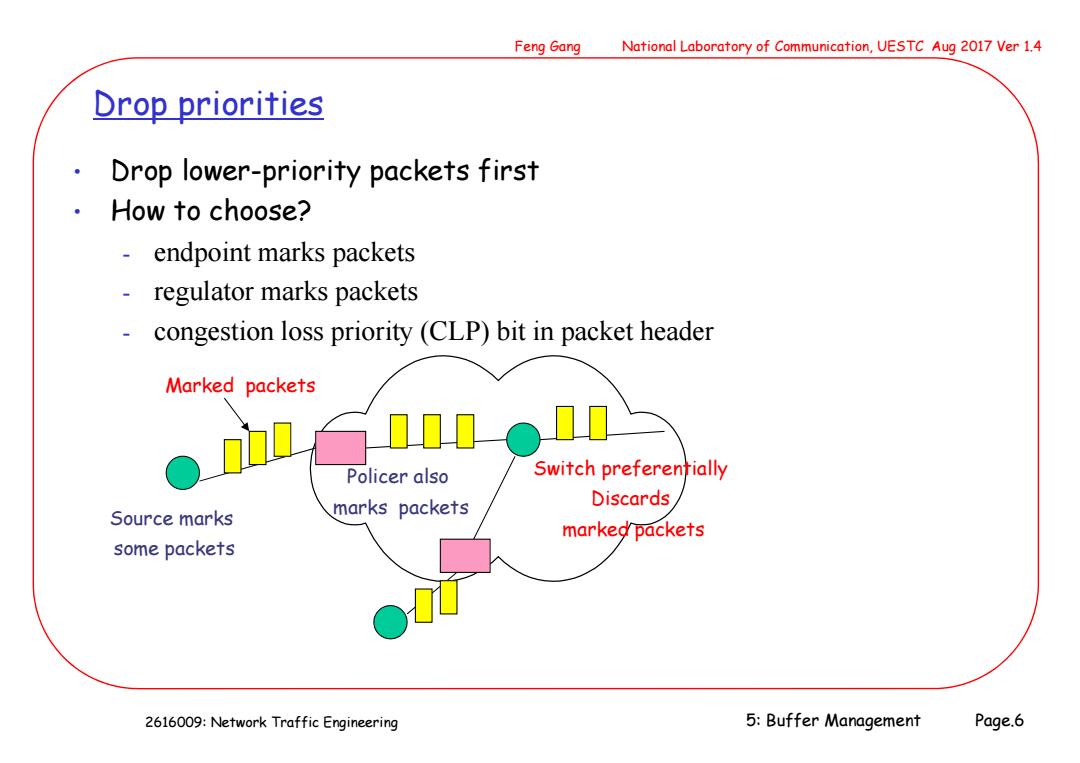
Feng Gang National Laboratory of Communication,UESTC Aug 2017 Ver 1.4 Drop priorities Drop lower-priority packets first 。 How to choose? endpoint marks packets - regulator marks packets congestion loss priority(CLP)bit in packet header Marked packets Policer also Switch preferentially Discards Source marks marks packets marked packets some packets 2616009:Network Traffic Engineering 5:Buffer Management Page.6
2616009: Network Traffic Engineering Feng Gang National Laboratory of Communication, UESTC Aug 2017 Ver 1.4 5: Buffer Management Page.6 Drop priorities • Drop lower-priority packets first • How to choose? - endpoint marks packets - regulator marks packets - congestion loss priority (CLP) bit in packet header Source marks some packets Marked packets Policer also marks packets Switch preferentially Discards marked packets

Feng Gang National Laboratory of Communication,UESTC Aug 2017 Ver 1.4 CLP bit:pros and cons Pros if network has spare capacity,all traffic is carried - during congestion,load is automatically shed Cons - separating priorities within a single connection is hard - what prevents all packets being marked as high priority? 2616009:Network Traffic Engineering 5:Buffer Management Page.7
2616009: Network Traffic Engineering Feng Gang National Laboratory of Communication, UESTC Aug 2017 Ver 1.4 5: Buffer Management Page.7 CLP bit: pros and cons • Pros - if network has spare capacity, all traffic is carried - during congestion, load is automatically shed • Cons - separating priorities within a single connection is hard - what prevents all packets being marked as high priority?
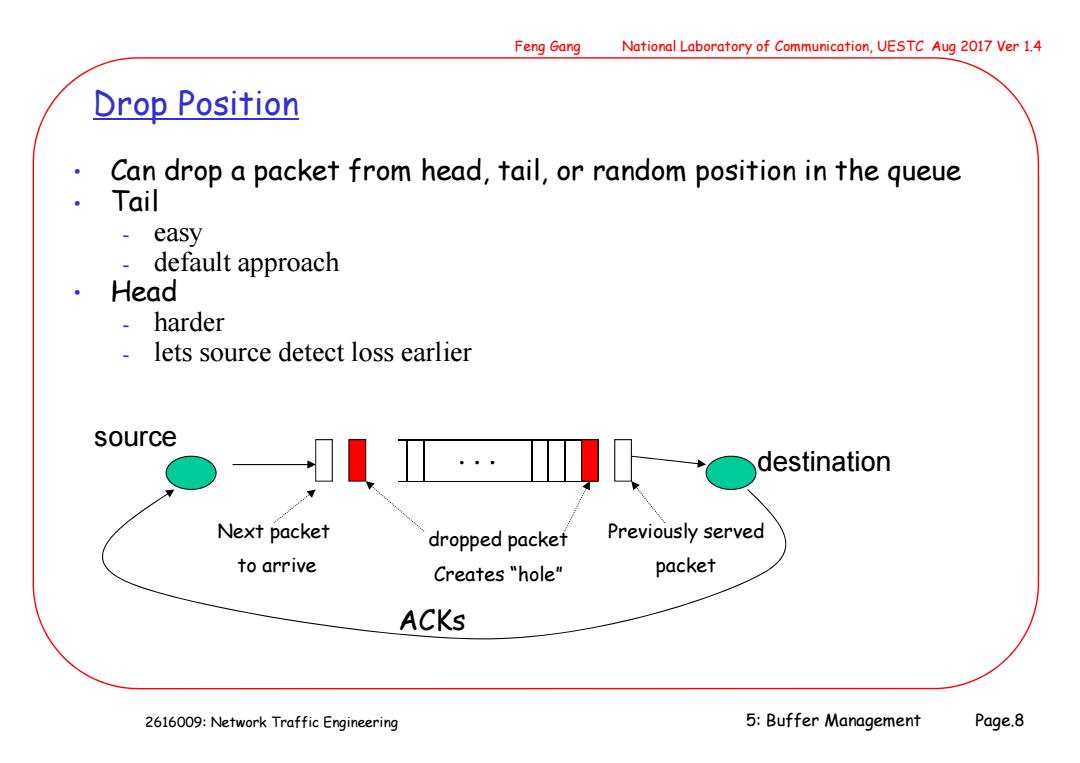
Feng Gang National Laboratory of Communication,UESTC Aug 2017 Ver 1.4 Drop Position Can drop a packet from head,tail,or random position in the queue Tail - easy default approach Head harder lets source detect loss earlier source destination Next packet dropped packet Previously served to arrive Creates "hole" packet ACKs 2616009:Network Traffic Engineering 5:Buffer Management Page.8
2616009: Network Traffic Engineering Feng Gang National Laboratory of Communication, UESTC Aug 2017 Ver 1.4 5: Buffer Management Page.8 Drop Position • Can drop a packet from head, tail, or random position in the queue • Tail - easy - default approach • Head - harder - lets source detect loss earlier . . . source destination Next packet to arrive dropped packet Creates “hole” Previously served packet ACKs

Feng Gang National Laboratory of Communication,UESTC Aug 2017 Ver 1.4 Drop Position (cont.) Random -hardest if no aggregation,hurts hogs most unlikely to make it to real routers 。 Drop entire longest queue easy almost as effective as drop tail from longest queue 2616009:Network Traffic Engineering 5:Buffer Management Page.9
2616009: Network Traffic Engineering Feng Gang National Laboratory of Communication, UESTC Aug 2017 Ver 1.4 5: Buffer Management Page.9 Drop Position (cont.) • Random - hardest - if no aggregation, hurts hogs most - unlikely to make it to real routers • Drop entire longest queue - easy - almost as effective as drop tail from longest queue
Feng Gang National Laboratory of Communication,UESTC Aug 2017 Ver 1.4 Router Support For Congestion Management Traditional Internet Congestion control mechanisms at end-systems, mainly implemented in TCP Routers play little role ·Traditional routers FIFO -Tail drop 2616009:Network Traffic Engineering 5:Buffer Management Page.10
2616009: Network Traffic Engineering Feng Gang National Laboratory of Communication, UESTC Aug 2017 Ver 1.4 5: Buffer Management Page.10 Router Support For Congestion Management • Traditional Internet - Congestion control mechanisms at end-systems, mainly implemented in TCP - Routers play little role • Traditional routers - FIFO - Tail drop