
In equilibrium: n-p)=y+n-p)9 2-1 (y+2;)+p 1+7y-7 y-1 p= y+p 1+7y-7 y=0? → m=p? y=m-p 电子科大经管学院马捷 6 元元元元
6 In equilibrium: ( ) 1 1 p p i y zi ( pi p) ? 0 ? 1 1 ( ) 1 1 m p y m p y p y p p y z p i i 电子科大经管学院 马捷
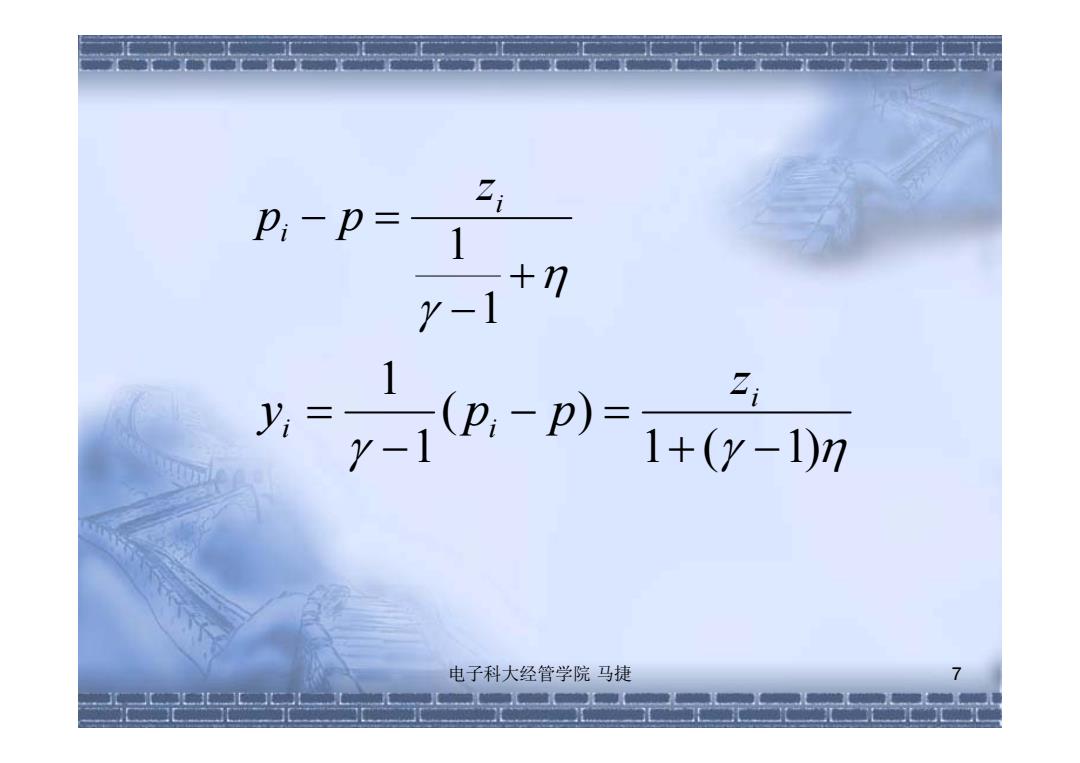
2 P,-p= 1 +门 y-1 21 y:= y-1 (D.-B)= +(y-1)m 电子科大经管学院马捷 7 5元元元元元元
电子科大经管学院 马捷 7 1 1 i i z p p 1 ( 1) ( ) 1 1 i i i z y p p

Lucas Model with Imperfect Information Relative price of good i:=p,-p Two assumptions: (1)Certainty equivalency. (2)Rational expectation. Supely -1E(:) y-1 电子科大经管学院马捷 8 元元元
8 Relative price of good i: Two assumptions: (1) Certainty equivalency. (2) Rational expectation. ( | ) 1 1 ( ) 1 1 Supply : i i i pi l p p E r 电子科大经管学院 马捷 Lucas Model with Imperfect Information ri pi p

Assume m and =are independent and normally distributed,E[z]=0,so p;and r;are independent and normally distributed. up,), v.Ip:-Elpll if p,=E[p],EIrp]=0; if pi>E[p],E[rpi]>O; if p;<E[p],E[r,p ]<0. 电子科大经管学院马捷 9
9 Assume m and zi are independent and normally distributed, E[zi]=0, so pi and ri are independent and normally distributed. ( | ) [ p E[ p]] v v v E r p i r p r i i if [ ], [ | ] 0. if [ ], [ | ] 0; if [ ], [ | ] 0; i i i i i i i i i p E p E r p p E p E r p p E p E r p 电子科大经管学院 马捷

Lucas Supply Curve 1 Vr y-Ivr+vp (p,-E[p]) =b(p,-E[p])→ Aggregate supply y=b(p-E[p]), b>0 Price surprise 电子科大经管学院马捷 10
10 ( [ ]), 0 Aggregate supply : ( [ ]) ( [ ]) 1 1 y b p E p b b p E p p E p v v v l i i r p r i 电子科大经管学院 马捷 Lucas Supply Curve Price surprise