1907 03-11 The Variety of Demand Curves ·Perfectly Inelastic -Quantity demanded does not respond to price changes. ·Perfectly Elastic -Quantity demanded changes infinitely with any change in price. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 03-11 The Variety of Demand Curves • Perfectly Inelastic – Quantity demanded does not respond to price changes. • Perfectly Elastic – Quantity demanded changes infinitely with any change in price

190 03-12 Perfectly Elastic and Inelastic Demands 200 DI Perfectly inelastic 150 demand D D 100 Perfectly elastic demand 50 0 100 200 300 Quantity Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 03-12 Perfectly Elastic and Inelastic Demands

1907 03-13 The Variety of Demand Curves 。 Because the price elasticity of demand measures how much quantity demanded responds to the price,it is closely related to the slope of the demand curve. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 03-13 The Variety of Demand Curves • Because the price elasticity of demand measures how much quantity demanded responds to the price, it is closely related to the slope of the demand curve
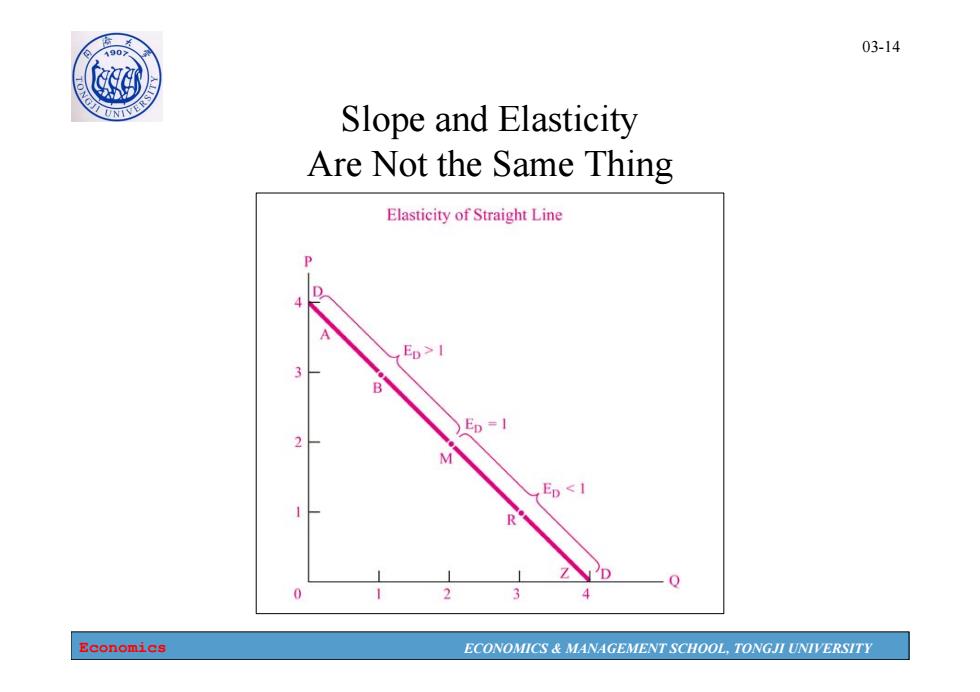
190 03-14 Slope and Elasticity Are Not the Same Thing Elasticity of Straight Line Ep>I )Ep=1 M Ep<I 一Q Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 03-14 Slope and Elasticity Are Not the Same Thing

490 03-15 ⑩ Total Revenue and the Price Elasticity of Demand Total revenue is the amount paid by buyers and received by sellers of a good. Computed as the price of the good times the quantity sold. TR=P x Q Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 03-15 Total Revenue and the Price Elasticity of Demand • Total revenue is the amount paid by buyers and received by sellers of a good. • Computed as the price of the good times the quantity sold. TR = P x Q