
8/17/2016 Microbes Microbes in Our Lives Learning Objectives Invisible Invaders List several ways in which microbes Amazing Allies affect our lives Chapter 1 The Microbial World and you What is Microbiology? Microorganisms or Microbes-collective term Microbiology-a specialized area of biology that for organisms visualized by a microscope studies living organisms too small to be seen without magnification In the context of infectious disease,less clear terms,such as germs,agents,and bugs,may be used and may place undue emphasis on a negative reputation of microorganisms. In fact,only a small number of microorganisms cause harm to other living organisms. h上mm广n 0.05%of known species,about 583 species Many are useful or essential for human life
8/17/2016 1 Invisible Invaders Amazing Allies Chapter 1 The Microbial World and You Learning Objectives List several ways in which microbes affect our lives Microbes in Our Lives Microbiology - a specialized area of biology that studies living organisms too small to be seen without magnification What is Microbiology? Microorganisms or Microbes – collective term for organisms visualized by a microscope In the context of infectious disease, less clear terms, such as germs, agents, and bugs, may be used and may place undue emphasis on a negative reputation of microorganisms. In fact, only a small number of microorganisms cause harm to other living organisms. 0.05% of known species, about 583 species Many are useful or essential for human life

8/17/2016 Many Diverse Microbiology Disciplines Impact of Microbes on the Earth Public Health Microbiology and Epidemiology monitor and control the spread of disea Medical Microbiology es in communities Microorganisms have a profound influence on all aspects of the earth and its residents. homicroorgnicuse disese in hmns nd Microorganisms have influenced the evolution of other life forms. Immunology study of the host response to infection Evolution is the accumulation of changes that occur in organisms as they adapt to their environment gene therapy herobes and damestic plants and nmental Microbiology study of how microbes affect the earth's habitats Microorganisms are Ubiquitous Microbial Involvement in Energy and Nutrient Flow within Ecosystems Found nearly everywhere Ecosystems are communities of and Occur in large numbers their surrounding environment. Live in places other organisms cannot Bacteria performed Photosynthetic Influence landscapes essential to life photosynthesis well before plants did. eyhloe Photosynthesis is the light fueled conversion of carbon dioxide to oxygen. Microorganisms account for >70% of photosynthesis and contribute the majority of oxygen to the atmosphere. 2
8/17/2016 2 Public Health Microbiology and Epidemiology monitor and control the spread of diseases in communities Medical Microbiology study of how microorganisms cause disease in humans and animals Immunology study of the host response to infection Industrial Microbiology safeguard for food and water and use of microbes to produce products ranging from beer, cheese, yogurt, etc. to gene therapy Agricultural Microbiology relationship between microbes and domestic plants and animals Environmental Microbiology study of how microbes affect the earth’s habitats Many Diverse Microbiology Disciplines Microorganisms have a profound influence on all aspects of the earth and its residents. Microorganisms have influenced the evolution of other life forms. Evolution is the accumulation of changes that occur in organisms as they adapt to their environment Impact of Microbes on the Earth Microorganisms are Ubiquitous Hot Springs Dead Sea Found nearly everywhere Occur in large numbers Live in places other organisms cannot Influence landscapes essential to life Microbial Involvement in Energy and Nutrient Flow within Ecosystems Ecosystems are communities of living organisms and their surrounding environment. Bacteria performed photosynthesis well before plants did. Photosynthesis is the light fueled conversion of carbon dioxide to oxygen. Microorganisms account for >70% of photosynthesis and contribute the majority of oxygen to the atmosphere. Photosynthetic ecosystem with algae mats

8/17/2016 and nutrient cycling involves the Human Use of Microorganisms compounds/nutrients that can be reused in the Humans have used microorganisms for thousands natural cycles of living organisms. of years to improve life and to shape civilization. are the main forces that structure etCGc38iofhesolwateaaomospherg Baker's and Brewer's yeast are a type of single-cell fungi used to make bread rise and to ferment sugar into alcohol to make beer and wine. Fungi are also used to make cheeses such as Camembert or Blue Cheese Ancient Egyptians applied moldy aagosin9P9 bread to their wounds as it acted as an antibiotic. Infectious Diseases and Microorganisms Naming and Classifying Microorganisms Microorganisms can also cause great human misery and death. Learning Objectives Pathogen is a disease-causing organism,such as a bacterium,virus,fungus,protozoan,or helminth. Recognize scientific nomenclature that Infectious diseases are disorders caused by uses two names:genus and species microorganisms. Differentiate major characteristics of each group of microorganisms MRSA List the three domains of organisms
8/17/2016 3 Decomposition and nutrient cycling involves the breakdown of dead matter and wastes into simple compounds/nutrients that can be reused in the natural cycles of living organisms. Microorganisms are the main forces that structure the content of the soil, water, and atmosphere. Fungi on a decomposing log Garden compost Decomposing pig carcass Baker’s and Brewer’s yeast are a type of single-cell fungi used to make bread rise and to ferment sugar into alcohol to make beer and wine. Fungi are also used to make cheeses such as Camembert or Blue Cheese Ancient Egyptians applied moldy bread to their wounds as it acted as an antibiotic. Humans have used microorganisms for thousands of years to improve life and to shape civilization. Human Use of Microorganisms Microorganisms can also cause great human misery and death. Pathogen is a disease-causing organism, such as a bacterium, virus, fungus, protozoan, or helminth. Infectious diseases are disorders caused by microorganisms. Infectious Diseases and Microorganisms Learning Objectives Recognize scientific nomenclature that uses two names: genus and species Differentiate major characteristics of each group of microorganisms List the three domains of organisms Naming and Classifying Microorganisms
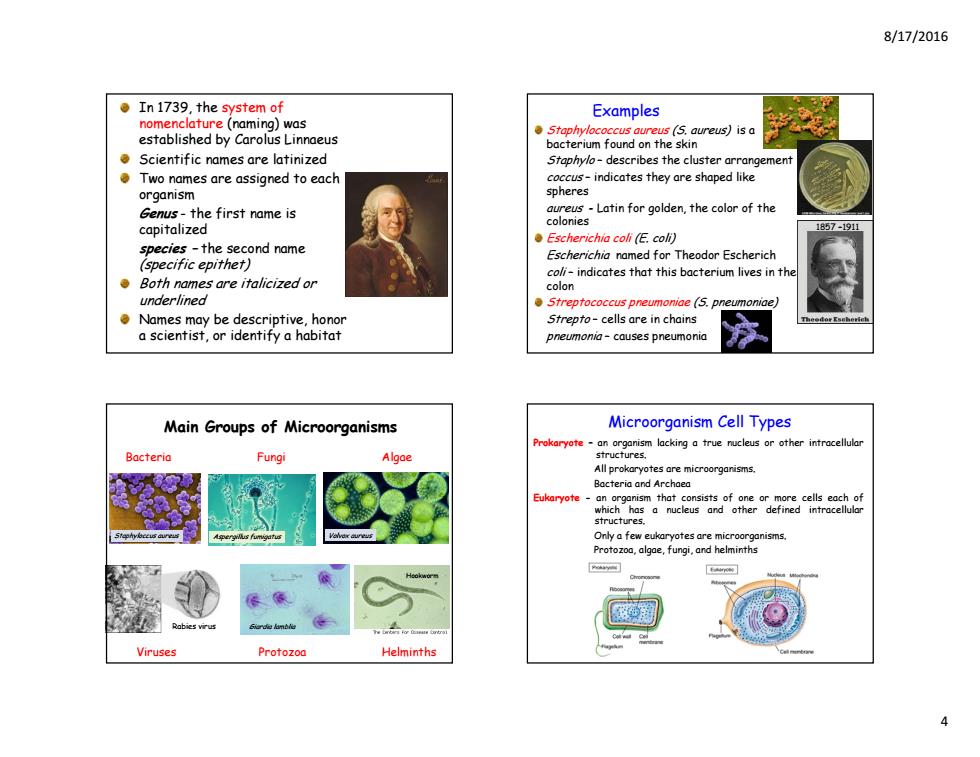
8/17/2016 。In1739,the system of Examples nomenclature(naming)was established by Carolus Linnaeus Staphylococcus aureus (S.aureus)isa bacterium found on the skin Scientific names are latinized Staphylo-describes the cluster arrangement Two names are assigned to each coccus-indicates they are shaped like organism spheres Genus-the first name is Lin for golden,the colr of the capitalized ●Escherichia coli(E.colj species-the second name Escherichia named for Theodor Escherich (specific epithet) coli-indicates that this bacterium lives in the Both names are italicized or colon underlined Streptococcus pneumoniae (5.pneumoniae) Names may be descriptive,honor Strepto-cells are in chains a scientist,or identify a habitat pneumonia-causes pneumonia Main Groups of Microorganisms Microorganism Cell Types Bacteria Fungi Algae All prokaryotes are microorganisms. Bacteria and Archaea Eukaryote-an organism that consists of one or more cells each of which has a nucleus and other defined intracellular structures. Only a few eukaryotes are microorganisms. Protozoa,algae,fungi,and helminths Rabes vrus Girdie lambl恤 Viruses Protozoa Helminths 4
8/17/2016 4 In 1739, the system of nomenclature (naming) was established by Carolus Linnaeus Scientific names are latinized Two names are assigned to each organism Genus - the first name is capitalized species – the second name (specific epithet) Both names are italicized or underlined Names may be descriptive, honor a scientist, or identify a habitat Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is a bacterium found on the skin Staphylo – describes the cluster arrangement coccus – indicates they are shaped like spheres aureus - Latin for golden, the color of the colonies Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia named for Theodor Escherich coli – indicates that this bacterium lives in the colon Streptococcus pneumoniae (S. pneumoniae) Strepto – cells are in chains pneumonia – causes pneumonia Examples 1857 –1911 Main Groups of Microorganisms Viruses Protozoa Helminths Bacteria Fungi Algae Hookworm Rabies virus Giardia lamblia Staphyloccus aureus Aspergillus fumigatus Volvox aureus Prokaryote – an organism lacking a true nucleus or other intracellular structures. All prokaryotes are microorganisms. Bacteria and Archaea Eukaryote - an organism that consists of one or more cells each of which has a nucleus and other defined intracellular structures. Only a few eukaryotes are microorganisms. Protozoa, algae, fungi, and helminths Microorganism Cell Types
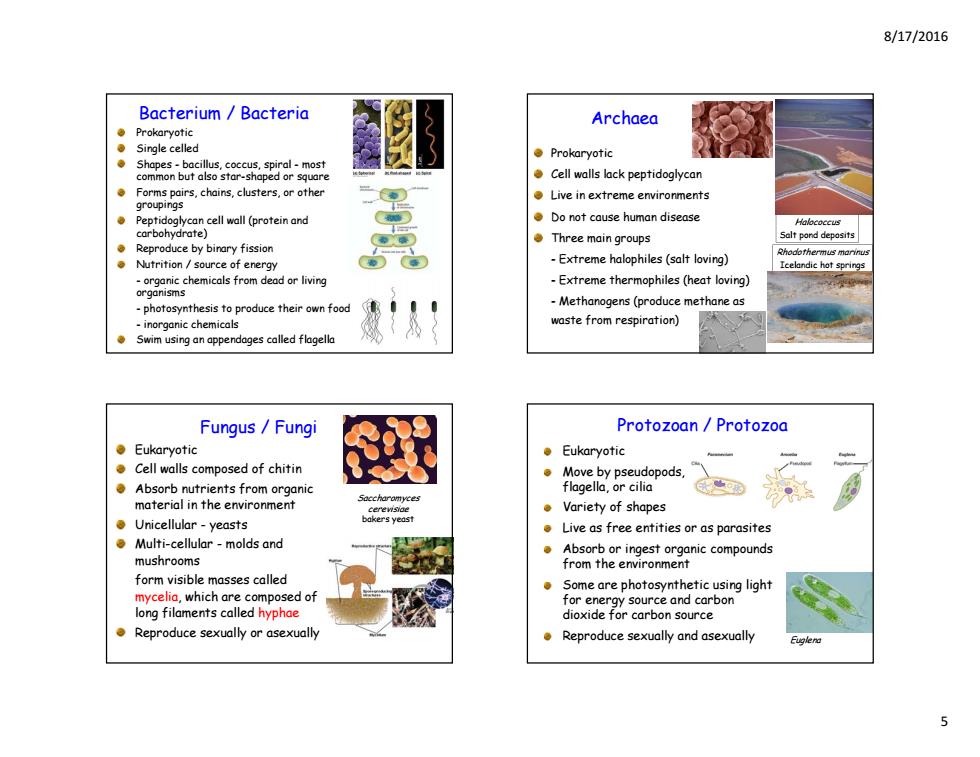
8/17/2016 Bacterium Bacteria Archaea ●Prokaryotic Single celled ●Prokaryotic Shapes-bacillus,coccus,spiral-most common but also star-shaped or square Cell walls lack peptidoglycan Live in extreme environments Peptidoglycan cell wall(protein and Do not cause human disease carbohydrate) ●Three main groups Sclt pond depasits Reproduce by binary fission Nutrition/source of energy -Extreme halophiles(salt loving) the Icelandic hot sprin -organic chemicals from dead or living -Extreme thermophiles(heat loving) organisms photosynthesis to produce their own food -Methanogens(produce methane as -inorganic chemicals waste from respiration) ● Swim using an appendages called flagella Fungus/Fungi Protozoan Protozoa ●Eukaryotic ●Eukaryotic Cell walls composed of chitin 。Move,by pseudopods, Absorb nutrients from organic flagella,or cilia material in the environment ●Variety of shapes ●Unicellular-yeasts Live as free entities or as parasites Multi-cellular-molds and Absorb or ingest organic compounds mushrooms from the environment form visible masses called Some are photosynthetic using light mycelia,which are composed of for energy source and carbon long filaments called hyphae dioxide for carbon source Reproduce sexually or asexually Reproduce sexually and asexually e
8/17/2016 5 Bacterium / Bacteria Prokaryotic Single celled Shapes - bacillus, coccus, spiral - most common but also star-shaped or square Forms pairs, chains, clusters, or other groupings Peptidoglycan cell wall (protein and carbohydrate) Reproduce by binary fission Nutrition / source of energy - organic chemicals from dead or living organisms - photosynthesis to produce their own food - inorganic chemicals Swim using an appendages called flagella Archaea Prokaryotic Cell walls lack peptidoglycan Live in extreme environments Do not cause human disease Three main groups - Extreme halophiles (salt loving) - Extreme thermophiles (heat loving) - Methanogens (produce methane as waste from respiration) Halococcus Salt pond deposits Rhodothermus marinus Icelandic hot springs Eukaryotic Cell walls composed of chitin Absorb nutrients from organic material in the environment Unicellular - yeasts Multi-cellular - molds and mushrooms form visible masses called mycelia, which are composed of long filaments called hyphae Reproduce sexually or asexually Fungus / Fungi Saccharomyces cerevisiae bakers yeast Protozoan / Protozoa Eukaryotic Move by pseudopods, flagella, or cilia Variety of shapes Live as free entities or as parasites Absorb or ingest organic compounds from the environment Some are photosynthetic using light for energy source and carbon dioxide for carbon source Reproduce sexually and asexually Euglena