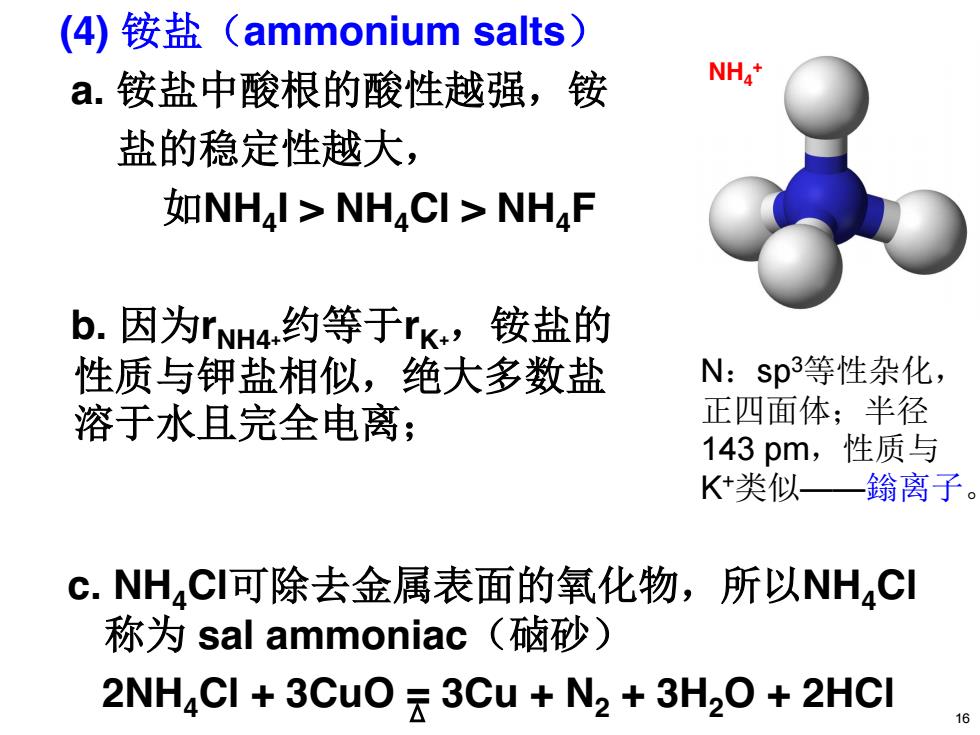
(4)铵盐(ammonium salts) a.铵盐中酸根的酸性越强,铵 NH4* 盐的稳定性越大, 如NH4I>NH,CI>NH4F b.因为rNH4约等于rK,铵盐的 性质与钾盐相似,绝大多数盐 N:sp3等性杂化, 溶于水且完全电离; 正四面体;半径 143pm,性质与 K+类似—鎓离子。 c.NH,CI可除去金属表面的氧化物,所以NH4CI 称为sal ammoniac(硵砂) 2NH CI +3CuO 3Cu N2 3H2O 2HCI
c. NH4Cl可除去金属表面的氧化物,所以NH4Cl 称为 sal ammoniac(硵砂) 2NH4Cl + 3CuO = 3Cu + N2 + 3H2O + 2HCl (4) 铵盐(ammonium salts) a. 铵盐中酸根的酸性越强,铵 盐的稳定性越大, 如NH4I > NH4Cl > NH4F b. 因为rNH4+约等于rK+,铵盐的 性质与钾盐相似,绝大多数盐 溶于水且完全电离; N:sp3等性杂化, 正四面体;半径 143 pm,性质与 K+类似——鎓离子。 NH4 + 16
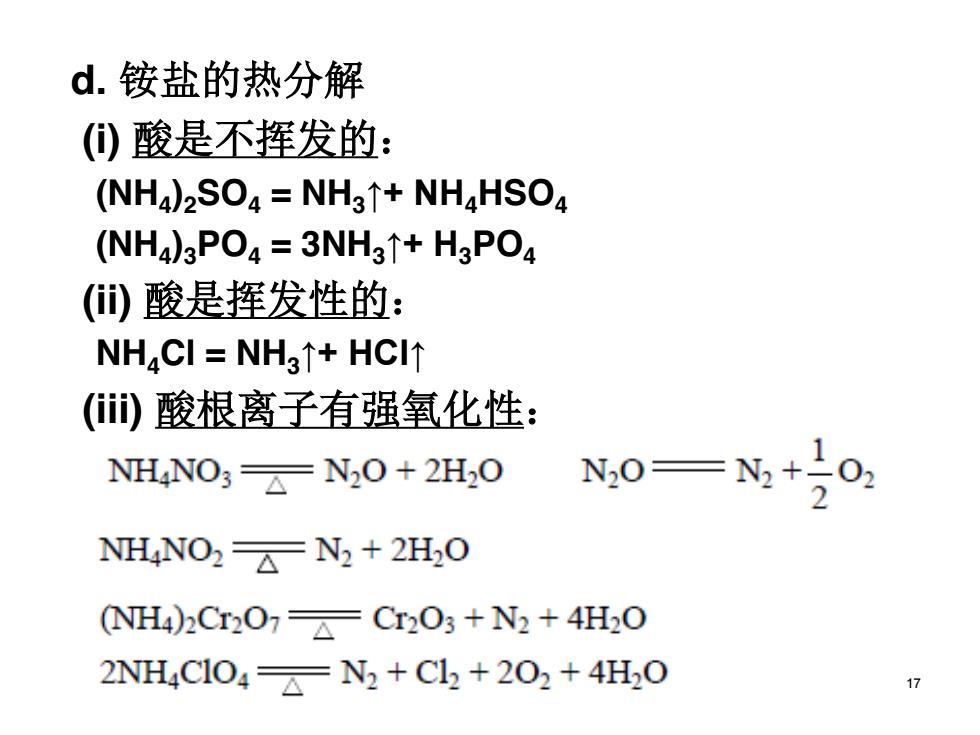
d.铵盐的热分解 (0酸是不挥发的: (NH4)2SO=NH3T+NHaHSO (NHa)3POa=3NH31+H3PO (酸是挥发性的: NH4CI=NH3↑+HCI↑ ()酸根离子有强氧化性: NH4NO3 N2O+2H2O N20=N2+ 10 NH4NO2 N2 2H2O (NH4)2Cr207 Cr2O3+N2+4H2O 2NH4C104N2+Cl2+202+4H0 17
d. 铵盐的热分解 (i) 酸是不挥发的: (NH4)2SO4 = NH3↑+ NH4HSO4 (NH4)3PO4 = 3NH3↑+ H3PO4 (ii) 酸是挥发性的: NH4Cl = NH3↑+ HCl↑ (iii) 酸根离子有强氧化性: 17

(5)氮化物(nitride)[-3] 0.s. Na3N Mg3N2 AIN Si3N4 I P3N5 S3N4 Cl3N basic amphoteric acidic (1)Hydrolysis: LiaN +3H2O =3LiOH NH31 (2)Reduction: 2NH3+3CuO =N2+3Cu +3H2O (3)共价型大分子晶体:AIN,Si3N4,BN,Ge3N4具有高 熔点,高硬度,高强度
(5)氮化物(nitride)[ -3 ] O.S. Na3N Mg3N2 AlN Si3N4 P3N5 S3N4 Cl3N basic amphoteric acidic (1) Hydrolysis: Li3N + 3H2O = 3LiOH + NH3↑ (2) Reduction: 2NH3 + 3CuO = N2↑ + 3Cu + 3H2O (3) 共价型大分子晶体: AlN , Si3N4 , BN , Ge3N4具有高 熔点,高硬度,高强度。 18

AIN >Its wurtzite(纤锌矿)phase(w-AlN)is a wide band gap(6.2 eV)semiconductor material, giving it potential application for deep ultraviolet optoelectronics. >Stable at high temperatures in inert atmospheres and melts at 2800 OC.In a vacuum,AIN decomposes at ~1800 OC.In the air,surface oxidation occurs above700C, and even at room temperature,surface oxide layers of 5-10 nm have been detected.This oxide layer protects the material up to 1370 OC Figure I:Aluminum nitride structure. Figura 1:Nitreto de Aluminio -estrutura wurtizte. Above this temperature bulk oxidation occurs. Aluminium nitride is stable in hydrogen and carbon dioxide atmospheres up to 980 OC. ◆opto-electronics, dielectric layers in optical storage media, electronic substrates,chip carriers where high thermal conductivity is essential, military applications, as a crucible to grow crystals of gallium arsenide, steel and semiconductor manufacturing. 19
AlN ¾ Its wurtzite(纤锌矿) phase (w -AlN) is a wide band gap (6.2 eV) semiconductor material, giving it potential application for deep ultraviolet optoelectronics. ¾ Stable at high temperatures in inert atmospheres and melts at 2800 OC. In a vacuum, AlN decomposes at ~1800 OC. In the air, surface oxidation occurs above 700 OC, and even at room temperature, surface oxide layers of 5 -10 nm have been detected. This oxide layer protects the material up to 1370 OC. Above this temperature bulk oxidation occurs. Aluminium nitride is stable in hydrogen and carbon dioxide atmospheres up to 980 OC. opto -electronics, dielectric layers in optical storage media, electronic substrates, chip carriers where high thermal conductivity is essential, military applications, as a crucible to grow crystals of gallium arsenide, steel and semiconductor manufacturing. 19
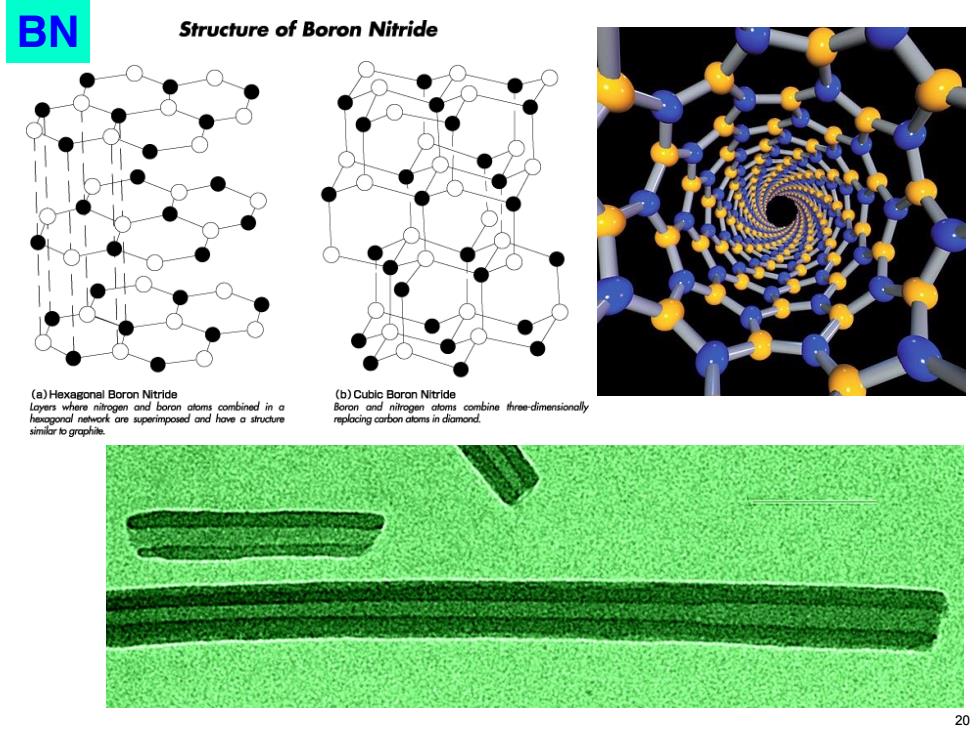
BN Structure of Boron Nitride (b)Cubic Boron Nitride Boron and nitn similr o graphie 20
BN 20