
RSA:another important property The following property will be very useful later: KeKm》=m=KKgm) use public key use private key first,followed by first,followed by private key public key result is the same! Network Security 8-26
Network Security 8-26 RSA: another important property The following property will be very useful later: K (K (m)) = m B B - + K (K (m) ) B B + - = use public key first, followed by private key use private key first, followed by public key result is the same!
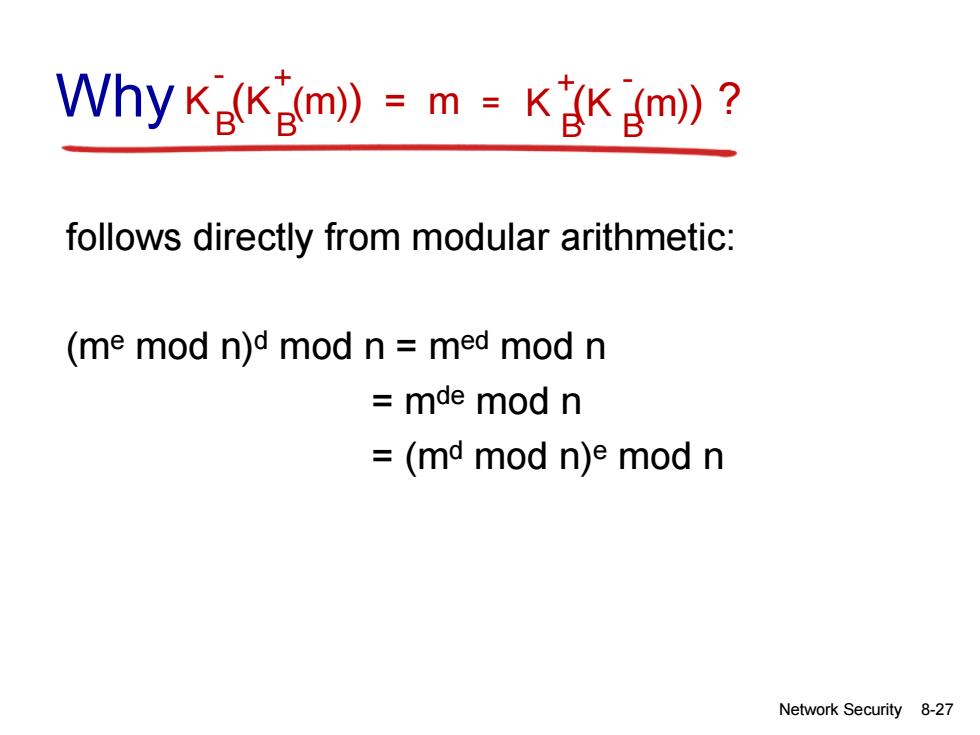
Why K(Km))=m=KKgm)? follows directly from modular arithmetic: (me mod n)d mod n med mod n mde mod n =(md mod n)e mod n Network Security 8-27
Network Security 8-27 follows directly from modular arithmetic: (me mod n)d mod n = med mod n = mde mod n = (md mod n)e mod n K (K (m)) = m B B - + K (K (m) ) B B + - Why = ?

Why is RSA secure? suppose you know Bob's public key(n,e). How hard is it to determine d? essentially need to find factors of n without knowing the two factors p and q -fact:factoring a big number is hard Network Security 8-28
Network Security 8-28 Why is RSA secure? suppose you know Bob’s public key (n,e). How hard is it to determine d? essentially need to find factors of n without knowing the two factors p and q fact: factoring a big number is hard

RSA in practice:session keys exponentiation in RSA is computationally intensive DES is at least 100 times faster than RSA use public key cryto to establish secure connection,then establish second key symmetric session key-for encrypting data session key,Ks Bob and Alice use RSA to exchange a symmetric key Ks once both have Ks,they use symmetric key cryptography Network Security 8-29
Network Security 8-29 RSA in practice: session keys exponentiation in RSA is computationally intensive DES is at least 100 times faster than RSA use public key cryto to establish secure connection, then establish second key – symmetric session key – for encrypting data session key, KS Bob and Alice use RSA to exchange a symmetric key K S once both have KS , they use symmetric key cryptography

Chapter 8 roadmap 8.1 What is network security? 8.2 Principles of cryptography 8.3 Message integrity,authentication 8.4 Securing e-mail 8.5 Securing TCP connections:SSL 8.6 Network layer security:IPsec 8.7 Securing wireless LANs 8.8 Operational security:firewalls and IDS Network Security 8-30
Network Security 8-30 Chapter 8 roadmap 8.1 What is network security? 8.2 Principles of cryptography 8.3 Message integrity, authentication 8.4 Securing e-mail 8.5 Securing TCP connections: SSL 8.6 Network layer security: IPsec 8.7 Securing wireless LANs 8.8 Operational security: firewalls and IDS