
1/26/2016 Coagulase-negative staphylococci Staphylococcal Skin Infections urface of catheter Staphylococcus aureus -Can survive for months on surfaces -Larger genome than 5.epidermidis (300,000 bp) Coagulase-positive -May produce damaging toxins and cause sepsis Avoids host defenses in the skin 四 6) 四m Secretes proteins and toxins that ll phagocytic cells MRSA strains are antibiotic-resistant ·methicillin-resistant三.cres is beginning to appear. the biofilm. Staphylococcal Skin Infections Often transported from nasal passages to the skin where it can enter through openings such as the hair follicles Folliculitis:infections of the hair follicles Sty:folliculitis of an eyelash Furuncle (boil):a type of abscess;localized region of pus surrounded by inflamed tissue antibiotics do not penetrate well making it difficult to treat Carbuncle:damage and inflammation of deep ading furuncle group of Impetigo:crusting (nonbullous)sores, spread by autoinoculation 6
1/26/2016 6 Coagulase-negative staphylococci Biofilm Surface of catheter Biofilm Catheter surface with adhering bacteria. Biofilm, light green, is beginning to appear. Most of the bacteria producing the slime are not visible under the biofilm. Staphylococcal Skin Infections • Staphylococcus aureus – Carried in the nasal passages of 20% of the population py y y ermanently; 60% carry it transiently – Can survive for months on surfaces – Golden-yellow colonies; pigment protects against sunlight and killing by neutrophils – Larger genome than S. epidermidis (300,000 bp) – Coagulase-positive – M d d i i d i May produce damaging toxins and cause sepsis – Avoids host defenses in the skin • Secretes proteins and toxins that kill phagocytic cells – MRSA strains are antibiotic-resistant • methicillin-resistant S. aureus Staphylococcal Skin Infections Often transported from nasal passages to the skin where it can enter through openings such as the hair follicles • Folliculitis: infections of the hair follicles • Sty: folliculitis of an eyelash • Furuncle (boil): a type of abscess; localized region of pus surrounded by inflamed tissue - antibiotics do not penetrate well making it diffi lt t t t difficult to treat • Carbuncle: damage and inflammation of deep tissue from a spreading furuncle, group of hair follicles are infected • Impetigo: crusting (nonbullous) sores, spread by autoinoculation
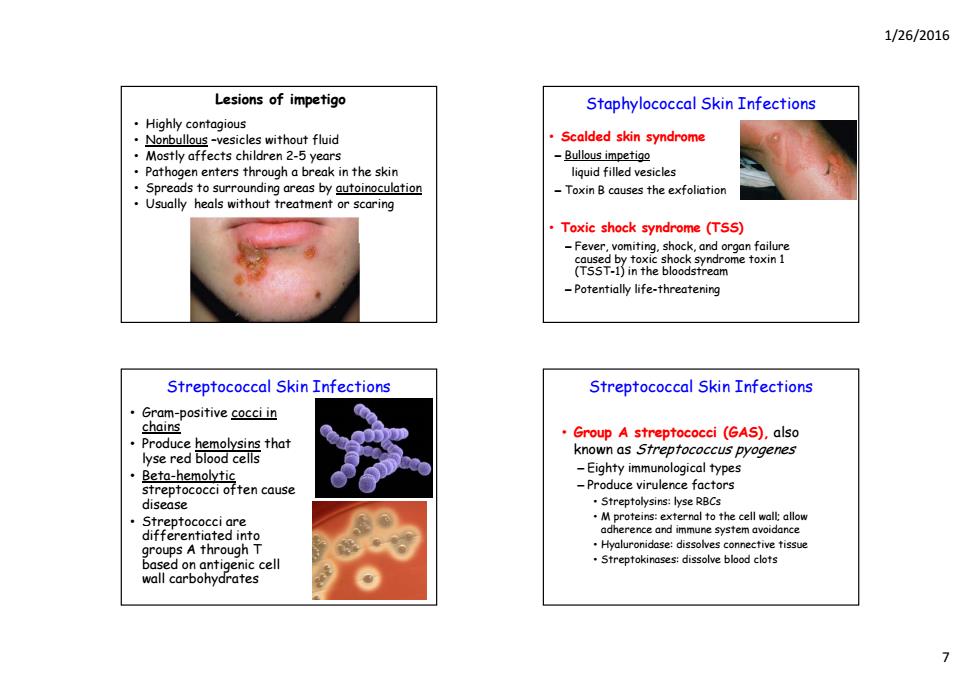
1/26/2016 Lesions of impetigo Staphylococcal Skin Infections Highly contagious Nonbullous -vesicles without fluid Scalded skin syndrome Mostly affects children 2-5 years -Bullous impetigo Pathogen enters through a break in the skin liguid filled vesicles Spreads to surrounding areas by autoinoculation Toxin B causes the exfoliation Usually heals without treatment or scaring Toxic shock syndrome (TSS) -Fever,vomiting,shock,and organ failure caused by toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST-1)in the bloodstream -Potentially life-threatening Streptococcal Skin Infections Streptococcal Skin Infections Gram-positive cocci in chains Produce hemolysins that Group A streptococci (GAS).also lyse red blood cells known as Strepfococcus pyogenes ·Beto-hemolytic -Eighty immunological types streptococci often cause -Produce virulence factors disease Streptolysins:lyse RBCs ·Streptococci are differentiated into groups A through T Hyaluronidase:dissolves connective tissue based on antigenic cell Streptokinases:dissolve blood clots wall carbohydrates
1/26/2016 7 Lesions of impetigo • Highly contagious • Nonbullous –vesicles without fluid • Mostly affects children 2-5 years • Pathogen enters through a break in the skin • Spreads to surrounding areas by autoinoculation • Usually heals without treatment or scaring Staphylococcal Skin Infections • Scalded skin syndrome – Bullous impetigo liquid filled vesicles – Toxin B causes the exfoliation • Toxic shock syndrome (TSS) – F iti h k d f il Fever, vomiting, shock, and organ failure caused by toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST-1) in the bloodstream – Potentially life-threatening Streptococcal Skin Infections • Gram-positive cocci in chains • Produce hemolysins that lyse red blood cells • Beta-hemolytic streptococci often cause disease • Streptococci are differentiated into groups A through T based on antigenic cell wall carbohydrates Streptococcal Skin Infections • Group A streptococci (GAS), also known as Streptococcus pyogenes – Eighty immunological types – Produce virulence factors • Streptolysins: lyse RBCs • M proteins: external to the cell wall; allow adh d i t id dherence and immune system avoidance • Hyaluronidase: dissolves connective tissue • Streptokinases: dissolve blood clots