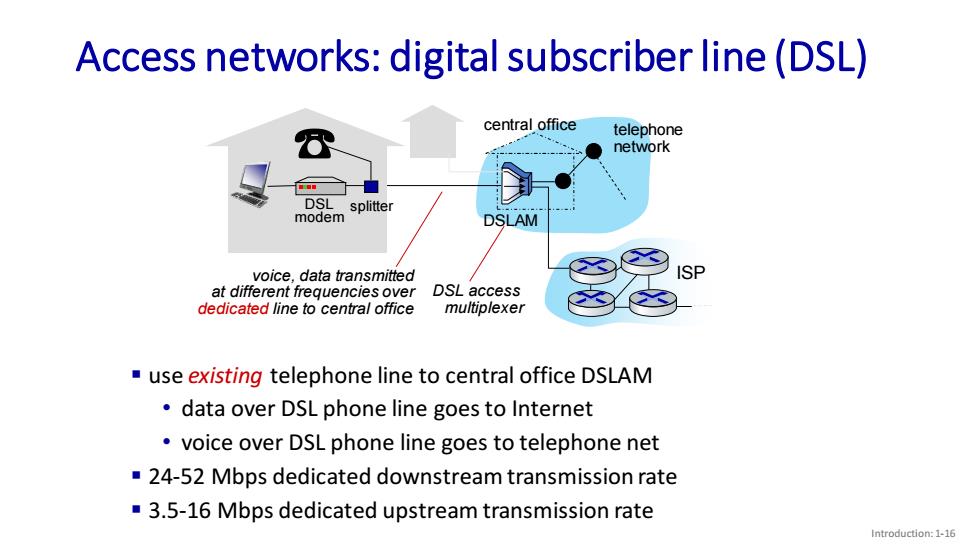
Access networks:digital subscriber line(DSL) central office telephone network DSL splitter modem DSLAM voice,data transmitted ISP at different frequencies over DSL access dedicated line to central office multiplexer use existing telephone line to central office DSLAM data over DSL phone line goes to Internet voice over DSL phone line goes to telephone net 24-52 Mbps dedicated downstream transmission rate 3.5-16 Mbps dedicated upstream transmission rate Introduction:1-16
ISP Introduction: 1-16 Access networks: digital subscriber line (DSL) central office telephone network DSLAM voice, data transmitted at different frequencies over dedicated line to central office ▪ use existing telephone line to central office DSLAM • data over DSL phone line goes to Internet • voice over DSL phone line goes to telephone net ▪ 24-52 Mbps dedicated downstream transmission rate ▪ 3.5-16 Mbps dedicated upstream transmission rate DSL modem splitter DSL access multiplexer
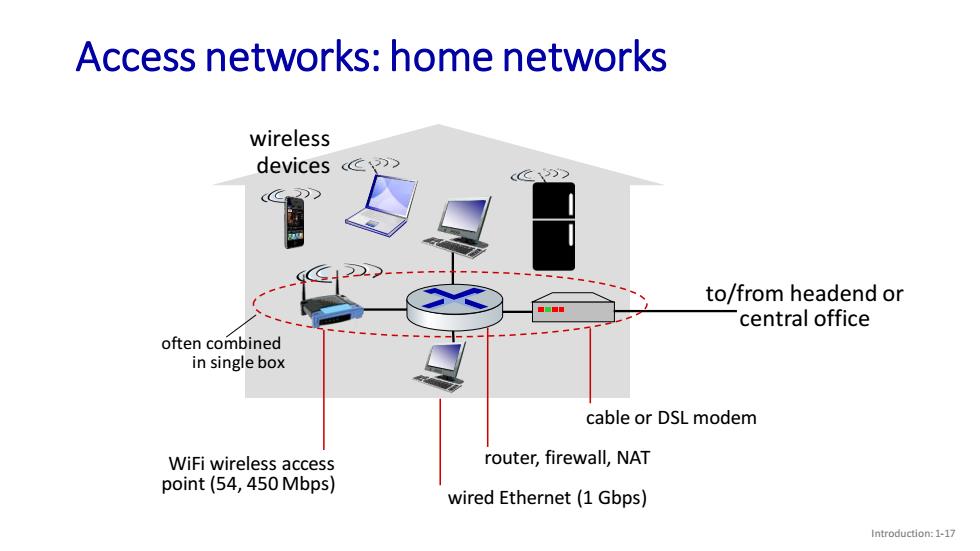
Access networks:home networks wireless devices> ccC1)> to/from headend or central office often combined in single box cable or DSL modem WiFi wireless access router,firewall,NAT point(54,450 Mbps) wired Ethernet(1 Gbps) Introduction:1-17
Introduction: 1-17 Access networks: home networks to/from headend or central office cable or DSL modem router, firewall, NAT wired Ethernet (1 Gbps) WiFi wireless access point (54, 450 Mbps) wireless devices often combined in single box
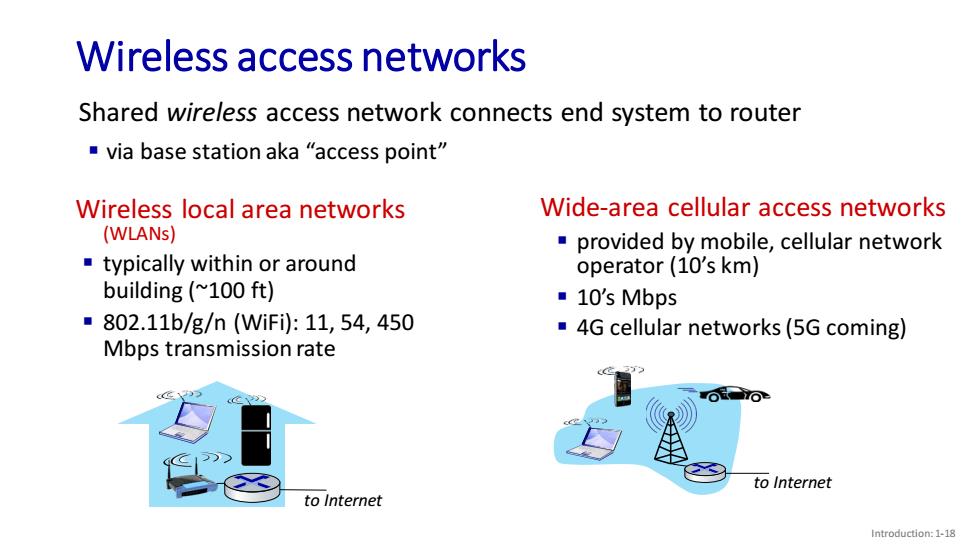
Wireless access networks Shared wireless access network connects end system to router via base station aka "access point" Wireless local area networks Wide-area cellular access networks (WLANs) provided by mobile,cellular network typically within or around operator(10's km) building (~100 ft) ■10's Mbps ■802.11b/g/n(WiFi:11,54,450 4G cellular networks(5G coming) Mbps transmission rate to Internet to Internet Introduction:1-18
Introduction: 1-18 Wireless access networks Shared wireless access network connects end system to router ▪ via base station aka “access point” Wireless local area networks (WLANs) ▪ typically within or around building (~100 ft) ▪ 802.11b/g/n (WiFi): 11, 54, 450 Mbps transmission rate to Internet to Internet Wide-area cellular access networks ▪ provided by mobile, cellular network operator (10’s km) ▪ 10’s Mbps ▪ 4G cellular networks (5G coming)
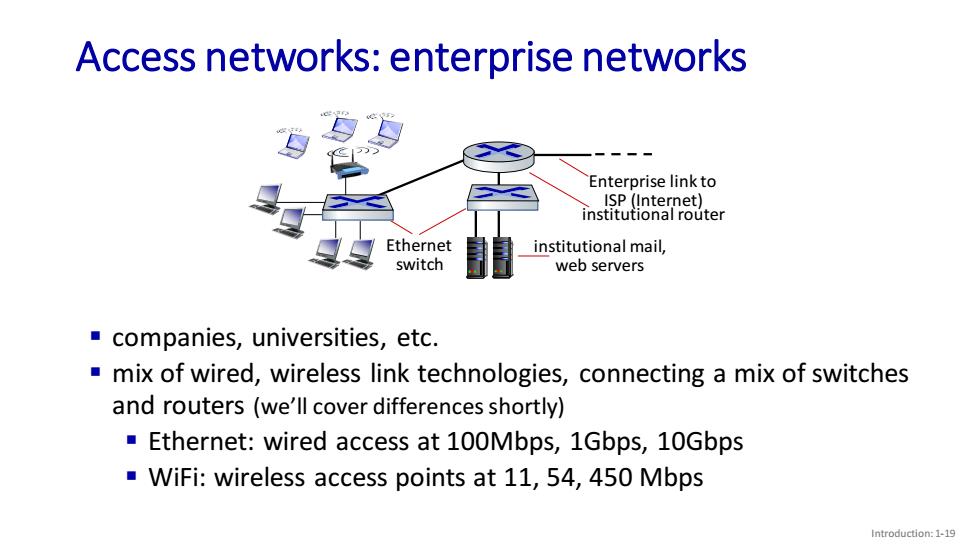
Access networks:enterprise networks Enterprise link to ISP(Internet) institutional router Ethernet institutional mail, switch web servers companies,universities,etc. mix of wired,wireless link technologies,connecting a mix of switches and routers (we'll cover differences shortly) Ethernet:wired access at 100Mbps,1Gbps,10Gbps WiFi:wireless access points at 11,54,450 Mbps Introduction:1-19
Introduction: 1-19 Access networks: enterprise networks ▪ companies, universities, etc. ▪ mix of wired, wireless link technologies, connecting a mix of switches and routers (we’ll cover differences shortly) ▪ Ethernet: wired access at 100Mbps, 1Gbps, 10Gbps ▪ WiFi: wireless access points at 11, 54, 450 Mbps Ethernet switch institutional mail, web servers institutional router Enterprise link to ISP (Internet)

Host:sends packets of data host sending function: takes application message breaks into smaller chunks, two packets, known as packets,of length L bits L bits each transmits packet into access network at transmission rate R link transmission rate,aka link host capacity,aka link bandwidth R:link transmission rate packet time needed to transmission transmit L-bit L(bits) delay packet into link R(bits/sec) Introduction:1-20
Introduction: 1-20 Host: sends packets of data host sending function: ▪ takes application message ▪ breaks into smaller chunks, known as packets, of length L bits ▪ transmits packet into access network at transmission rate R • link transmission rate, aka link capacity, aka link bandwidth R: link transmission rate host 2 1 two packets, L bits each packet transmission delay time needed to transmit L-bit packet into link L (bits) R (bits/sec) = =