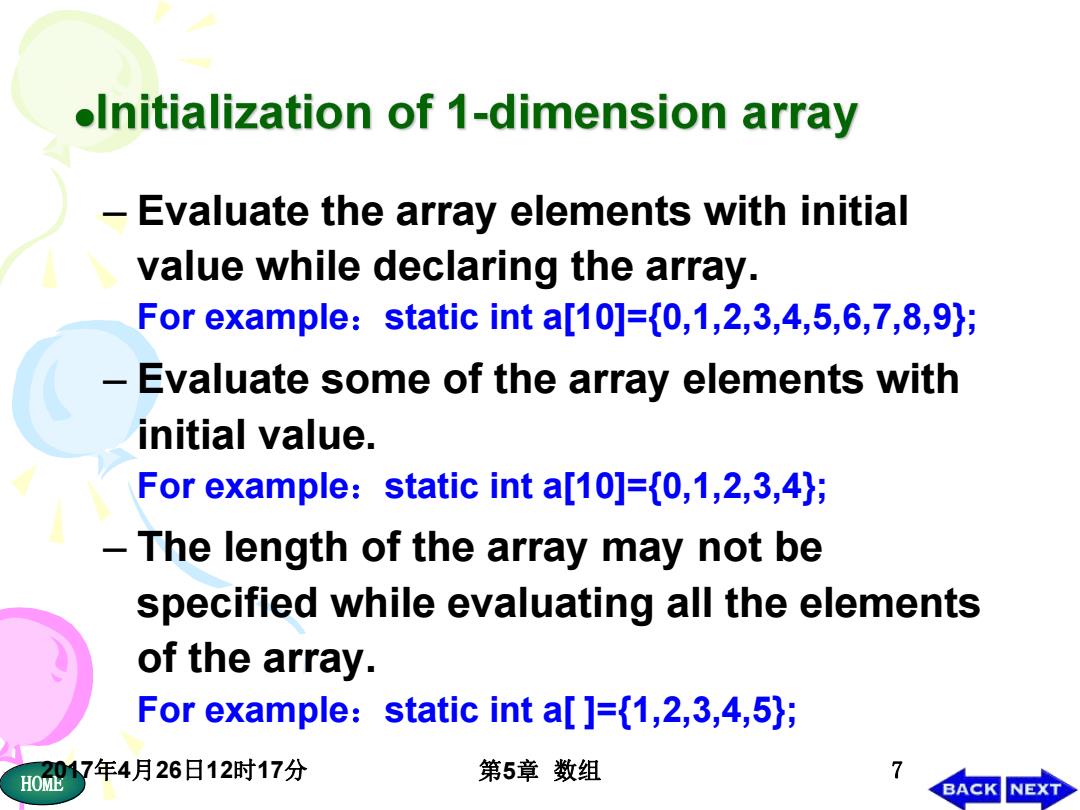
oInitialization of 1-dimension array Evaluate the array elements with initial value while declaring the array. For example:static int a[10]={0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9); Evaluate some of the array elements with initial value. For example:static int a[10]={0,1,2,3,4); The length of the array may not be specified while evaluating all the elements of the array. For example:static int a[]={1,2,3,4,5); 2017年4月26日12时17分 7 HOM 第5章数组 BACK NEXT
HOME2017年4月26日12时17分 第5章 数组 7 – Evaluate the array elements with initial value while declaring the array. For example:static int a[10]={0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; – Evaluate some of the array elements with initial value. For example:static int a[10]={0,1,2,3,4}; – The length of the array may not be specified while evaluating all the elements of the array. For example:static int a[ ]={1,2,3,4,5};
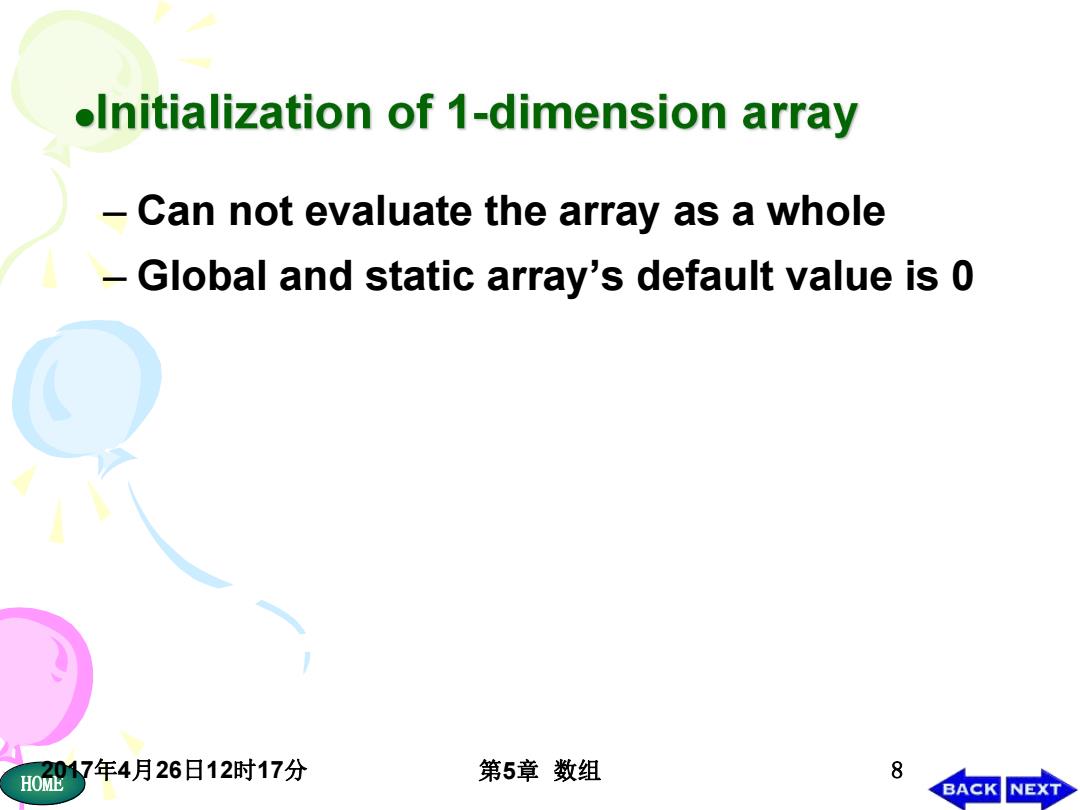
oInitialization of 1-dimension array Can not evaluate the array as a whole Global and static array's default value is 0 017年4月26日12时17分 8 HOME 第5章数组 BACK NEXT
HOME2017年4月26日12时17分 第5章 数组 8 – Can not evaluate the array as a whole – Global and static array’s default value is 0

5.2.4一维数组程序举例 例5.2用数组来处理求例3.13 Fibonacci数列问题。 这是一个有趣的古典数学问题:有一对兔子,从出生后第3个 月起每个月都生一对兔子。小兔子长到第3个月后每个月又生 一对兔子。假设所有兔子都不死,问每个月的兔子总数为多 少? 这个数列有如下特点:第1、2个数为1、1。从第3个数开始, 每个数是其前面两个数之和。即 F1=1 (n=1) F2=1 (n=2) Fn=Fn-1+Fn-2 (n23) 可以用20个元素代表数列中的20个数,从第3个数开始,可 以直接用表达式 f叮=fi-2]+fi-1]求出各数。 2017年4月26日12时17分 第5章数组 BACK NEX
HOME2017年4月26日12时17分 第5章 数组 9 例5.2 用数组来处理求例3.13 Fibonacci数列问题。 这是一个有趣的古典数学问题:有一对兔子,从出生后第3个 月起每个月都生一对兔子。小兔子长到第3个月后每个月又生 一对兔子。假设所有兔子都不死,问每个月的兔子总数为多 少? 这个数列有如下特点:第1、2个数为1、1。从第3个数开始, 每个数是其前面两个数之和。即 F1=1 (n=1) F2=1 (n=2) Fn=Fn-1+Fn-2 (n≥3) 可以用20个元素代表数列中的20个数,从第3个数开始,可 以直接用表达式 f[i]=f[i-2]+f[i-1]求出各数

#include <iostream> #include <iomanip> using namespace std; int main() long f1,f2; int i; f1=f2=1; for(i=1;i<=20;it+) cout<<setw(12)<<f1<<setw(12)<<f2; if(i%2==0)cout<<endl; f1=f1+f2; f2=f2+f1; } return 0; 2017年4月26日12时17分 HOM正 第5章数组 10 BACK NEXT
HOME2017年4月26日12时17分 第5章 数组 10 #include <iostream> #include <iomanip> using namespace std; int main( ) { long f1,f2; int i; f1=f2=1; for(i=1;i<=20;i++) { cout<<setw(12)<<f1<<setw(12)<<f2; if(i%2==0) cout<<endl; f1=f1+f2; f2=f2+f1; } return 0; }

#include <iostream> #include <iomanip> using namespace std; int main() {inti,f20]={1,1; for(i=2;i<20;i++) f[0=f[i-2]+fi-1]; for(i=0;i<20;i++) if(i%5==0)cout<<endl; cout<<setw(8)<<f[i] cout<<endl;return 0; 2017年4月26日12时17分 HOM正 第5章数组 11 BACK NEXT
HOME2017年4月26日12时17分 第5章 数组 11 #include <iostream> #include <iomanip> using namespace std; int main( ) { int i,f[20]={1,1}; for(i=2;i<20;i++) f[i]=f[i-2]+f[i-1]; for(i=0;i<20;i++) { if(i%5==0) cout<<endl; cout<<setw(8)<<f[i]; }cout<<endl; return 0; }