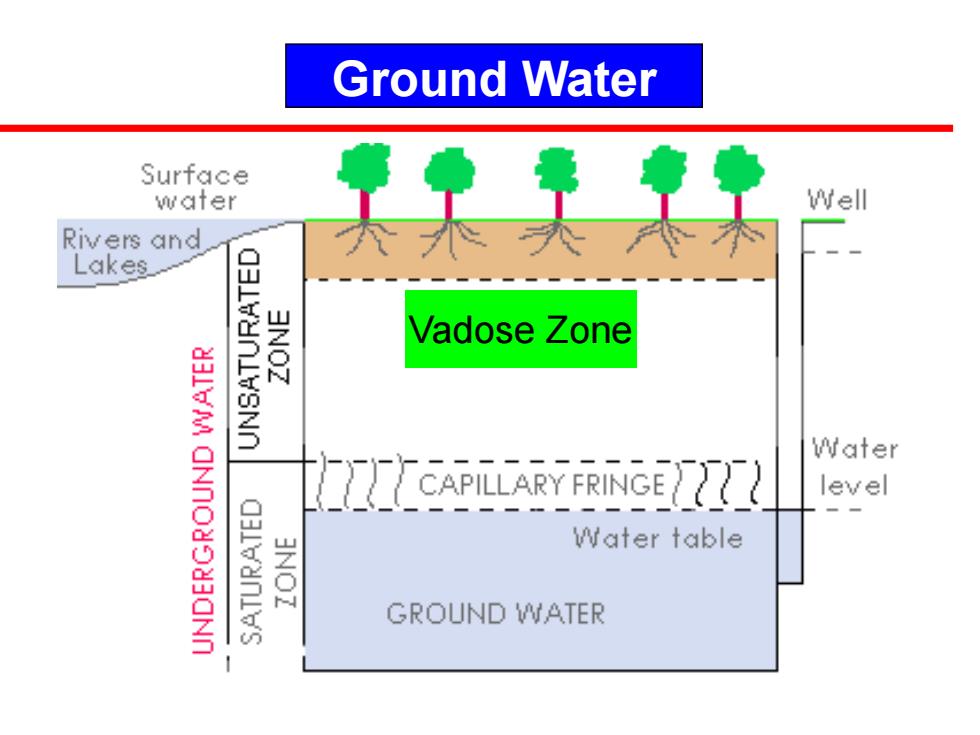
Ground Water Surface water Well Rivers and Lakes_ 3NOZ Vadose Zone Water level Water table 3NOZ GROUND WATER
Ground Water Vadose Zone
Groundwater Groundwater is recharged from,and eventually flows to, the surface naturally;natural discharge often occurs at springs and seeps,and can form oases or wetlands. Groundwater is also often withdrawn for agricultural, municipal and industrial use by constructing and operating extraction wells.The study of the distribution and movement of groundwater is hydrogeology,also called groundwater hydrology
Groundwater is recharged from, and eventually flows to, the surface naturally; natural discharge often occurs at springs and seeps, and can form oases or wetlands. Groundwater is also often withdrawn for agricultural, municipal and industrial use by constructing and operating extraction wells. The study of the distribution and movement of groundwater is hydrogeology, also called groundwater hydrology. Groundwater

Groundwater Groundwater is hypothesized to provide lubrication that can possibly influence the movement of faults.It is likely that much of the Earth's subsurface contains some water,which may be mixed with other fluids in some instances.Groundwater may not be confined only to the Earth
Groundwater is hypothesized to provide lubrication that can possibly influence the movement of faults. It is likely that much of the Earth's subsurface contains some water, which may be mixed with other fluids in some instances. Groundwater may not be confined only to the Earth. Groundwater

Some basic concepts of Aquifers An aquifer is a layer of relatively porous substrate that contains and transmits groundwater.When water can flow directly between the surface and the saturated zone of an aquifer,the aquifer is unconfined.The deeper parts of unconfined aquifers are usually more saturated with groundwater since gravity causes water to flow downward
Some basic concepts of Aquifers An aquifer is a layer of relatively porous substrate that contains and transmits groundwater. When water can flow directly between the surface and the saturated zone of an aquifer, the aquifer is unconfined. The deeper parts of unconfined aquifers are usually more saturated with groundwater since gravity causes water to flow downward
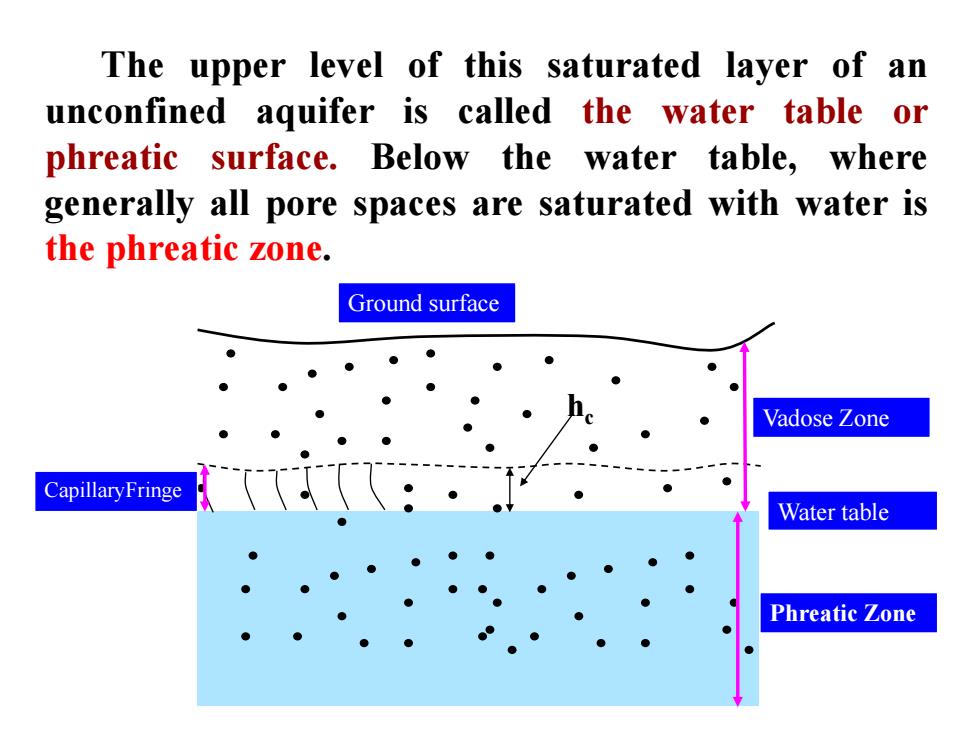
The upper level of this saturated layer of an unconfined aquifer is called the water table or phreatic surface.Below the water table,where generally all pore spaces are saturated with water is the phreatic zone. Ground surface Vadose Zone Capillary Fringe Water table Phreatic Zone
The upper level of this saturated layer of an unconfined aquifer is called the water table or phreatic surface. Below the water table, where generally all pore spaces are saturated with water is the phreatic zone. Ground surface hc Vadose Zone CapillaryFringe Phreatic Zone Water table