
Link layer services framing,link access: encapsulate datagram into frame,adding header,trailer channel access if shared medium ·“MAC”addresses used in frame headers to identify source,destination different from IP address! reliable delivery between adjacent nodes we learned how to do this already (chapter 3)! seldom used on low bit-error link(fiber,some twisted pair) wireless links:high error rates Q:why both link-level and end-end reliability? Link Layer and LANs 6-6
Link layer services ▪ framing, link access: • encapsulate datagram into frame, adding header, trailer • channel access if shared medium • “MAC” addresses used in frame headers to identify source, destination • different from IP address! ▪ reliable delivery between adjacent nodes • we learned how to do this already (chapter 3)! • seldom used on low bit-error link (fiber, some twisted pair) • wireless links: high error rates • Q: why both link-level and end-end reliability? Link Layer and LANs 6-6

Link layer services(more) ■flow control: pacing between adjacent sending and receiving nodes error detection: errors caused by signal attenuation,noise. receiver detects presence of errors: signals sender for retransmission or drops frame error correction: receiver identifies and corrects bit error(s)without resorting to retransmission half-duplex and full-duplex with half duplex,nodes at both ends of link can transmit,but not at same time Link Layer and LANs 6-7
▪ flow control: • pacing between adjacent sending and receiving nodes ▪ error detection: • errors caused by signal attenuation, noise. • receiver detects presence of errors: • signals sender for retransmission or drops frame ▪ error correction: • receiver identifies and corrects bit error(s) without resorting to retransmission ▪ half-duplex and full-duplex • with half duplex, nodes at both ends of link can transmit, but not at same time Link layer services (more) Link Layer and LANs 6-7

Where is the link layer implemented? ■in each and every host link layer implemented in “adaptor”(aka network interface card NIC)or on a chip application Ethernet card,802.1I transport network cpu memory card;Ethernet chipset link implements link,physical host layer bus (e.g.,PCI) attaches into host's system link physical buses physical trans ssion combination of hardware, software,firmware network adapter card Link Layer and LANs 6-8
Where is the link layer implemented? ▪ in each and every host ▪ link layer implemented in “adaptor” (aka network interface card NIC) or on a chip • Ethernet card, 802.11 card; Ethernet chipset • implements link, physical layer ▪ attaches into host’s system buses ▪ combination of hardware, software, firmware controller physical transmission cpu memory host bus (e.g., PCI) network adapter card application transport network link link physical Link Layer and LANs 6-8
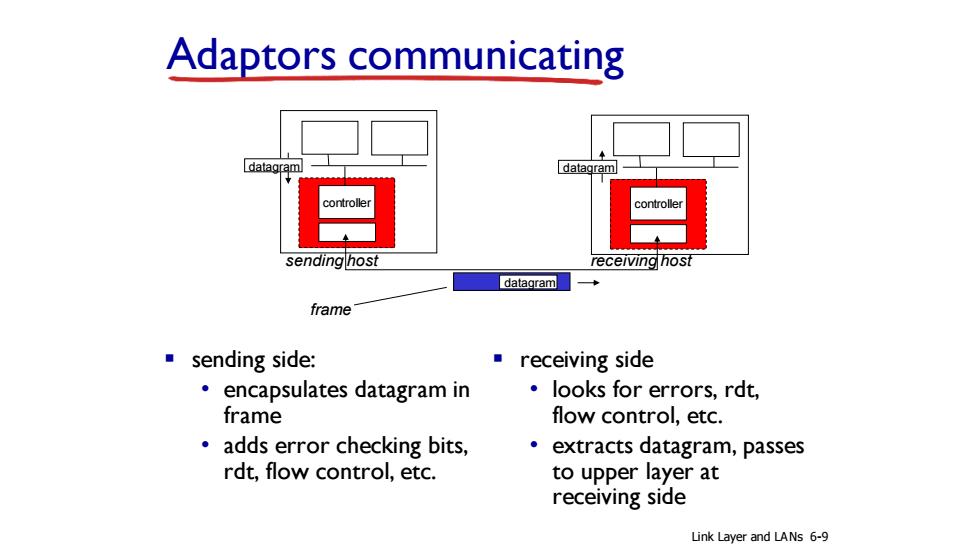
Adaptors communicating datagram datagram controlle sending host receiving host datagram frame sending side: receiving side encapsulates datagram in looks for errors,rdt, frame flow control,etc. adds error checking bits, extracts datagram,passes rdt,flow control,etc. to upper layer at receiving side Link Layer and LANs 6-9
Adaptors communicating ▪ sending side: • encapsulates datagram in frame • adds error checking bits, rdt, flow control, etc. ▪ receiving side • looks for errors, rdt, flow control, etc. • extracts datagram, passes to upper layer at receiving side controller controller sending host receiving host datagram datagram datagram frame Link Layer and LANs 6-9
Link layer,LANs:outline 6.I introduction,services 6.5 link virtualization: 6.2 error detection, MPLS correction 6.6 data center 6.3 multiple access networking protocols 6.7 a day in the life of a 6.4 LANs web request ·addressing,ARP ·Ethernet ·switches ·VLANS Link Layer and LANs 6-10
Link layer, LANs: outline 6.1 introduction, services 6.2 error detection, correction 6.3 multiple access protocols 6.4 LANs • addressing, ARP • Ethernet • switches • VLANS 6.5 link virtualization: MPLS 6.6 data center networking 6.7 a day in the life of a web request Link Layer and LANs 6-10