
上游充通大 ParisTech SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY INSTITUT DES SCIENCES ET TECHNOLOGIES PARIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Sample Problem: Simple Statistics The median is the data value that splits the data into equal-sized parts. For the data 2,4,6,9,13,the median is 6, since there are two values greater than 6 and two values that are smaller. One way to determine the median is to store all the numbers,sort them,and identify the middle value. 6
Sample Problem: Simple Statistics • The median is the data value that splits the data into equal-sized parts. • For the data 2, 4, 6, 9, 13, the median is 6, since there are two values greater than 6 and two values that are smaller. • One way to determine the median is to store all the numbers, sort them, and identify the middle value. 6
上游充通大 ParisTech SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY INSTITUT DES SCIENCES ET TECHNOLOGIES PARIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Sample Problem: Simple Statistics The standard deviation is a measure of how spread out the data is relative to the mean. If the data is tightly clustered around the mean, then the standard deviation is small.If the data is more spread out,the standard deviation is larger. The standard deviation is a yardstick to measure/express how exceptional the data is. 7
Sample Problem: Simple Statistics • The standard deviation is a measure of how spread out the data is relative to the mean. • If the data is tightly clustered around the mean, then the standard deviation is small. If the data is more spread out, the standard deviation is larger. • The standard deviation is a yardstick to measure/express how exceptional the data is. 7
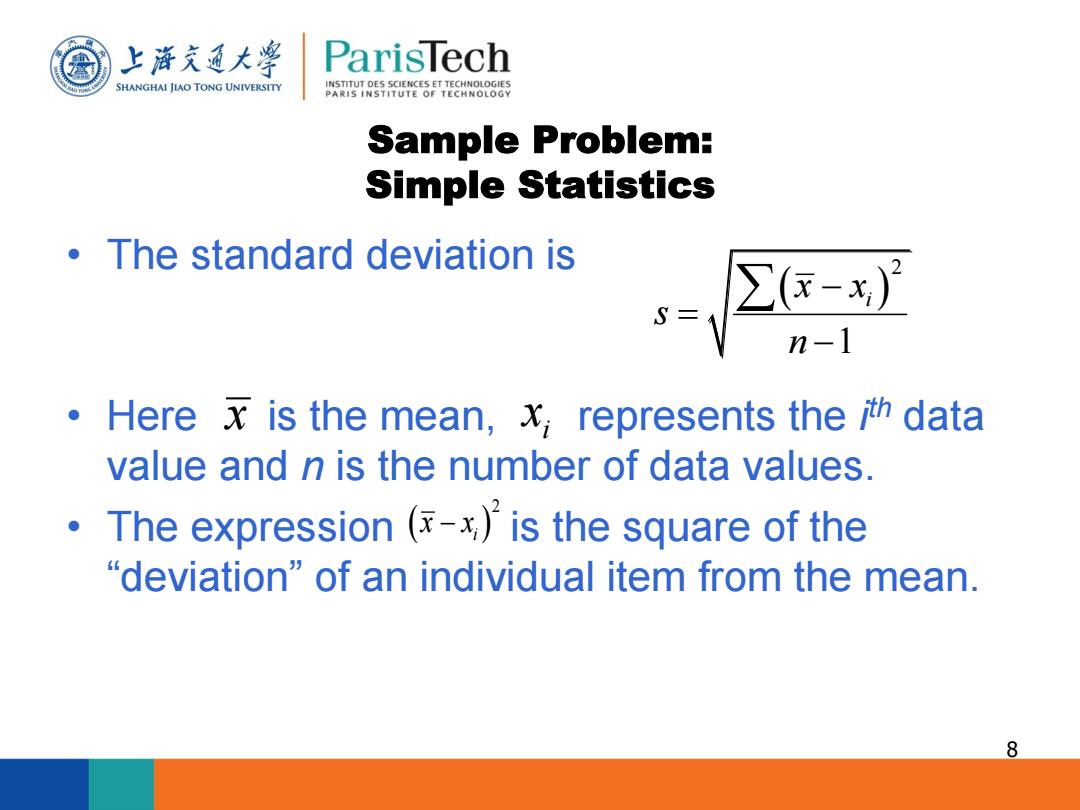
上游充通大 ParisTech SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY INSTITUT DES SCIENCES ET TECHNOLOGIES PARIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Sample Problem: Simple Statistics The standard deviation is 2 Here x is the mean,x represents the ith data value and n is the number of data values. The expression (-x)is the square of the "deviation of an individual item from the mean. 8
Sample Problem: Simple Statistics • The standard deviation is • Here is the mean, represents the i th data value and n is the number of data values. • The expression is the square of the “deviation” of an individual item from the mean. 8 2 1 i x x s n x i x 2 i x x
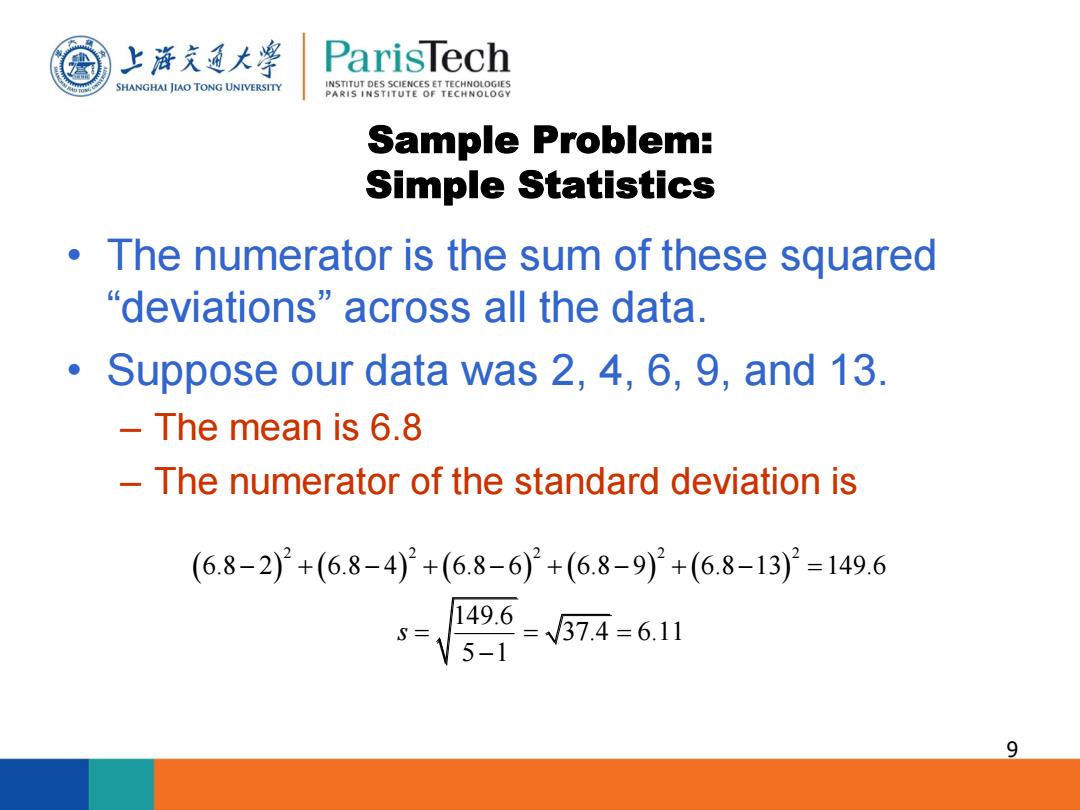
上游充通大 ParisTech SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY INSTITUT DES SCIENCES ET TECHNOLOGIES PARIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Sample Problem: Simple Statistics The numerator is the sum of these squared “deviations”across all the data. Suppose our data was 2,4,6,9,and 13. The mean is 6.8 The numerator of the standard deviation is (6.8-2)}+(6.8-4)2+(6.8-6)}2+(6.8-9)2+(6.8-13)°=149.6 s9574-61 9
Sample Problem: Simple Statistics • The numerator is the sum of these squared “deviations” across all the data. • Suppose our data was 2, 4, 6, 9, and 13. – The mean is 6.8 – The numerator of the standard deviation is 9 2 2 2 2 2 6.8 2 6.8 4 6.8 6 6.8 9 6.8 13 149.6 149.6 37.4 6.11 5 1 s
上游充通大 ParisTech SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY INSTITUT DES SCIENCES ET TECHNOLOGIES PARIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Sample Problem: Simple Statistics As you can see,calculating the standard deviation not only requires the mean (which can't be calculated until all the data is entered), but also each individual data element! We need some way to remember these values as they are entered. 10
Sample Problem: Simple Statistics • As you can see, calculating the standard deviation not only requires the mean (which can‟t be calculated until all the data is entered), but also each individual data element! • We need some way to remember these values as they are entered. 10