
Client-server paradigm server: mobile network always-on host national or global ISP ■permanent IP address often in data centers,for scaling clients: contact,communicate with server may be intermittently connected home twork content provider may have dynamic IP addresses network datacenter network do not communicate directly with each other enterprise examples:HTTP,IMAP,FTP network Application Layer:2-6
mobile network home network enterprise network national or global ISP local or regional ISP datacenter network content provider network Client-server paradigm server: ▪ always-on host ▪ permanent IP address ▪ often in data centers, for scaling clients: ▪ contact, communicate with server ▪ may be intermittently connected ▪ may have dynamic IP addresses ▪ do not communicate directly with each other ▪ examples: HTTP, IMAP, FTP Application Layer: 2-6
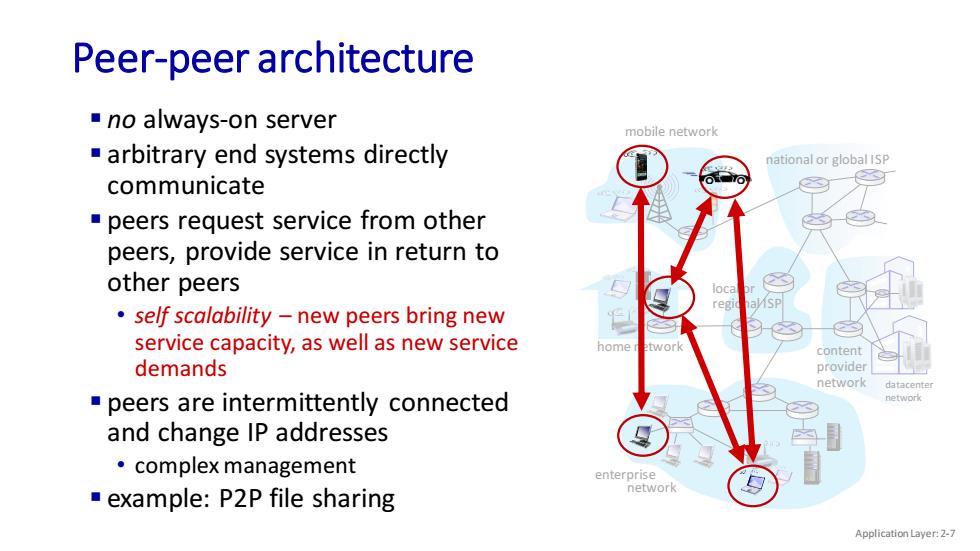
Peer-peer architecture ■no always-on server mobile network arbitrary end systems directly national or global ISP communicate peers request service from other peers,provide service in return to other peers loca regi self scalability -new peers bring new service capacity,as well as new service home twork content demands provider network datacente peers are intermittently connected network and change IP addresses ·complex management enterprise example:P2P file sharing network Application Layer:2-7
mobile network home network enterprise network national or global ISP local or regional ISP datacenter network content provider network Peer-peer architecture ▪ no always-on server ▪ arbitrary end systems directly communicate ▪ peers request service from other peers, provide service in return to other peers • self scalability – new peers bring new service capacity, as well as new service demands ▪ peers are intermittently connected and change IP addresses • complex management ▪ example: P2P file sharing Application Layer: 2-7
Processes communicating process:program running clients,servers within a host client process:process that initiates communication -within same host,two server process:process processes communicate that waits to be contacted using inter-process communication(defined by 0S) note:applications with P2P architectures have processes in different hosts client processes communicate by exchanging server processes messages Application Layer:2-8
Processes communicating process: program running within a host ▪within same host, two processes communicate using inter-process communication (defined by OS) ▪processes in different hosts communicate by exchanging messages Application Layer: 2-8 client process: process that initiates communication server process: process that waits to be contacted ▪ note: applications with P2P architectures have client processes & server processes clients, servers
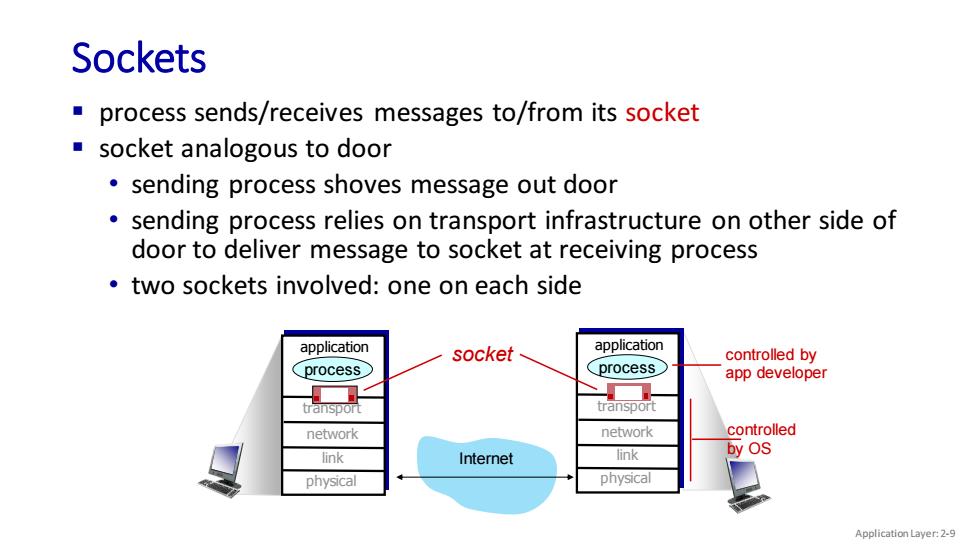
Sockets process sends/receives messages to/from its socket socket analogous to door sending process shoves message out door sending process relies on transport infrastructure on other side of door to deliver message to socket at receiving process two sockets involved:one on each side application socket application controlled by process process app developer transpor transport network network controlled by OS link Internet link physical physical Application Layer:2-9
Sockets Application Layer: 2-9 ▪ process sends/receives messages to/from its socket ▪ socket analogous to door • sending process shoves message out door • sending process relies on transport infrastructure on other side of door to deliver message to socket at receiving process • two sockets involved: one on each side Internet controlled by OS controlled by app developer transport application physical link network process transport application physical link network process socket

Addressing processes to receive messages,process identifier includes both IP address must have identifier and port numbers associated with host device has unique 32-bit process on host. IP address example port numbers: Q:does IP address of host on ·HTTP server::80 which process runs suffice for ·mail server:25 identifying the process? -to send HTTP message to A:no,many processes gaia.cs.umass.edu web server: can be running on ·1 address:128.119.245.12 same host 。port number:&0 more shortly... Application Layer:2-10
Addressing processes Application Layer: 2-10 ▪ to receive messages, process must have identifier ▪ host device has unique 32-bit IP address ▪Q: does IP address of host on which process runs suffice for identifying the process? ▪ identifier includes both IP address and port numbers associated with process on host. ▪ example port numbers: • HTTP server: 80 • mail server: 25 ▪ to send HTTP message to gaia.cs.umass.edu web server: • IP address: 128.119.245.12 • port number: 80 ▪ more shortly… ▪ A: no, many processes can be running on same host