
2.Working Capital Policy Working capital policy:Involves decisions about a company's current assets C/A and current liabilities (C/L What they consist of How they are used How their mix affects the risk-return characteristics of the company Working capital management Firm's optimal level of C/A Optimal mix of S-T and L-T debt Level of investment in each type of C/A Specific sources and mix of S-T credit the firm should employ 渊补楂价货多方号 YO年NEB证事0000
2. Working Capital Policy 2. Working Capital Policy z Working capital policy: Involves decisions about a company’s current assets ( C/A ) and current liabilities (C/L ) – What they consist of – How they are used – How their mix affects the risk-return characteristi cs of the company z Working capital management – Firm’s optimal level of C/A – Optimal mix of S-T and L-T debt – Level of investment in each type of C/A – Specific sources and mix of S-T credit the firm should employ

Continued... Working capital Represents assets that flow through the firm o Turned over at a rapid rate o Usually recovered during the operating cycle when inventories are sold and receivables are collected Needed because of the asynchronous nature of cash receipts and disbursements 渊外经价货多方是 YO年N0事0E000
Continued Continued… zWorking capital – Represents assets that flow through the firm o Turned over at a rapid rate o Usually recovered during the operating cycle when inventories are sold and receivables are collected – Needed because of the asynchronous nature of cash receipts and disbursements

Continued... Operating Cycle:Characterized by the time intervals between the following dates: Date 1 Purchase of resources Operating cycle 1 to 4 Date 2 Pay for resource Inventory conversion period purchases =1to3 Date 3 Sell product on credit Receivables conversion period Date 4 Collect receivables =3to4 Payables deferral period=1 to 2 Cash conversion cycle =2 to 4 渊外校价货多方号 YO年N0l到8E事0E00h03
Continued Continued… z Operating Cycle: Characterized by the time intervals between the following dates: Date 1 Purchase of resources Date 2 Pay for resource purchases Date 3 Sell product on credit Date 4 Collect receivables Operating cycle = 1 to 4 Inventory conversion period = 1 to 3 Receivables conversion period = 3 to 4 Payables deferral period = 1 to 2 Cash conversion cycle = 2 to 4

Continued... Receivables Operating Inventory Cycle Conversion+ Conversion Period Period Inventory Average inventory Conversion Period Cost of Sales/365 Receivables Accounts receivable Conversion Period Annual Credit Sales/365 剥外经价贫多方居 YO年NEB证事00003
Continued Continued… Operating Cycle = Inventory Conversion Period + Receivables Conversion Period Inventory Conversion Period = Average Inventory Cost of Sales/ 365 Receivables Conversion Period = Accounts Receivable Annual Credit Sales/ 365
Continued... Salaries,Benefits Accounts Payables +Payroll Taxes Payable Deferral Payable Period Cost of Selling,Gen, /365 Sales Admin Exp Cash Operating Payables Conversion Cycle Deferral Cycle Period 剥外校价贫多方号 YO年NEB证事00003
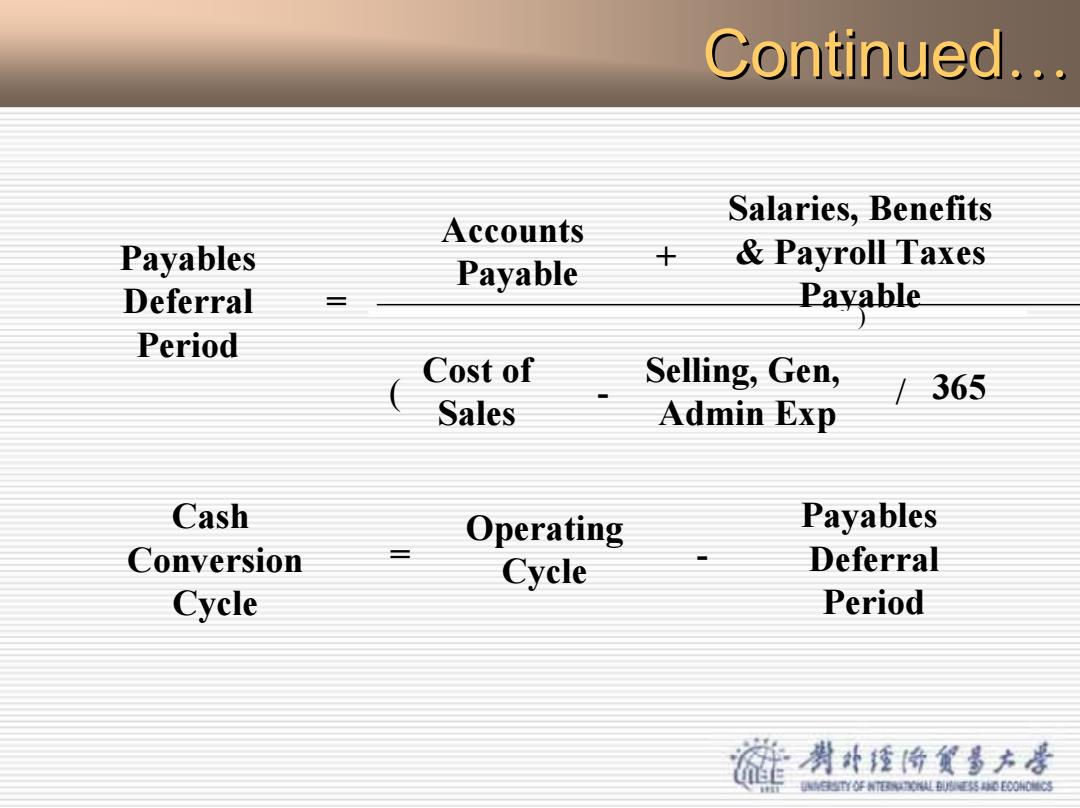
Continued Continued… Payables Deferral Period = Accounts Payable + Salaries, Benefits & Payroll Taxes Payable Cost of Sales - Selling, Gen, Admin Exp ( / 365 ) Cash Conversion Cycle = Operating Cycle - Payables Deferral Period