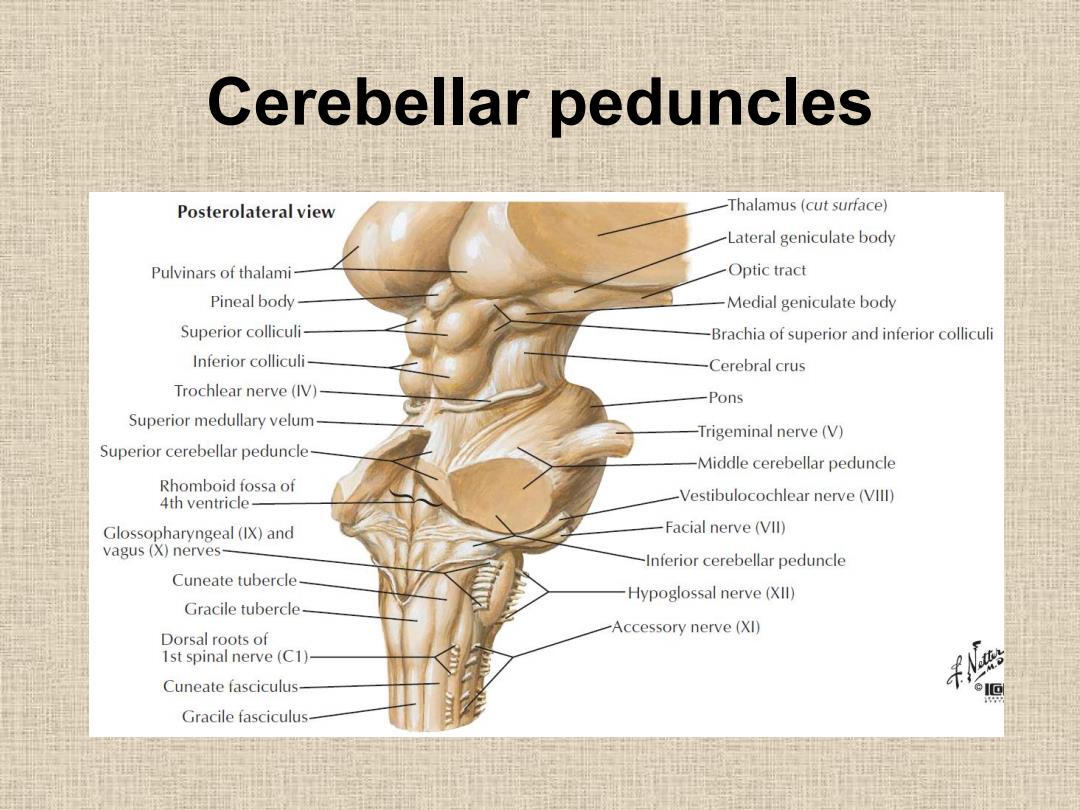
Cerebellar peduncles Posterolateral view Thalamus (cut surface) Lateral geniculate body Pulvinars of thalami Optic tract Pineal body Medial geniculate body Superior colliculi- -Brachia of superior and inferior colliculi Inferior colliculi- Cerebral crus Trochlear nerve(IV)- -Pons Superior medullary velum -Trigeminal nerve(V) Superior cerebellar peduncle Middle cerebellar peduncle Rhomboid fossa of 4th ventricle- -Vestibulocochlear nerve(VIll) Glossopharyngeal(IX)and -Facial nerve (VIl) vagus(X)nerves- Inferior cerebellar peduncle Cuneate tubercle Hypoglossal nerve(XIl) Gracile tubercle Accessory nerve(XI) Dorsal roots of 1st spinal nerve(C1)- Cuneate fasciculus- Gracile fasciculus
Cerebellar peduncles
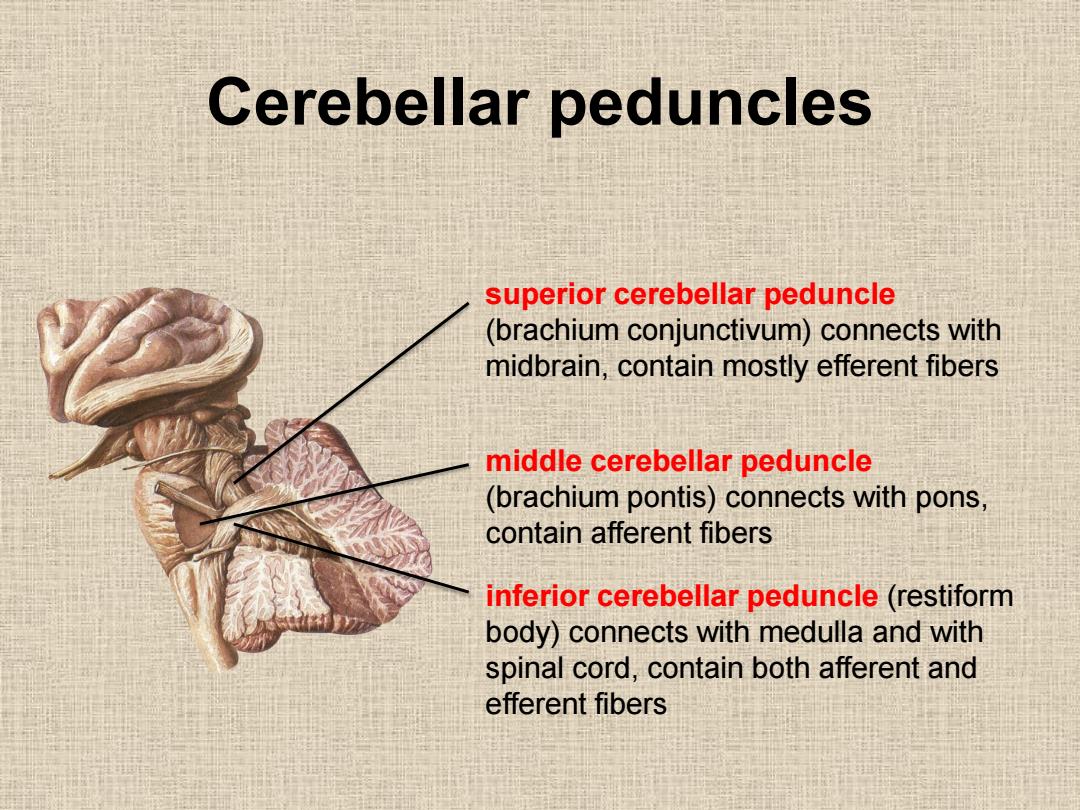
Cerebellar peduncles superior cerebellar peduncle (brachium conjunctivum)connects with midbrain,contain mostly efferent fibers middle cerebellar peduncle (brachium pontis)connects with pons. contain afferent fibers inferior cerebellar peduncle(restiform body)connects with medulla and with spinal cord,contain both afferent and efferent fibers
Cerebellar peduncles inferior cerebellar peduncle (restiform body) connects with medulla and with spinal cord, contain both afferent and efferent fibers middle cerebellar peduncle (brachium pontis) connects with pons, contain afferent fibers superior cerebellar peduncle (brachium conjunctivum) connects with midbrain, contain mostly efferent fibers
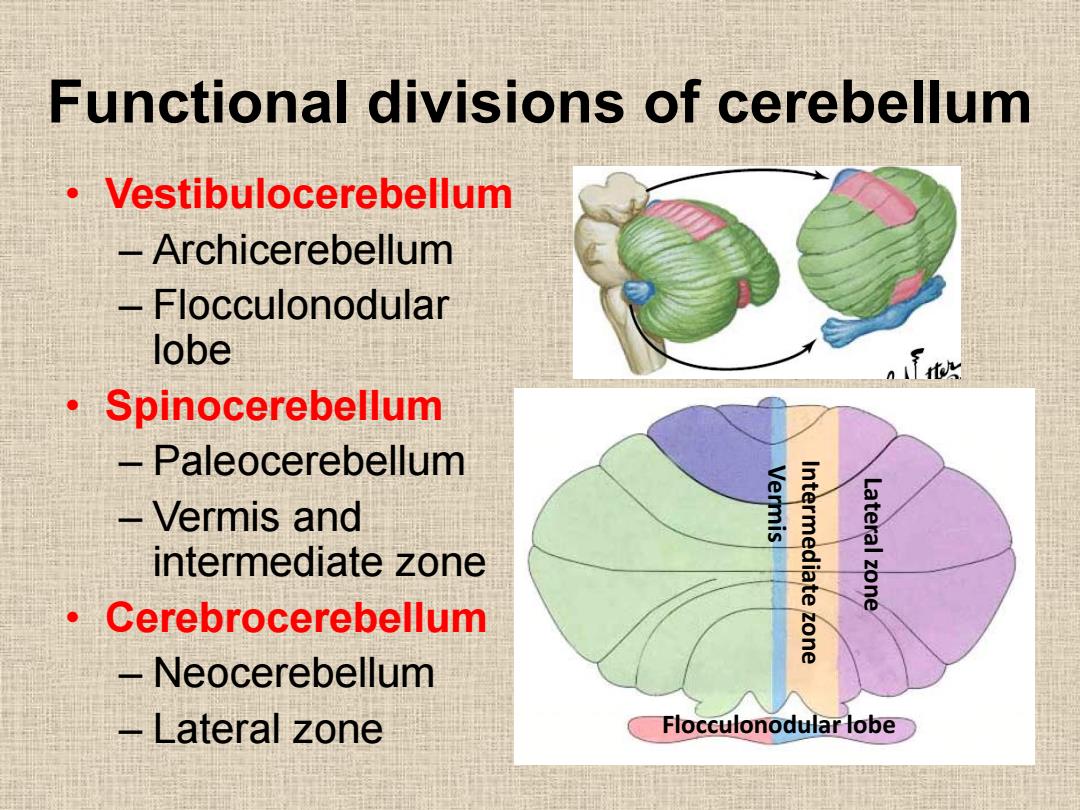
Functional divisions of cerebellum Vestibulocerebellum -Archicerebellum -Flocculonodular lobe ·Spinocerebellum -Paleocerebellum Vermis and Vermis intermediate zone Intermediate zone Lateral zone ·Cerebrocerebellum -Neocerebellum Lateral zone Flocculonodular lobe
Functional divisions of cerebellum • Vestibulocerebellum – Archicerebellum – Flocculonodular lobe • Spinocerebellum – Paleocerebellum – Vermis and intermediate zone • Cerebrocerebellum – Neocerebellum – Lateral zone Flocculonodular lobe Vermis Intermediate zone Lateral zone
Connections and functions of cerebellum Vestibulocerebellum 。Connections -Afferents:receives inputs from vestibular nuclei and vestibular ganglion -Efferents:projects to the vestibular nucleus vestibulospinal tract and medial longitudinal fasciculus-motor neurons of anterior horn and cranial nuclei innervating extraocular muscles
Connections and functions of cerebellum Vestibulocerebellum • Connections – Afferents: receives inputs from vestibular nuclei and vestibular ganglion – Efferents: projects to the vestibular nucleus → vestibulospinal tract and medial longitudinal fasciculus → motor neurons of anterior horn and cranial nuclei innervating extraocular muscles
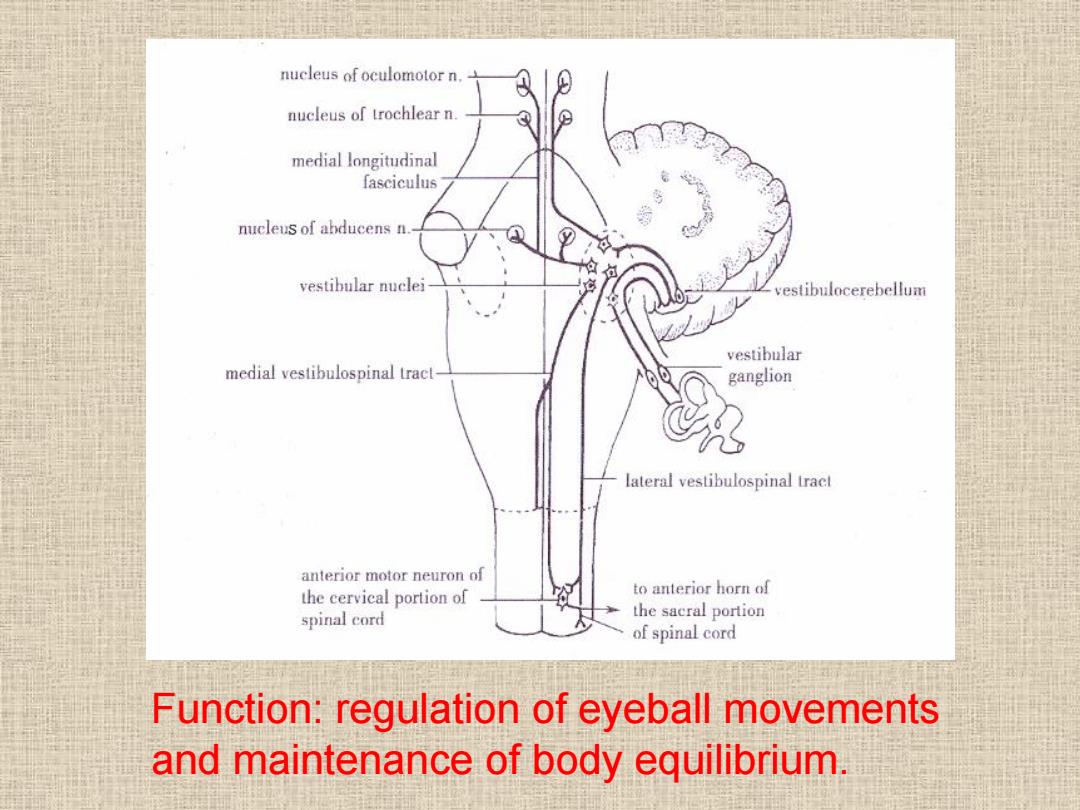
nucleus of oculomotor n. nucleus of trochlear n. medial longitudinal fasciculus nucleus of abducens n. vestibular nuclei vestibulocerebellum vestibular medial vestibulospinal tract ganglion lateral vestibulospinal tract anterior motor neuron of the cervical portion of to anterior horn of spinal cord the sacral portion of spinal cord Function:regulation of eyeball movements and maintenance of body equilibrium
Function: regulation of eyeball movements and maintenance of body equilibrium