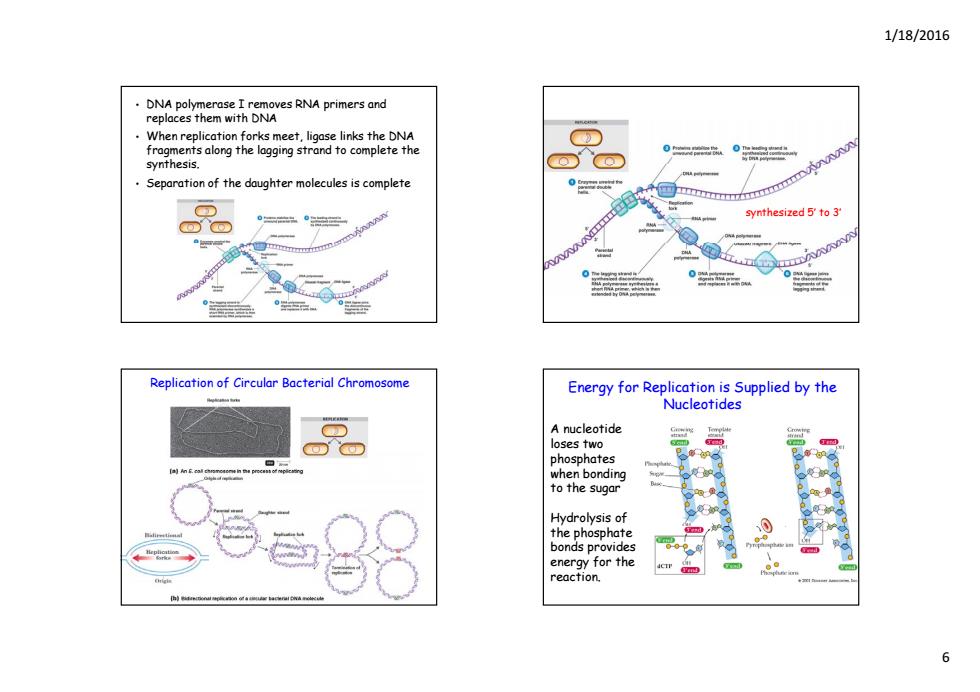
1/18/2016 DNA polymerase I removes RNA primers and replaces them with DNA When replication forks meet,ligase links the DNA fragments along the lagging strand to complete the 00 synthesis. Separation of the daughter molecules is complete synthesized 5'to 3 Replication of Circular Bacterial Chromosome Energy for Replication is Supplied by the Nucleotides A nucleotide loses two phosphates when bonding to the sugar Hydrolysis of the phosphate bonds provides eneray for the reaction h 6
1/18/2016 6 • DNA polymerase I removes RNA primers and replaces them with DNA • When replication forks meet, ligase links the DNA fragments along the lagging strand to complete the synthesis synthesis. • Separation of the daughter molecules is complete synthesized 5′ to 3′ Replication of Circular Bacterial Chromosome Energy for Replication is Supplied by the Nucleotides A nucleotide loses two phosphates when bonding to the sugar Hydrolysis of the phosphate bonds provides energy for the reaction
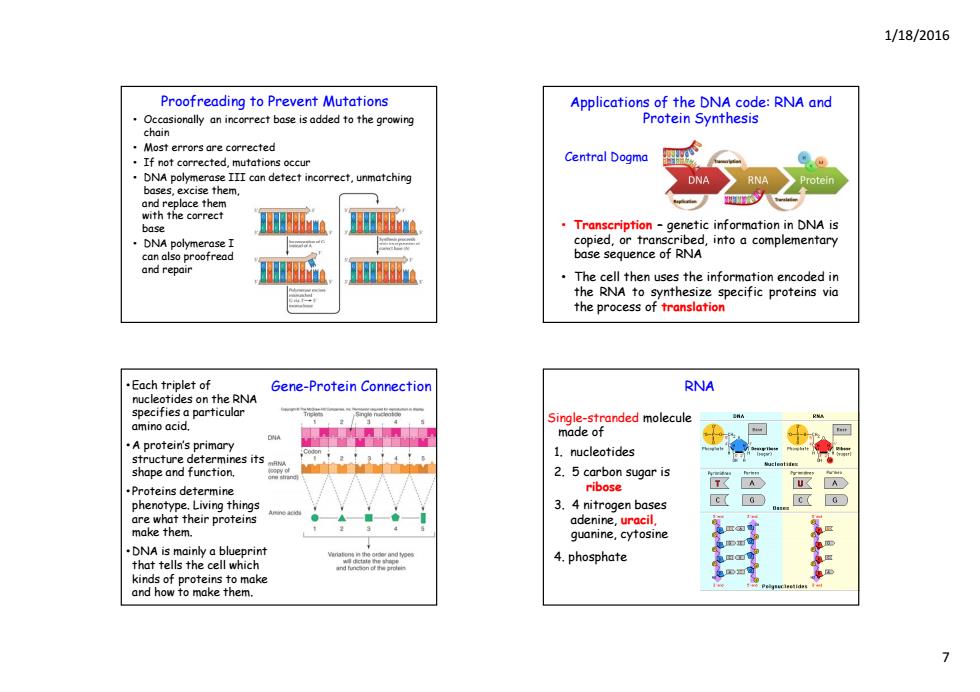
1/18/2016 Proofreading to Prevent Mutations Applications of the DNA code:RNA and Occasionally an incorrect base is added to the growing Protein Synthesis chain Most errors are corrected If not corrected.mutations occur Central Dogmo DNA polymerase III can detect incorrect,unmatching ONA RNA Protein bases,excise them, and replace them with the correct base Transcription genetic information in DNA is DNA polymerase can also proofread complementary and repair The cell then uses the information encoded in the RNA to synthesize specific proteins via the process of translation .Each triplet of Gene-Protein Connection RNA nucleotides on the RNA specifies a particular Single-stranded molecule amino acid. made of A protein's primary 1.nucleotides structure determines its shape and function. 2.5 carbon sugar is .Proteins determine ribose phenotype.Living things 3.4 nitrogen bases C(0 C(a are what their proteins adenine,uracil, make them. guanine,cytosine DNA is mainly a blueprint that tells the cell which 4.phosphate kinds of proteins to make and how to make them. >
1/18/2016 7 • Occasionally an incorrect base is added to the growing chain • Most errors are corrected • If not corrected mutations occur Proofreading to Prevent Mutations If not corrected, mutations occur • DNA polymerase III can detect incorrect, unmatching bases, excise them, and replace them with the correct base • DNA polymerase I can also proofread and repair Applications of the DNA code: RNA and Protein Synthesis Central Dogma • Transcription – genetic information in DNA is cop ed, i or transcr transcr bed, i into a complementary complementary base sequence of RNA • The cell then uses the information encoded in the RNA to synthesize specific proteins via the process of translation • Each triplet of Gene-Protein Connection nucleotides on the RNA specifies a particular amino acid. • A protein A protein s primary ’s primary structure determines its shape and function. • Proteins determine phenotype. Living things are what their proteins make them. • DNA is mainly a blueprint that tells the cell which kinds of proteins to make and how to make them. Single-stranded molecule made of 1 l id RNA . nucleotides 2. 5 carbon sugar is ribose 3. 4 nitrogen bases adenine, uracil, guanine, cytosine 4. phosphate