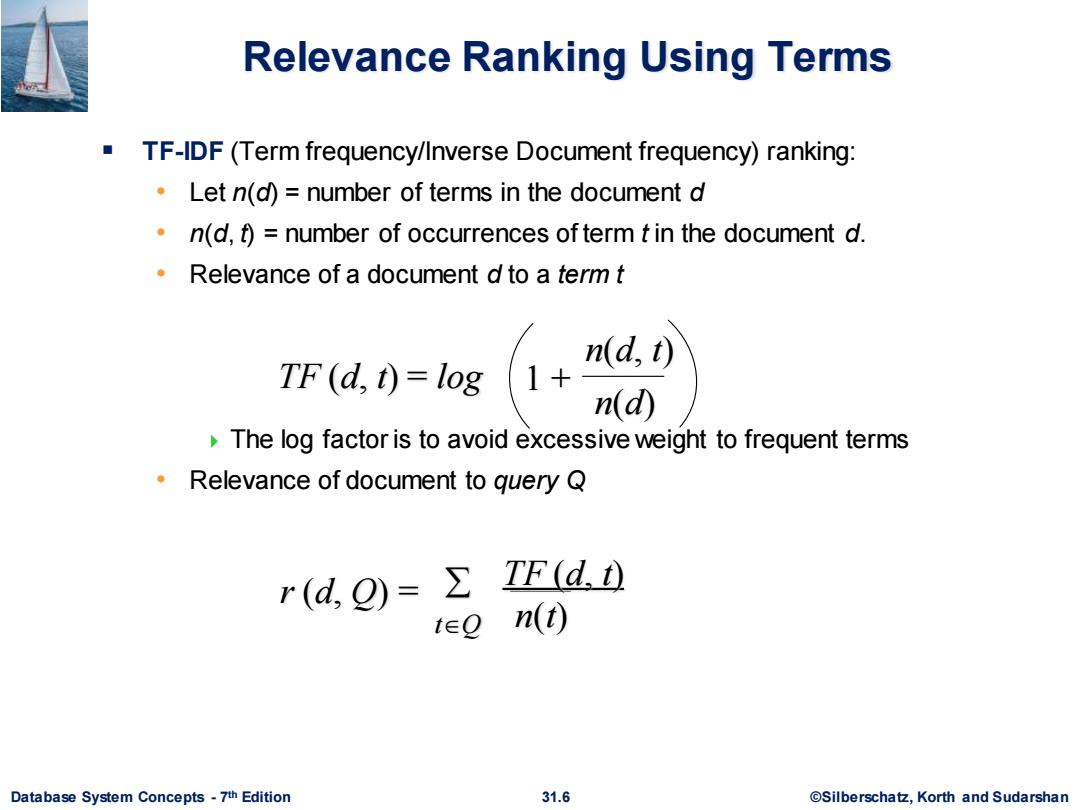
Relevance Ranking Using Terms TF-IDF (Term frequency/Inverse Document frequency)ranking: Let n(d)=number of terms in the document d n(d,)number of occurrences ofterm t in the document d. Relevance of a document d to a term t n(d,t) TF (d,t)=log 1+ n(d) The log factor is to avoid excessive weight to frequent terms Relevance of document to query Q r(d,Q)=∑ TF(d.t) t∈Q n(t) Database System Concepts-7th Edition 31.6 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 31.6 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Relevance Ranking Using Terms ▪ TF-IDF (Term frequency/Inverse Document frequency) ranking: • Let n(d) = number of terms in the document d • n(d, t) = number of occurrences of term t in the document d. • Relevance of a document d to a term t The log factor is to avoid excessive weight to frequent terms • Relevance of document to query Q n(d) n(d, t) TF (d, t) = log 1 + r (d, Q) = TF (d, t) tQ n(t)

Relevance Ranking Using Terms(Cont.) Most systems add to the above model Words that occur in title,author list,section headings,etc.are given greater importance Words whose first occurrence is late in the document are given lower importance ·Very common words such as“a”,“an”,“the”,“it'etc.are eliminated Called stop words Proximity:if keywords in query occur close together in the document, the document has higher importance than if they occur far apart Documents are returned in decreasing order of relevance score Usually only top few documents are returned,not all Database System Concepts-7th Edition 31.7 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 31.7 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Relevance Ranking Using Terms (Cont.) ▪ Most systems add to the above model • Words that occur in title, author list, section headings, etc. are given greater importance • Words whose first occurrence is late in the document are given lower importance • Very common words such as “a”, “an”, “the”, “it” etc. are eliminated ▪ Called stop words • Proximity: if keywords in query occur close together in the document, the document has higher importance than if they occur far apart ▪ Documents are returned in decreasing order of relevance score • Usually only top few documents are returned, not all

Similarity Based Retrieval Similarity based retrieval-retrieve documents similar to a given document Similarity may be defined on the basis of common words E.g.,find k terms in A with highest TF(d,t)/n (t)and use these terms to find relevance of other documents. Relevance feedback:Similarity can be used to refine answer set to keyword query User selects a few relevant documents from those retrieved by keyword query,and system finds other documents similar to these Vector space model:define an n-dimensional space,where n is the number of words in the document set. Vector for document d goes from origin to a point whose i th coordinate is TF(d,t)/n(t) The cosine of the angle between the vectors of two documents is used as a measure of their similarity. Database System Concepts-7th Edition 31.8 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 31.8 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Similarity Based Retrieval ▪ Similarity based retrieval - retrieve documents similar to a given document • Similarity may be defined on the basis of common words ▪ E.g., find k terms in A with highest TF (d, t ) / n (t ) and use these terms to find relevance of other documents. ▪ Relevance feedback: Similarity can be used to refine answer set to keyword query • User selects a few relevant documents from those retrieved by keyword query, and system finds other documents similar to these ▪ Vector space model: define an n-dimensional space, where n is the number of words in the document set. • Vector for document d goes from origin to a point whose i th coordinate is TF (d,t ) / n (t ) • The cosine of the angle between the vectors of two documents is used as a measure of their similarity