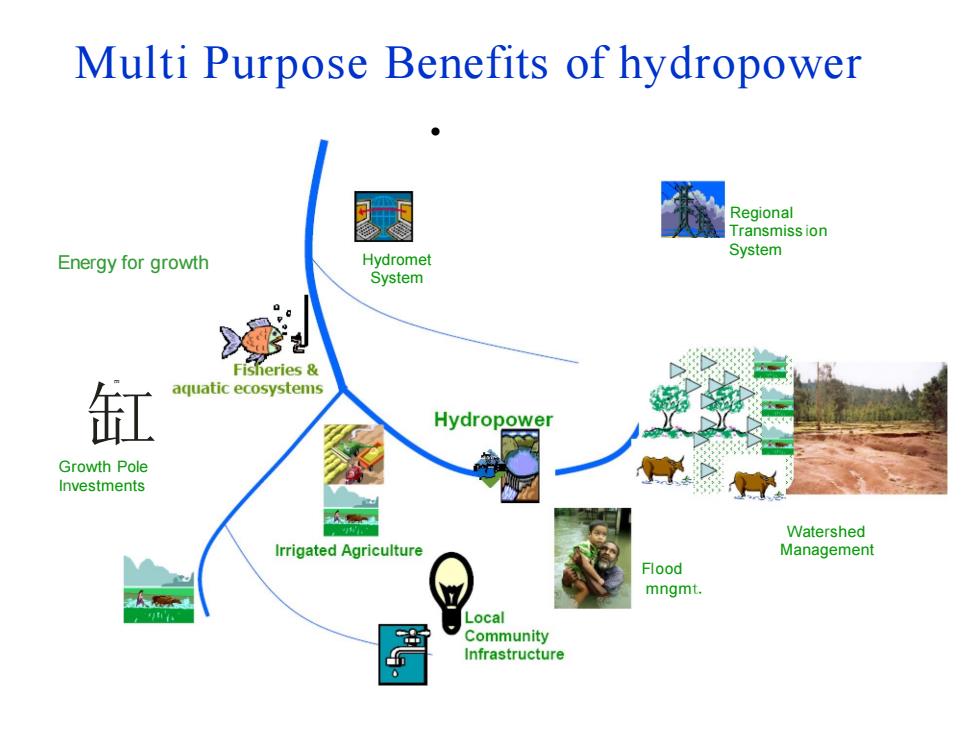
Multi Purpose Benefits of hydropower Regional Transmiss ion System Energy for growth Hydromet System Fisheries 缸 aquatic ecosystems Hydropower Growth Pole Investments Watershed Irrigated Agriculture Management Flood mngmt. Local Community Infrastructure
Multi Purpose Benefits of hydropower Energy for growth 缸 E Growth Pole Investments • Regional Transmiss ion System Hydromet System Watershed Management Flood mngmt
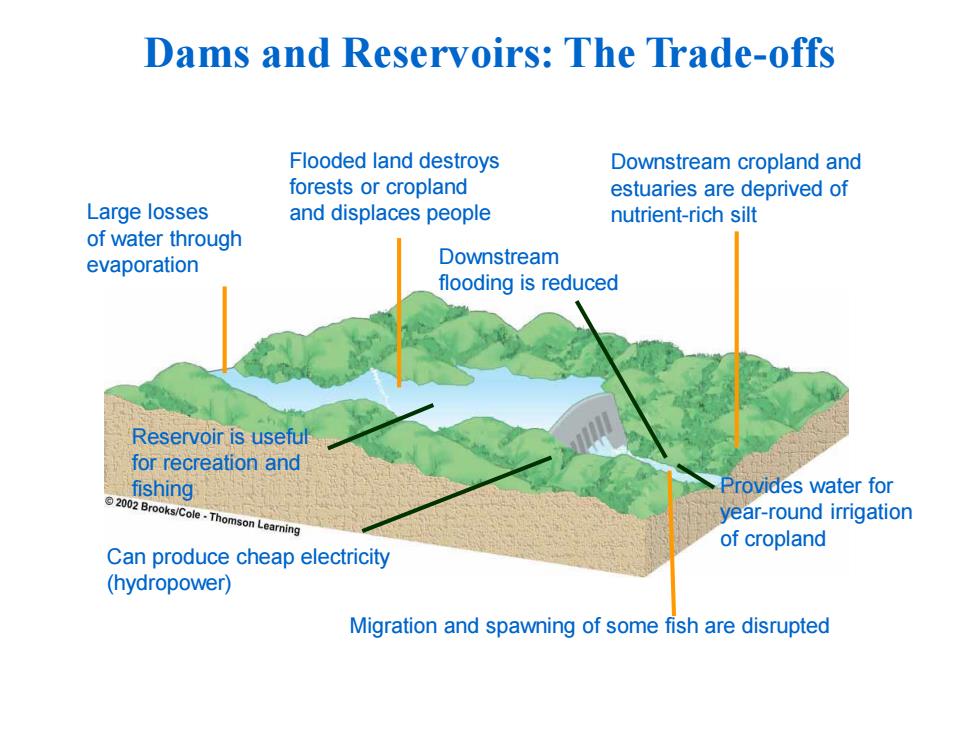
Dams and Reservoirs:The Trade-offs Flooded land destroys Downstream cropland and forests or cropland estuaries are deprived of Large losses and displaces people nutrient-rich silt of water through evaporation Downstream flooding is reduced Reservoir is useful for recreation and fishing Provides water for 2002 Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning year-round irrigation of cropland Can produce cheap electricity (hydropower) Migration and spawning of some fish are disrupted
Dams and Reservoirs: The Trade-offs Reservoir is useful for recreation and fishing Can produce cheap electricity (hydropower) Provides water for year-round irrigation of cropland Migration and spawning of some fish are disrupted Large losses of water through evaporation Flooded land destroys forests or cropland and displaces people Downstream flooding is reduced Downstream cropland and estuaries are deprived of nutrient-rich silt