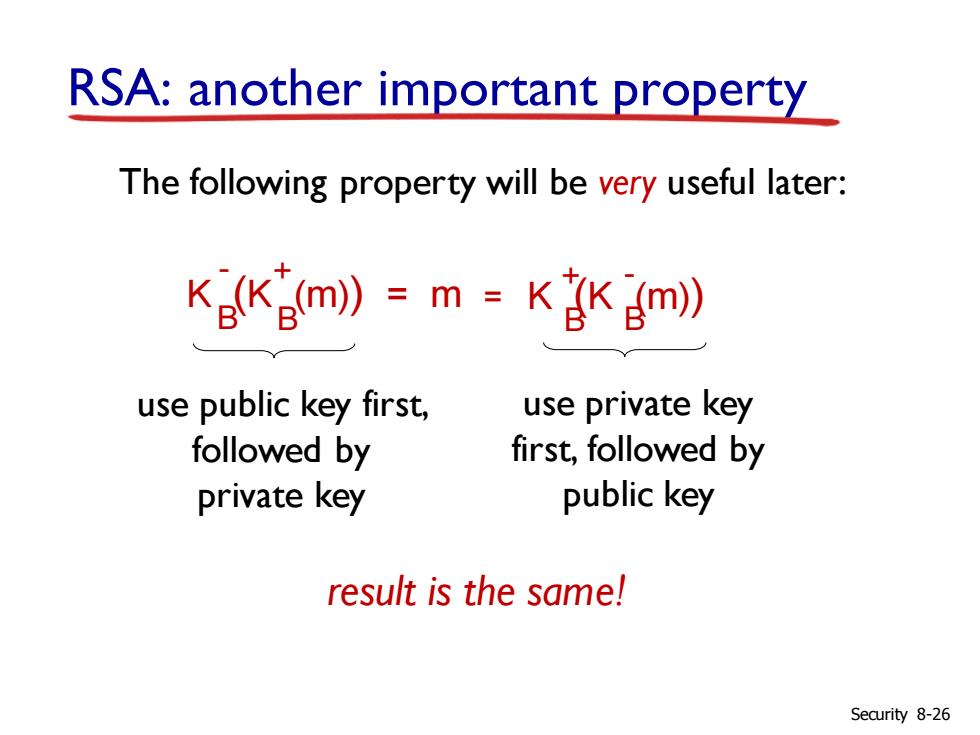
RSA:another important property The following property will be very useful later: KKgm》)=m=K含Km》 use public key first, use private key followed by first,followed by private key public key result is the same! Security 8-26
RSA: another important property The following property will be very useful later: K (K (m)) = m B B - + K (K (m)) B B + - = use public key first, followed by private key use private key first, followed by public key result is the same! Security 8-26
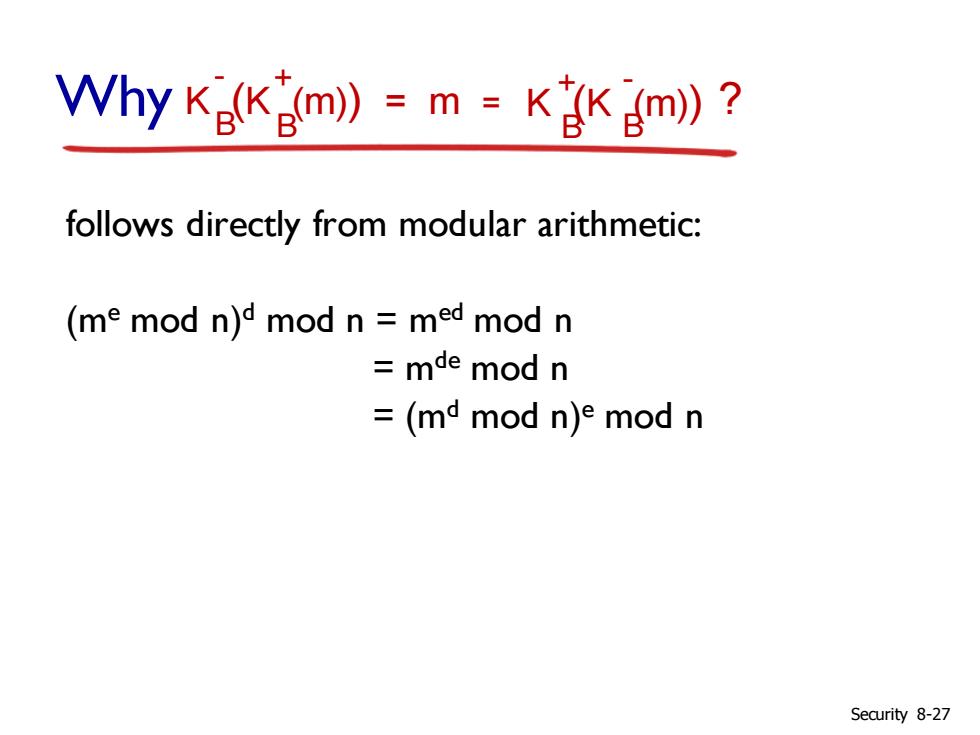
Vhy K(K(m》=m=KKgm)? follows directly from modular arithmetic: (me mod n)d mod n med mod n =mde mod n =(md mod n)e mod n Security 8-27
follows directly from modular arithmetic: (me mod n)d mod n = med mod n = mde mod n = (md mod n)e mod n K (K (m)) = m B B - + K (K (m)) B B + - Why = ? Security 8-27

Why is RSA secure? suppose you know Bob's public key(n,e).How hard is it to determine d? essentially need to find factors of n without knowing the two factors p and q fact:factoring a big number is hard Security 8-28
Why is RSA secure? ▪ suppose you know Bob’s public key (n,e). How hard is it to determine d? ▪ essentially need to find factors of n without knowing the two factors p and q • fact: factoring a big number is hard Security 8-28
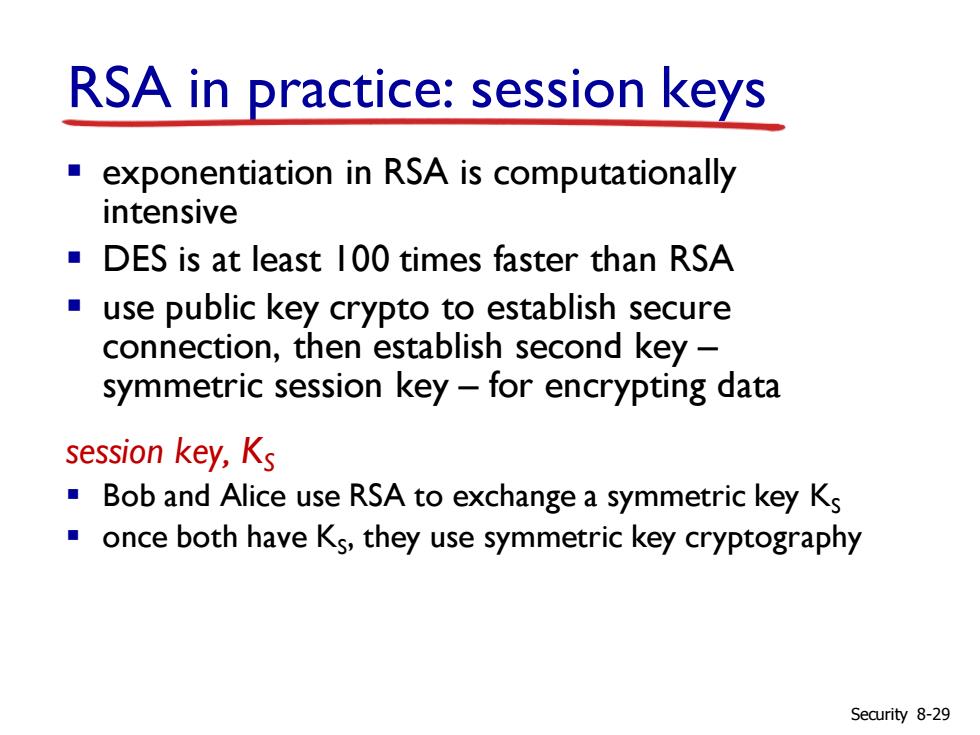
RSA in practice:session keys exponentiation in RSA is computationally intensive DES is at least 100 times faster than RSA use public key crypto to establish secure connection,then establish second key- symmetric session key-for encrypting data session key,Ks Bob and Alice use RSA to exchange a symmetric key Ks once both have Ks,they use symmetric key cryptography Security 8-29
RSA in practice: session keys ▪ exponentiation in RSA is computationally intensive ▪ DES is at least 100 times faster than RSA ▪ use public key crypto to establish secure connection, then establish second key – symmetric session key – for encrypting data session key, KS ▪ Bob and Alice use RSA to exchange a symmetric key KS ▪ once both have KS , they use symmetric key cryptography Security 8-29
Chapter 8 roadmap 8.I What is network security? 8.2 Principles of cryptography 8.3 Message integrity,authentication 8.4 Securing e-mail 8.5 Securing TCP connections:SSL 8.6 Network layer security:IPsec 8.7 Securing wireless LANs 8.8 Operational security:firewalls and IDS Security 8-30
Chapter 8 roadmap 8.1 What is network security? 8.2 Principles of cryptography 8.3 Message integrity, authentication 8.4 Securing e-mail 8.5 Securing TCP connections: SSL 8.6 Network layer security: IPsec 8.7 Securing wireless LANs 8.8 Operational security: firewalls and IDS Security 8-30