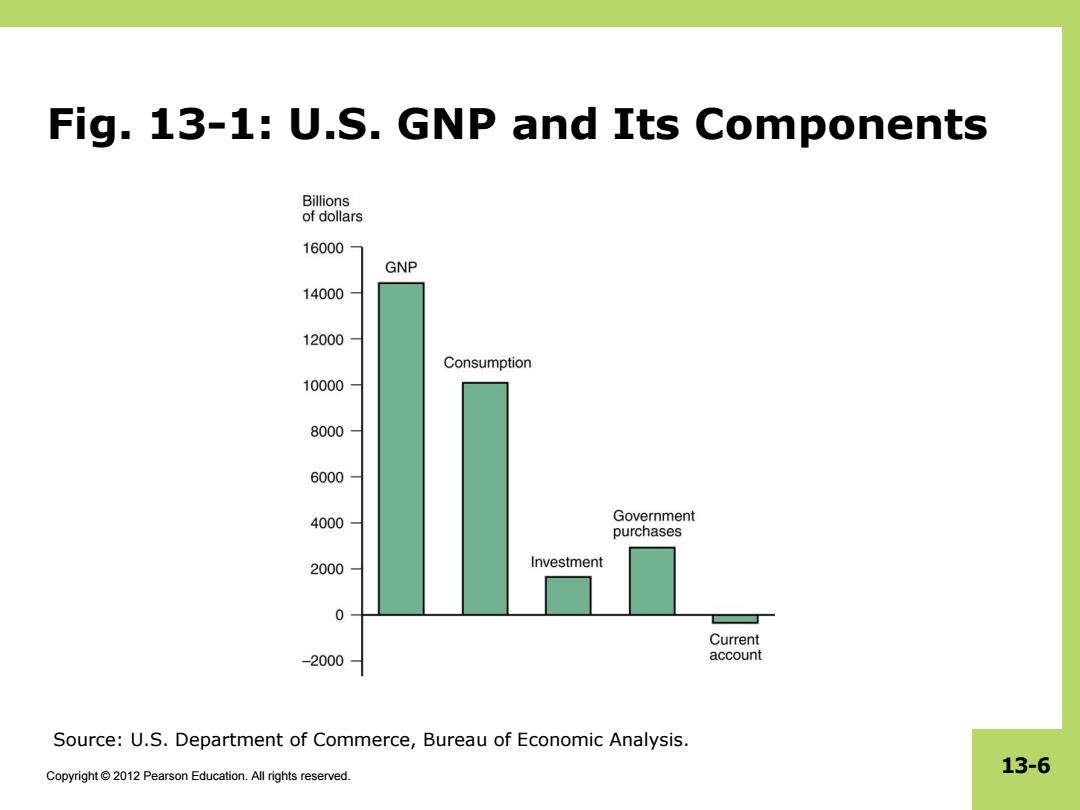
Fig.13-1:U.S.GNP and Its Components Billions of dollars 16000 GNP 14000 12000 Consumption 10000 8000 6000 4000 Government purchases 2000 Investment 0 Current -2000 account Source:U.S.Department of Commerce,Bureau of Economic Analysis. 13-6 Copyright 2012 Pearson Education.All rights reserved
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education. All rights reserved. 13-6 Fig. 13-1: U.S. GNP and Its Components Source: U.S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of Economic Analysis

National Income Accounts GNP is one measure of national income, but a more precise measure of national income is GNP adjusted for following: 1.Depreciation of physical capital results in a loss of income to capital owners,so the amount of depreciation is subtracted from GNP. 2.Unilateral transfers to and from other countries can change national income: payments of expatriate workers sent to their home countries,foreign aid and pension payments sent to expatriate retirees. Copyright 2012 Pearson Education.All rights reserved. 13-7
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education. All rights reserved. 13-7 National Income Accounts • GNP is one measure of national income, but a more precise measure of national income is GNP adjusted for following: 1. Depreciation of physical capital results in a loss of income to capital owners, so the amount of depreciation is subtracted from GNP. 2. Unilateral transfers to and from other countries can change national income: payments of expatriate workers sent to their home countries, foreign aid and pension payments sent to expatriate retirees

National Income Accounts (cont.) Another approximate measure of national income is gross domestic product (GDP): Gross domestic product measures the final value of all goods and services that are produced within a country in a given time period. - GDP GNP-payments from foreign countries for factors of production payments to foreign countries for factors of production 13-8 Copyright2012 Pearson Education.All rights reserved
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education. All rights reserved. 13-8 National Income Accounts (cont.) • Another approximate measure of national income is gross domestic product (GDP): – Gross domestic product measures the final value of all goods and services that are produced within a country in a given time period. – GDP = GNP – payments from foreign countries for factors of production + payments to foreign countries for factors of production

GNP Expenditure on a Country's Goods and Services The national income identity for an open economy is Y-C+I+G+EX-IM C+I+G +CA Expenditure by domestic Net expenditure by foreign individuals and institutions individuals and institutions 13-9 Copyright2012 Pearson Education.All rights reserved
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education. All rights reserved. 13-9 GNP = Expenditure on a Country’s Goods and Services • The national income identity for an open economy is Y = C + I + G + EX – IM = C + I + G + CA Expenditure by domestic individuals and institutions Net expenditure by foreign individuals and institutions
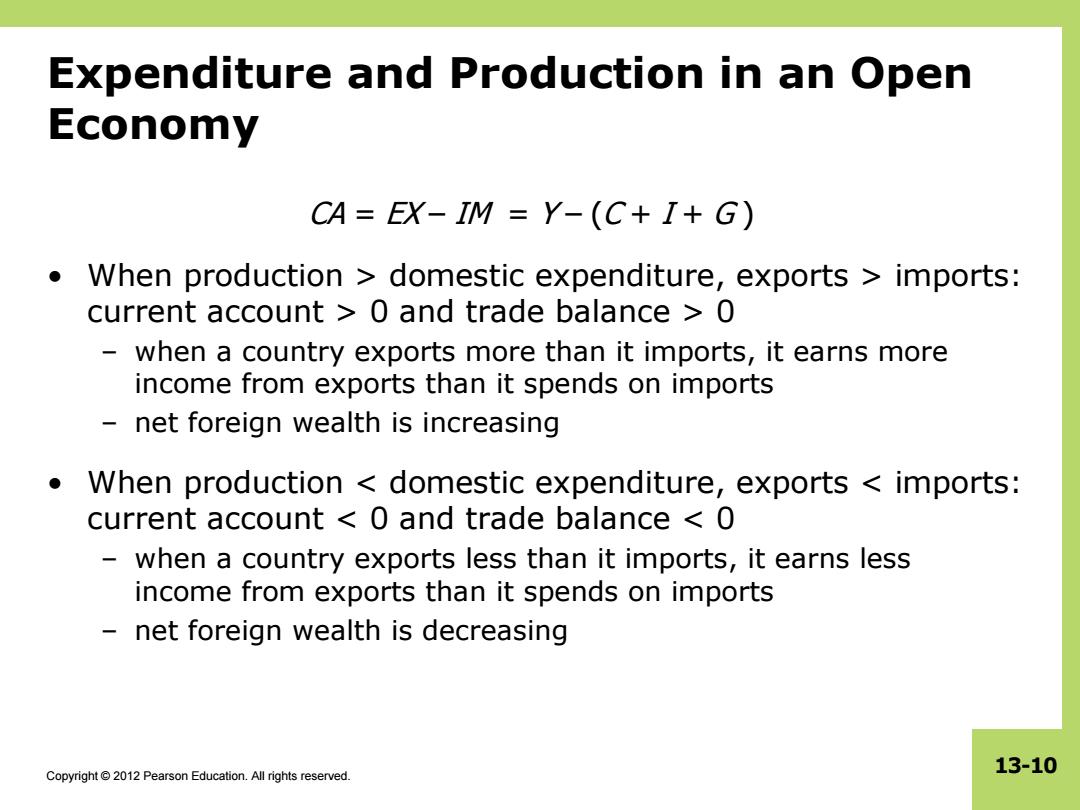
Expenditure and Production in an Open Economy CA=EX-IM Y-(C+I+G) When production domestic expenditure,exports imports: current account 0 and trade balance 0 when a country exports more than it imports,it earns more income from exports than it spends on imports net foreign wealth is increasing When production domestic expenditure,exports imports: current account 0 and trade balance 0 - when a country exports less than it imports,it earns less income from exports than it spends on imports net foreign wealth is decreasing Copyright2012 Pearson Education.All rights reserved. 13-10
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education. All rights reserved. 13-10 Expenditure and Production in an Open Economy CA = EX – IM = Y – (C + I + G ) • When production > domestic expenditure, exports > imports: current account > 0 and trade balance > 0 – when a country exports more than it imports, it earns more income from exports than it spends on imports – net foreign wealth is increasing • When production < domestic expenditure, exports < imports: current account < 0 and trade balance < 0 – when a country exports less than it imports, it earns less income from exports than it spends on imports – net foreign wealth is decreasing