
Drawing Hands and Feet Chapter Two:Proportions As different as hands seem,they all have similar proportions.The biggest differ- ence in hands is in the thickness of fin- gers and palms.The general proportions do not vary that much with the exception of small children that are still growing and in general stretching out.Try to de- velop a standard hand that you can draw from imagination,a prototype that you then modify to suit your subject.The proportion of the hand in scale to the rest of the figure becomes an expressive ele- ment.The large hands of a rough heavy worker,to the delicate hands of a lady, to pudgy,gnarled or cute hands of a child can be imagined by the adjectives we use to describe them. In this photograph,notice that the half- way point between the arm bones of the lower and the tip of the middle finger is the joint between the metacarpal and phalange bones.Also notice that the joints are not in a straight line but corre- spond to the ends of the fingers with the middle finger being the longest.The wrist is the same width as the middle three fingers,as indicated by the lines. 1.Carpal bones (wrist) 2.Metacarpal bones (palm)top of hand 3.Phalanges(fingers) Page 2

Drawing Hands and Feet The top of the hand is not normally a flat line,but slopes away from the middle fin- ger to either side,as shown in the photo. Notice that the flat of the thumb does not line up with the rest of the fingers. In looking at the profile of the hand you will notice that it is larger than the top of the hand.The muscles must go past the joint to have any leverage.If you put a pencil between your fingers,you will no- tice that the palm(A)actually comes to about half way between the first 2 joints. (B and C)of the fingers.Many students confuse the end of the palm with the point where the fingers actually bend. Bend your own hand to see where the 有版的黄刊 folds are. Each section of bone in your fingers get progressively shorter in a ratio of 3:2. Look at the diagram below.The length of the metacarpal bone to the phalanges is 3 units.The next section is two units of the previous one.Each section is shorter than the previous by one unit. Page3

Vippw Drawing Hands and Feet Chapter Three:Basic Anatomy and Construction As I draw,I am actually always focused 1.Abductor pollicis muscle upon the anatomy.The drawing is a pro 2.Dorsal interoseous muscles gression,starting with the gesture through 3.Abductor digiti minimi muscle construction,but always in relation to the 4.Extensors tendons of the hand anatomy.In the following drawings and 5.Abductor pollicis brevis diagrams you will see that there is really no separation.As you develop your un- derstanding and skill you will essentially use all of the elements at the same time emphasizing one or the other as needed In illustration *A*above I have indicated the abductor pollicis muscle that originates on the underside of the middle metacarpal bone as it attaches to the thumb.The first dorsal interos- seous muscle between the thumb and index fin- ger crosses over as shown in illustration *B*. In illustration *C*I have show a general plan of the extensor tendons of the hand.In moving the fingers of your own hand you should be able to see the large tendons as they pull over the joints when you move your fingers. Page4
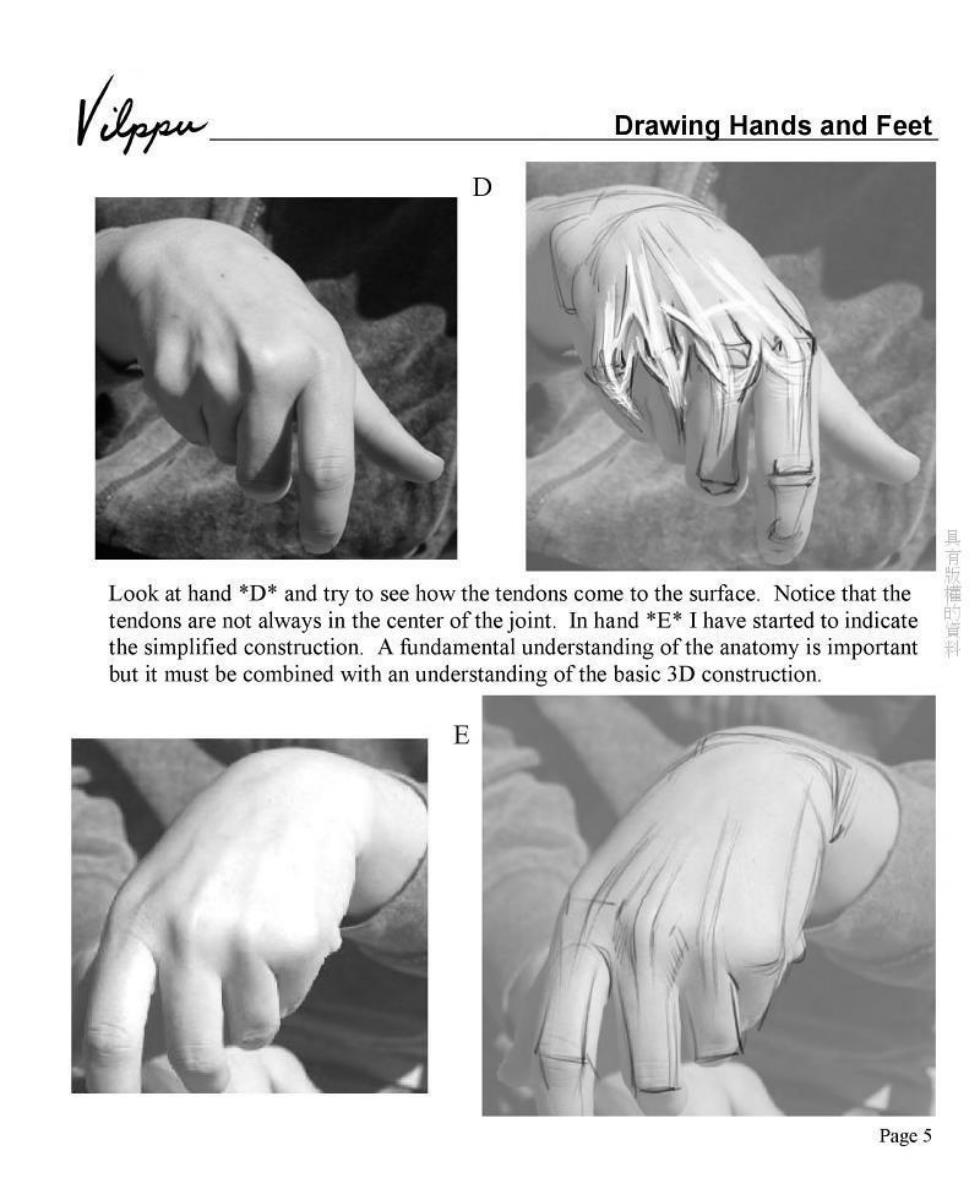
Drawing Hands and Feet Look at hand *D*and try to see how the tendons come to the surface.Notice that the tendons are not always in the center of the joint.In hand *E*I have started to indicate the simplified construction.A fundamental understanding of the anatomy is important but it must be combined with an understanding of the basic 3D construction E Page5
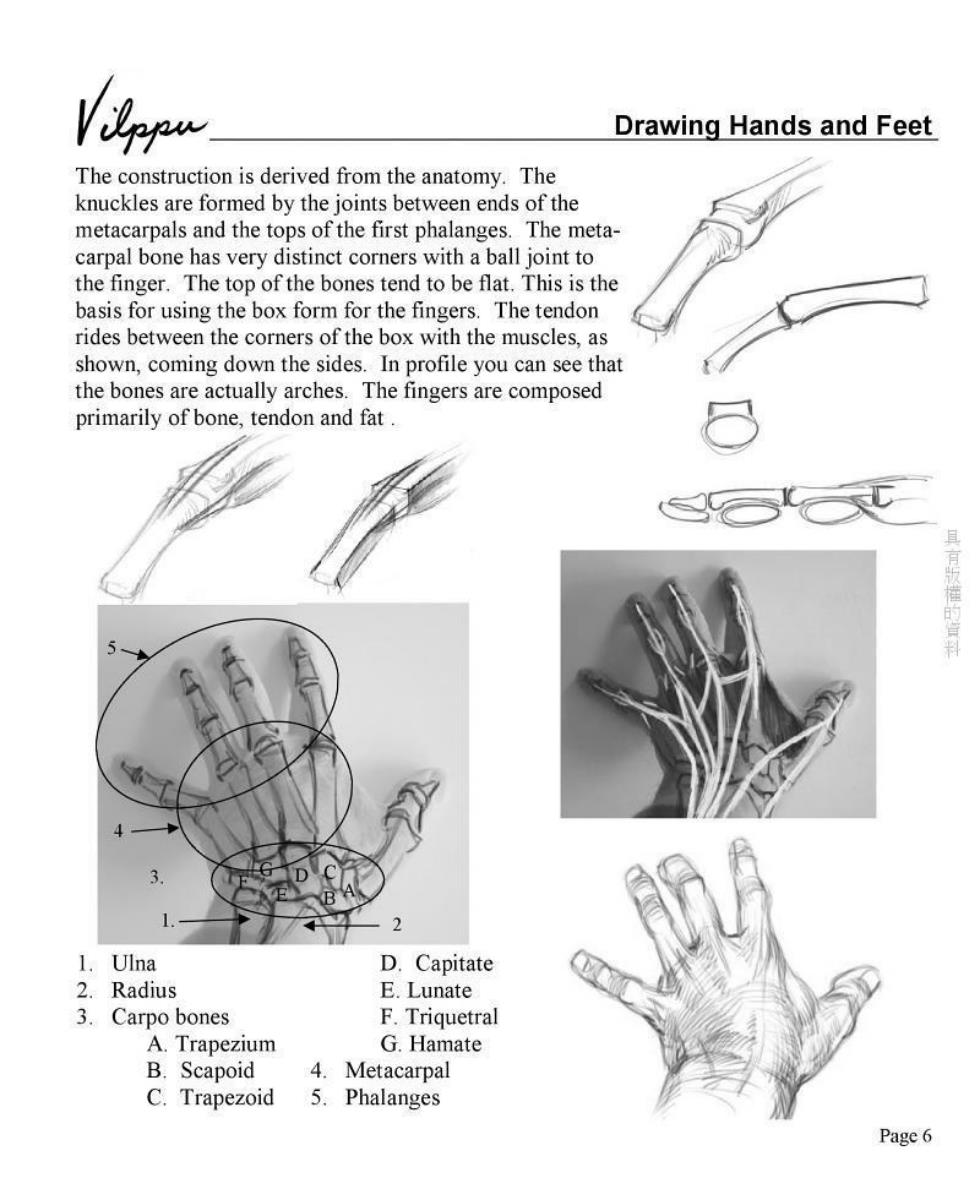
Drawing Hands and Feet The construction is derived from the anatomy.The knuckles are formed by the joints between ends of the metacarpals and the tops of the first phalanges.The meta- carpal bone has very distinct corners with a ball joint to the finger.The top of the bones tend to be flat.This is the basis for using the box form for the fingers.The tendon rides between the corners of the box with the muscles,as shown,coming down the sides.In profile you can see that the bones are actually arches.The fingers are composed primarily of bone,tendon and fat. 2 1.Ulna D.Capitate 2.Radius E.Lunate 3.Carpo bones F.Triquetral A.Trapezium G.Hamate B.Scapoid 4.Metacarpal C.Trapezoid 5. Phalanges Page6