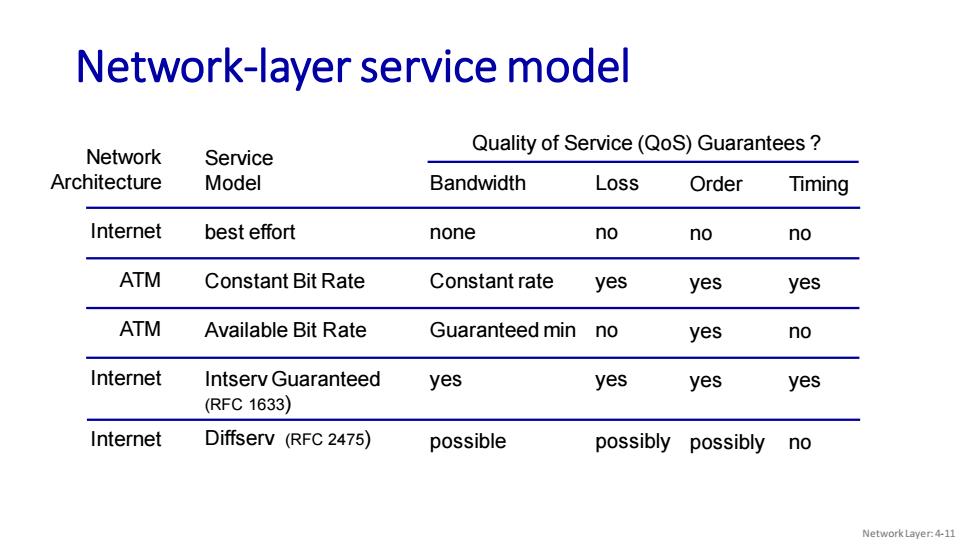
Network-layer service model Network Quality of Service(QoS)Guarantees Service Architecture Model Bandwidth Loss Order Timing Internet best effort none no no no ATM Constant Bit Rate Constant rate yes yes yes ATM Available Bit Rate Guaranteed min no yes no Internet Intserv Guaranteed yes yes yes yes (RFC1633) Internet Diffserv (RFC 2475) possible possibly possibly no Network Layer:4-11
Network-layer service model Network Architecture Internet ATM ATM Internet Internet Service Model best effort Constant Bit Rate Available Bit Rate Intserv Guaranteed (RFC 1633) Diffserv (RFC 2475) Bandwidth none Constant rate Guaranteed min yes possible Loss no yes no yes possibly Order no yes yes yes possibly Timing no yes no yes no Quality of Service (QoS) Guarantees ? Network Layer: 4-11

Reflections on best-effort service: simplicity of mechanism has allowed Internet to be widely deployed adopted -sufficient provisioning of bandwidth allows performance of real-time applications (e.g.,interactive voice,video)to be "good enough"for “most of the time” replicated,application-layer distributed services (datacenters,content distribution networks)connecting close to clients'networks,allow services to be provided from multiple locations congestion control of "elastic"services helps It's hard to argue with success of best-effort service model Network Laver:4-12
Reflections on best-effort service: ▪ simplicity of mechanism has allowed Internet to be widely deployed adopted ▪ sufficient provisioning of bandwidth allows performance of real-time applications (e.g., interactive voice, video) to be “good enough” for “most of the time” ▪ replicated, application-layer distributed services (datacenters, content distribution networks) connecting close to clients’ networks, allow services to be provided from multiple locations ▪ congestion control of “elastic” services helps It’s hard to argue with success of best-effort service model Network Layer: 4-12
Network layer:"data plane"roadmap Network layer:overview 。data plane 。control plane -What's inside a router input ports,switching,output ports buffer management,scheduling IP:the Internet Protocol 。datagram format Generalized Forwarding,SDN 。addressing Match+action network address translation OpenFlow:match+action in action ·IPv6 ■Middleboxes Network Layer:4-13
Network layer: “data plane” roadmap ▪ Network layer: overview • data plane • control plane ▪ What’s inside a router • input ports, switching, output ports • buffer management, scheduling ▪ IP: the Internet Protocol • datagram format • addressing • network address translation • IPv6 ▪ Generalized Forwarding, SDN • Match+action • OpenFlow: match+action in action ▪ Middleboxes Network Layer: 4-13

Router architecture overview high-level view of generic router architecture: routing,management routing control plane (software) processor operates in millisecond time frame forwarding data plane (hardware)operates in nanosecond timeframe high-speed switching ● fabric ● router input ports router output ports NetworkLayer:4-14
Router architecture overview high-level view of generic router architecture: high-speed switching fabric routing processor router input ports router output ports forwarding data plane (hardware) operates in nanosecond timeframe routing, management control plane (software) operates in millisecond time frame Network Layer: 4-14

Input port functions link lookup, line layer forwarding switch protocol termination (receive) M fabric queueing physical layer: bit-level reception decentralized switching: link layer: e.g.,Ethernet using header field values,lookup output port using (chapter 6) forwarding table in input port memory("match plus action") goal:complete input port processing at 'line speed' input port queuing:if datagrams arrive faster than forwarding rate into switch fabric Network Layer:4-15
Input port functions switch fabric line termination physical layer: bit-level reception link layer protocol (receive) link layer: e.g., Ethernet (chapter 6) lookup, forwarding queueing decentralized switching: ▪ using header field values, lookup output port using forwarding table in input port memory (“match plus action”) ▪ goal: complete input port processing at ‘line speed’ ▪ input port queuing: if datagrams arrive faster than forwarding rate into switch fabric Network Layer: 4-15