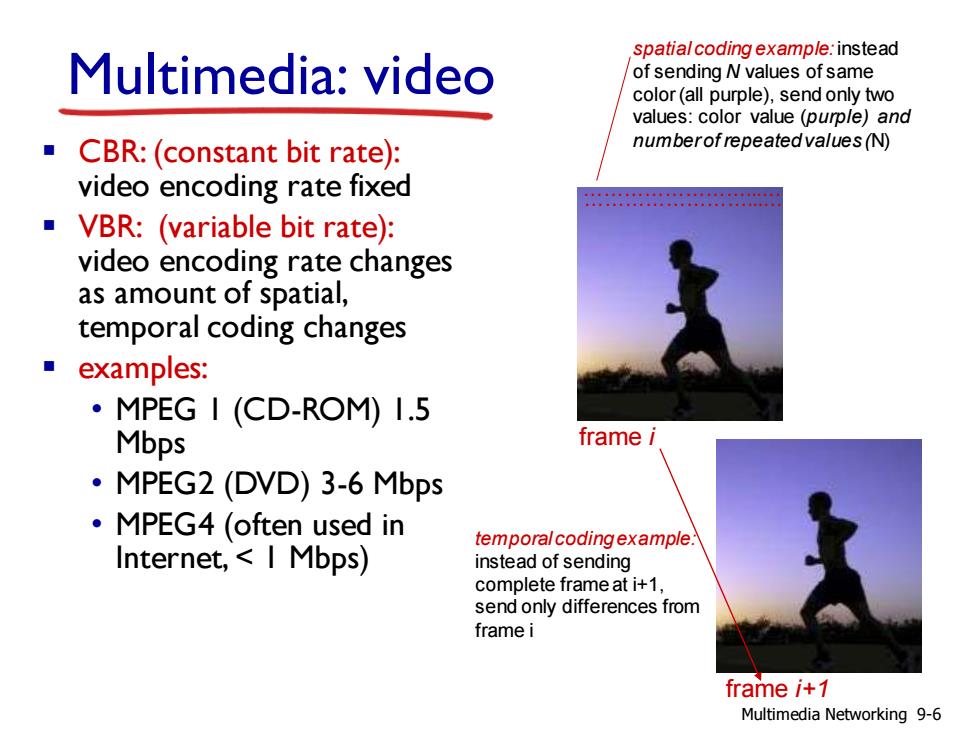
spatial coding example:instead Multimedia:video of sending N values of same color (all purple),send only two values:color value (purple)and CBR:(constant bit rate): numberof repeatedvalues(N) video encoding rate fixed 288800228022008890090 VBR:(variable bit rate): video encoding rate changes as amount of spatial, temporal coding changes examples: ·MPEG I(CD-ROM)I.5 Mbps frame i ·MPEG2(DVD)3-6MbPs ·MPEG4(often used in temporal coding example Internet,I Mbps) instead of sending complete frame at i+1, send only differences from frame i frame i+1 Multimedia Networking 9-6
Multimedia: video ……………………...… spatial coding example: instead of sending N values of same color (all purple), send only two values: color value (purple) and number of repeated values (N) ……………………...… frame i frame i+1 temporal coding example: instead of sending complete frame at i+1, send only differences from frame i ▪ CBR: (constant bit rate): video encoding rate fixed ▪ VBR: (variable bit rate): video encoding rate changes as amount of spatial, temporal coding changes ▪ examples: • MPEG 1 (CD-ROM) 1.5 Mbps • MPEG2 (DVD) 3-6 Mbps • MPEG4 (often used in Internet, < 1 Mbps) Multimedia Networking 9-6

Multimedia networking:3 application types streaming,stored audio,video streaming:can begin playout before downloading entire file stored (at server):can transmit faster than audio/video will be rendered (implies storing/buffering at client) e.g.,YouTube,Netflix,Hulu conversational voice/video over IP interactive nature of human-to-human conversation limits delay tolerance ·eg,Skype streaming live audio,video e.g.,live sporting event (futbol) Multimedia Networking 9-7
Multimedia networking: 3 application types ▪ streaming, stored audio, video • streaming: can begin playout before downloading entire file • stored (at server): can transmit faster than audio/video will be rendered (implies storing/buffering at client) • e.g., YouTube, Netflix, Hulu ▪ conversational voice/video over IP • interactive nature of human-to-human conversation limits delay tolerance • e.g., Skype ▪ streaming live audio, video • e.g., live sporting event (futbol) Multimedia Networking 9-7

Multimedia networking:outline 9.I multimedia networking applications 9.2 streaming stored video 9.3 voice-over-IP 9.4 protocols for real-time conversational applications 9.5 network support for multimedia Multimedia Networking 9-8
Multimedia networking: outline 9.1 multimedia networking applications 9.2 streaming stored video 9.3 voice-over-IP 9.4 protocols for real-time conversational applications 9.5 network support for multimedia Multimedia Networking 9-8
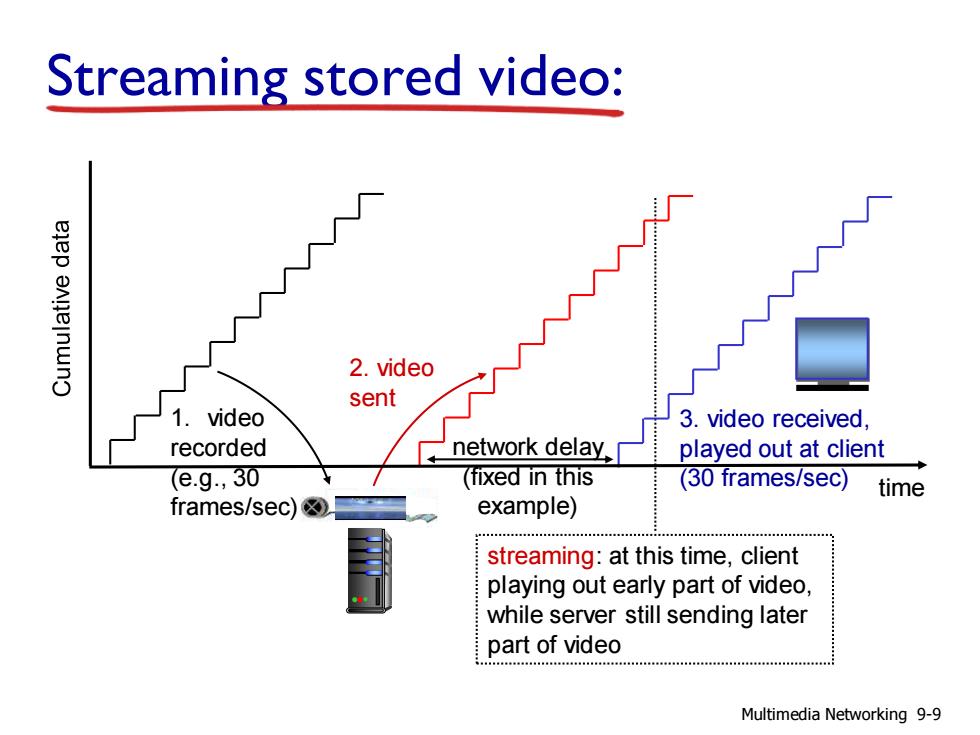
Streaming stored video: ejep enneinwno 2.video sent 1.video 3.video received, recorded network delay played out at client (e.g,30 (fixed in this (30 frames/sec) time frames/sec) example) streaming:at this time,client playing out early part of video while server still sending later part of video Multimedia Networking 9-9
Streaming stored video: 1. video recorded (e.g., 30 frames/sec) 2. video sent streaming: at this time, client playing out early part of video, while server still sending later part of video network delay (fixed in this example) time 3. video received, played out at client (30 frames/sec) Multimedia Networking 9-9

Streaming stored video:challenges continuous playout constraint:once client playout begins,playback must match original timing ...but network delays are variable (jitter),so will need client-side buffer to match playout requirements other challenges: client interactivity:pause,fast-forward,rewind, jump through video video packets may be lost,retransmitted Multimedia Networking 9-10
Streaming stored video: challenges ▪ continuous playout constraint: once client playout begins, playback must match original timing • … but network delays are variable (jitter), so will need client-side buffer to match playout requirements ▪ other challenges: • client interactivity: pause, fast-forward, rewind, jump through video • video packets may be lost, retransmitted Multimedia Networking 9-10