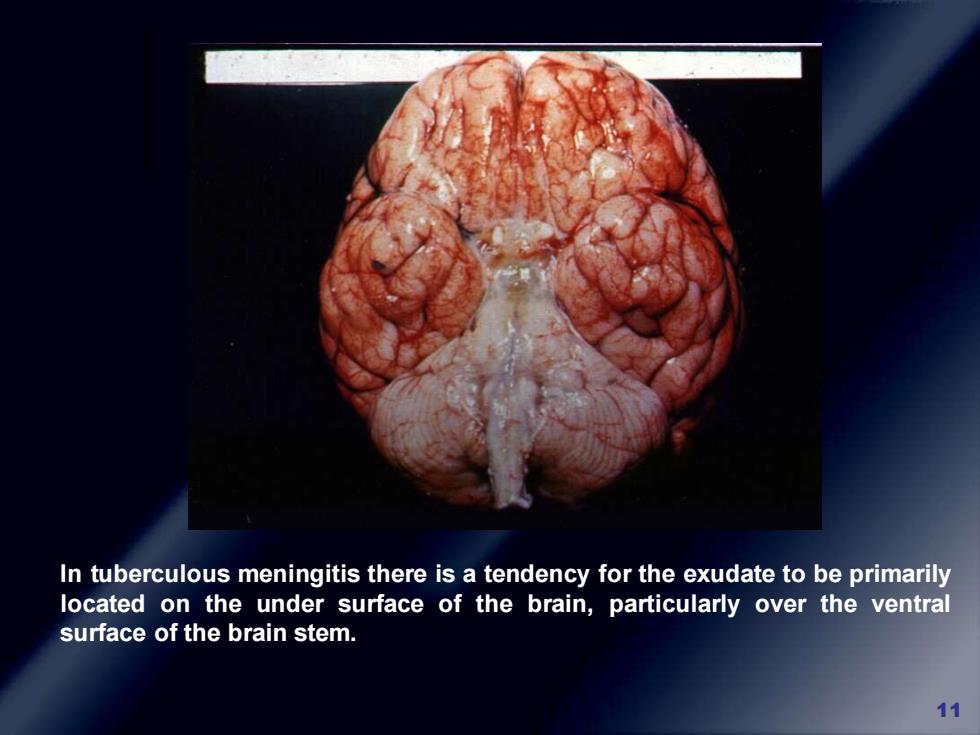
In tuberculous meningitis there is a tendency for the exudate to be primarily located on the under surface of the brain,particularly over the ventral surface of the brain stem. 11
11 In tuberculous meningitis there is a tendency for the exudate to be primarily located on the under surface of the brain, particularly over the ventral surface of the brain stem

CLINICAL MANIFESTIONS A.Prodrome (1-2 week) 1.Fever,fatigue,malaise,myalgia, drowsiness,headache,vomiting 2.Mental status changes 3.Focal neurologic signs are absent 4.CSF abnormity 12
12 CLINICAL MANIFESTIONS A. Prodrome (1-2 week) 1. Fever, fatigue, malaise, myalgia, drowsiness, headache, vomiting 2. Mental status changes 3. Focal neurologic signs are absent 4. CSF abnormity

CLINICAL MANIFESTIONS B.Meningeal Irritation Stage (1-2 week) 1. More serious TB toxic symptoms 2. Intracranial hypertension:severe headache,irritation, projectile vomiting,seizures; Bulging of anterior fontanelle,widening of cranial sutures in infant 3.Meningeal Irritation nuchal rigidity,hypertonia Kernig sign or Brudzinski sign 4. Cranial nerve abnormalities:3,6,7 5. Some children have no evidence of meningeal irritation but may have signs of encephalitis:disorientation, abnormal movements and speech impairment 13
13 CLINICAL MANIFESTIONS B. Meningeal Irritation Stage (1-2 week) 1. More serious TB toxic symptoms 2. Intracranial hypertension: severe headache, irritation, projectile vomiting, seizures; Bulging of anterior fontanelle, widening of cranial sutures in infant 3. Meningeal Irritation : nuchal rigidity, hypertonia Kernig sign or Brudzinski sign 4. Cranial nerve abnormalities: 3, 6, 7 5. Some children have no evidence of meningeal irritation but may have signs of encephalitis: disorientation, abnormal movements and speech impairment

CLINICAL MANIFESTIONS C.Coma Stage (1-3 week) 1.Frequent convulsion,progressive altered state of consciousness:lethargy,confusion, semicoma,deep coma,decerebrate or decorticate posturing 2.Depletion:extremely maransis, constipation,urinary retention 3. progressive abnormalities of vital signs, and eventual die from cerebral hernia 14
14 CLINICAL MANIFESTIONS C. Coma Stage (1-3 week) 1. Frequent convulsion, progressive altered state of consciousness: lethargy, confusion, semicoma, deep coma, decerebrate or decorticate posturing 2. Depletion: extremely maransis, constipation, urinary retention 3. progressive abnormalities of vital signs, and eventual die from cerebral hernia

Characteristics of TBM in infants and young children 1.A rapid onset with convulsion, abruptly high fever 2.Atypical miningeal irritation 3.Intracranial hypertension manifests as bulging of anterior fontanelle and widening of cranial sutures in infant 15
15 Characteristics of TBM in infants and young children 1. A rapid onset with convulsion, abruptly high fever 2. Atypical miningeal irritation 3. Intracranial hypertension manifests as bulging of anterior fontanelle and widening of cranial sutures in infant