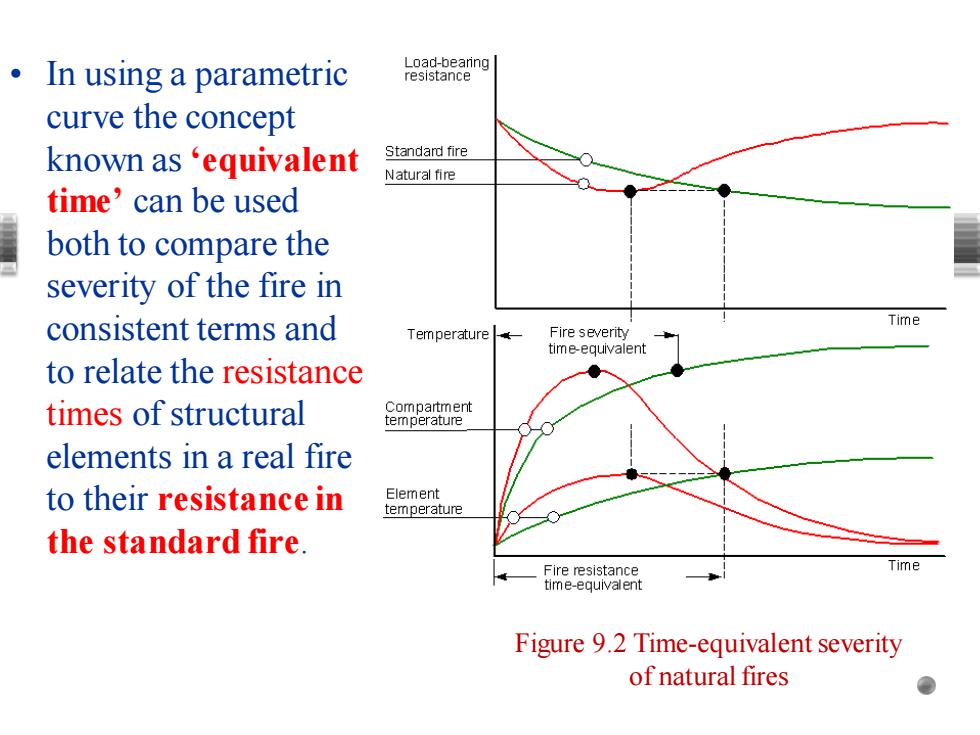
。In using a parametric Load-bearing resistance curve the concept known as‘equivalent Standard fire Natural fire time'can be used both to compare the severity of the fire in consistent terms and Time Temperature Fire severity time-equivalent to relate the resistance times of structural Compartment temperature elements in a real fire to their resistance in Element temperature the standard fire. Fire resistance ime time-equivalent Figure 9.2 Time-equivalent severity of natural fires
• In using a parametric curve the concept known as ‘equivalent time’ can be used both to compare the severity of the fire in consistent terms and to relate the resistance times of structural elements in a real fire to their resistance in the standard fire. Figure 9.2 Time-equivalent severity of natural fires
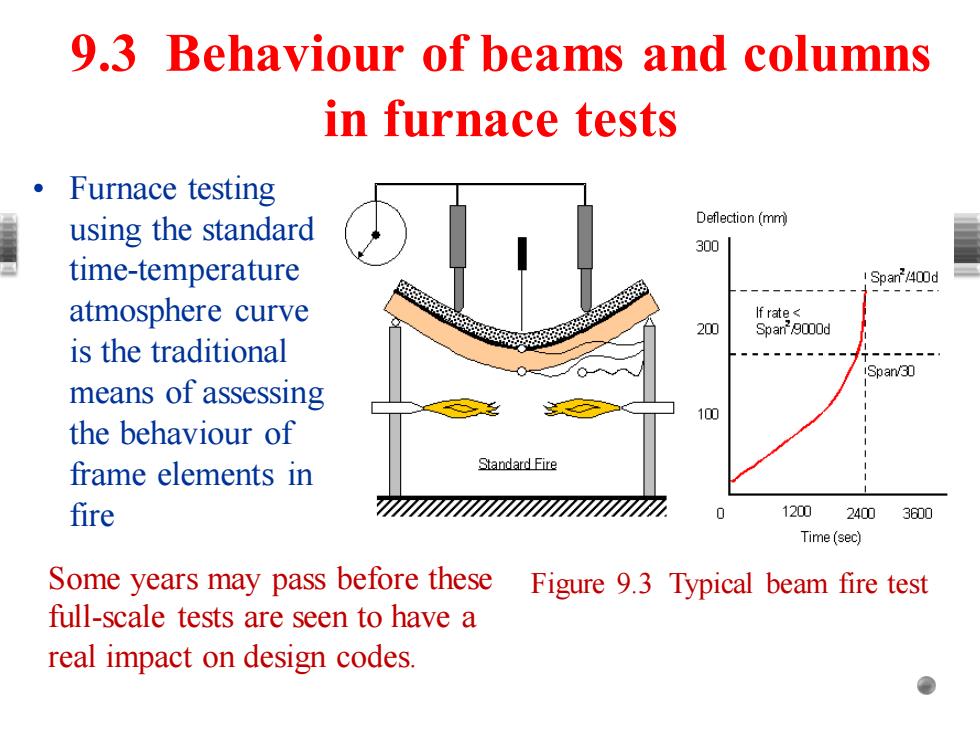
9.3 Behaviour of beams and columns in furnace tests 。Furnace testing using the standard Deflection(mm 300 time-temperature !Span/400d atmosphere curve If rate< 20m Span/9000d is the traditional Span/30 means of assessing 100 the behaviour of frame elements in Standard Fire fire 12002400 3600 Time(sec) Some years may pass before these Figure 9.3 Typical beam fire test full-scale tests are seen to have a real impact on design codes
• Furnace testing using the standard time-temperature atmosphere curve is the traditional means of assessing the behaviour of frame elements in fire 9.3 Behaviour of beams and columns in furnace tests Some years may pass before these Figure 9.3 Typical beam fire test full-scale tests are seen to have a real impact on design codes
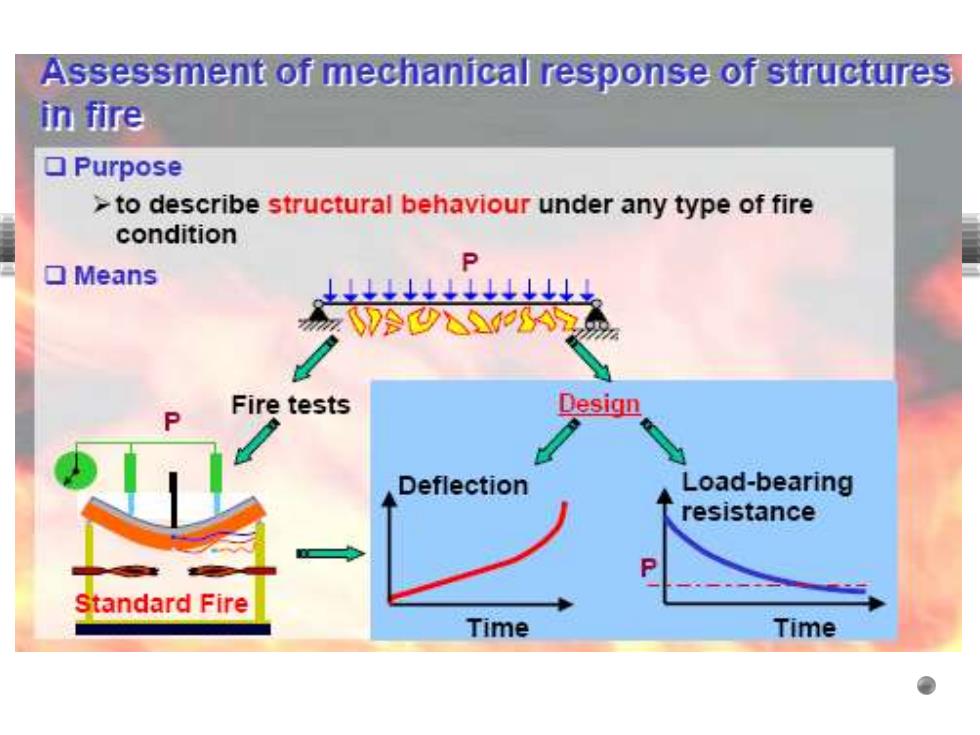
Assessment of mechanical response of structures in fire ▣Purpose >to describe structural behaviour under any type of fire condition ▣Means Q Fire tests Design Deflection Load-bearing resistance Standard Fire Time Time

9.4 Fire protection methods 。alternative forms: >Boarding (plasterboard or more specialised systems based on mineral fibre or vermiculite)fixed around the exposed parts of the steel members. >Sprays which build up a coating of prescribed thickness around the members >Intumescent paints,which provide a decorative finish under normal conditions,but which foam and swell when heated, producing an insulating char layer which is up to 50 times as thick as the original paint film. >Fire protection materials are routinely tested for insulation, integrity and load-carrying capacity in ISO834 furnace test. Material properties for design are determined from the results by semi-empirical means
• alternative forms: ➢ Boarding (plasterboard or more specialised systems based on mineral fibre or vermiculite) fixed around the exposed parts of the steel members. ➢ Sprays which build up a coating of prescribed thickness around the members. ➢ Intumescent paints, which provide a decorative finish under normal conditions, but which foam and swell when heated, producing an insulating char layer which is up to 50 times as thick as the original paint film. ➢ Fire protection materials are routinely tested for insulation, integrity and load-carrying capacity in ISO834 furnace test. Material properties for design are determined from the results by semi-empirical means. 9.4 Fire protection methods

Basic structural fire resistant design of members Loadings E- effect of actions G= permanent action 0- variable action Ra三 load-bearing resistance 1n= standard fire resistance time of a member In.requ standard fire resistance time nominal requirement 0= temperature 0.m= Critical temperature of a member y= partial safety factor load combination factor
Basic structural fire resistant design of members Loadings E = effect of actions G = permanent action Q = variable action Rfi = load-bearing resistance fi t = standard fire resistance time of a member fi requ . t = standard fire resistance time nominal requirement temperature cr = Critical = partial safety factor load combination factor