
Network layer:data plane,control plane Data plane Control plane local,per-router function network-wide logic determines how datagram determines how datagram is arriving on router input routed among routers along port is forwarded to end-end path from source host router output port to destination host forwarding function two control-plane approaches: traditional routing algorithms: values in arriving packet header implemented in routers software-defined networking 0111 (SDN):implemented in (remote)servers Network Layer:Data Plane 4-6
Network layer: data plane, control plane Data plane ▪ local, per-router function ▪ determines how datagram arriving on router input port is forwarded to router output port ▪ forwarding function Control plane ▪ network-wide logic ▪ determines how datagram is routed among routers along end-end path from source host to destination host ▪ two control-plane approaches: • traditional routing algorithms: implemented in routers • software-defined networking (SDN): implemented in (remote) servers 1 2 3 0111 values in arriving packet header Network Layer: Data Plane 4-6
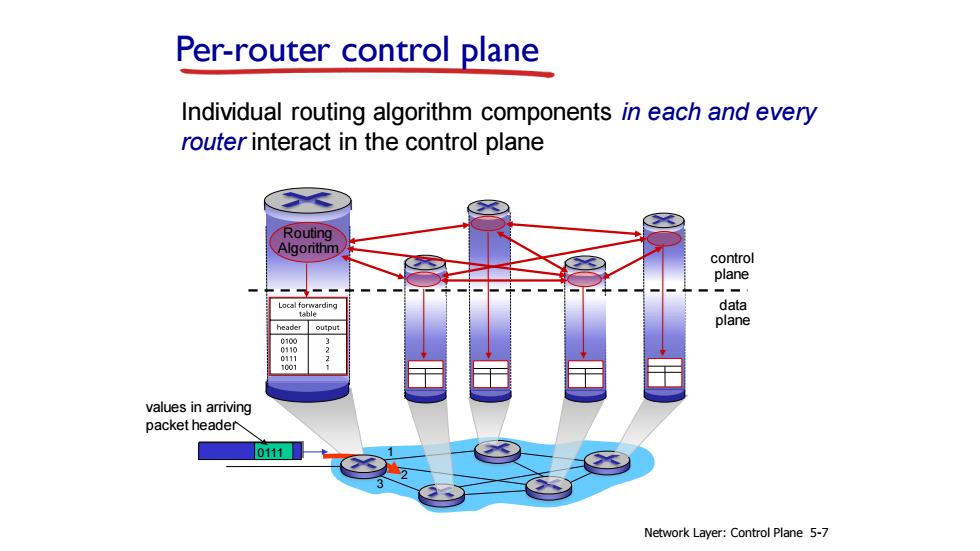
Per-router control plane Individual routing algorithm components in each and every router interact in the control plane Routing Algorithm control plane data header plane output 0100 values in arriving packet header 0111 Network Layer:Control Plane 5-7
Per-router control plane Routing Algorithm Individual routing algorithm components in each and every router interact in the control plane data plane control plane Network Layer: Control Plane 5-7 1 2 0111 values in arriving packet header 3
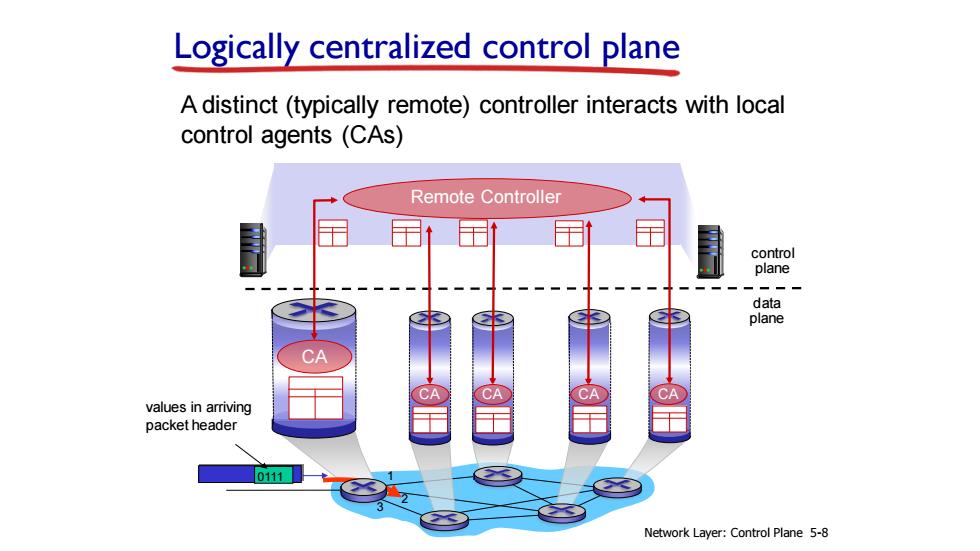
Logically centralized control plane A distinct(typically remote)controller interacts with local control agents(CAs) Remote Controller control plane data plane CA values in arriving packet header 0111 Network Layer:Control Plane 5-8
data plane control plane Logically centralized control plane A distinct (typically remote) controller interacts with local control agents (CAs) Remote Controller CA CA CA CA CA Network Layer: Control Plane 5-8 1 2 0111 3 values in arriving packet header
Network service model Q:What service model for "channel"transporting datagrams from sender to receiver? example services for example services for a flow individual datagrams: of datagrams: guaranteed delivery in-order datagram guaranteed delivery with delivery less than 40 msec delay guaranteed minimum bandwidth to flow restrictions on changes in inter-packet spacing Network Layer:Data Plane 4-9
Network service model Q:What service model for “channel” transporting datagrams from sender to receiver? example services for individual datagrams: ▪ guaranteed delivery ▪ guaranteed delivery with less than 40 msec delay example services for a flow of datagrams: ▪ in-order datagram delivery ▪ guaranteed minimum bandwidth to flow ▪ restrictions on changes in inter-packet spacing Network Layer: Data Plane 4-9
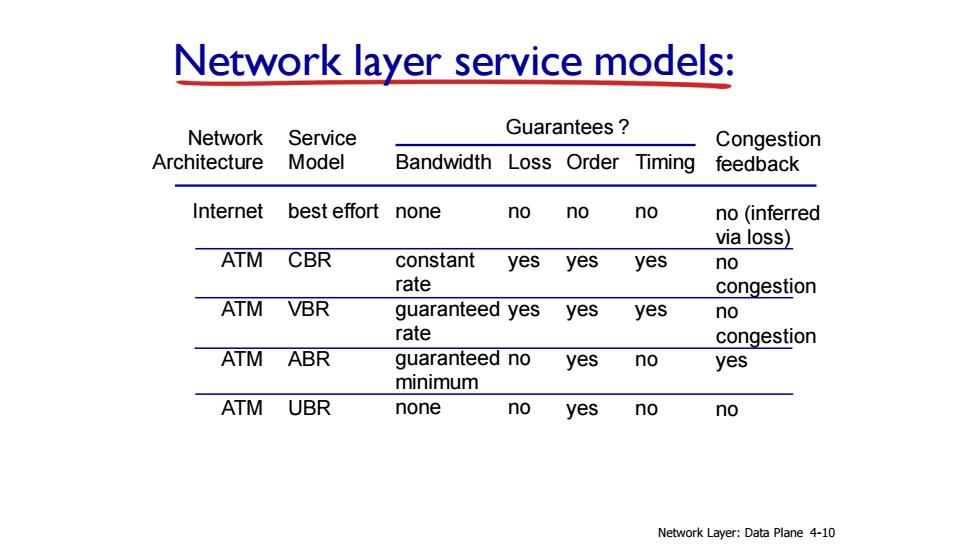
Network layer service models: Network Service Guarantees Congestion Architecture Model Bandwidth Loss Order Timing feedback Internet best effort none no no no no (inferred via loss】 ATM CBR constant yesyes yes no rate congestion ATM VBR guaranteed yesyesyes no rate congestion ATM ABR guaranteed no yes no yes minimum ATM UBR none no yes no no Network Layer:Data Plane 4-10
Network layer service models: Network Architecture Internet ATM ATM ATM ATM Service Model best effort CBR VBR ABR UBR Bandwidth none constant rate guaranteed rate guaranteed minimum none Loss no yes yes no no Order no yes yes yes yes Timing no yes yes no no Congestion feedback no (inferred via loss) no congestion no congestion yes no Guarantees ? Network Layer: Data Plane 4-10