
Pathogenesis Hyperglycemia may alter the expression of one or more genes,leading to increased (or decreased)amounts of certain gene products that can alter cellular functions. 。 Glycosylated proteins can undergo a series of reactions, leading to considerable alteration of proteins. Chronic hyperglycemia may produce oxidative stress in cells,leading to the formation of an excess of "toxic end products of oxidation"including peroxides,superoxides, nitric oxide,and oxygen free radicals. 。 Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF),FGF,etc Cell apoptosis Others
• Hyperglycemia may alter the expression of one or more genes, leading to increased (or decreased) amounts of certain gene products that can alter cellular functions. • Glycosylated proteins can undergo a series of reactions, leading to considerable alteration of proteins. • Chronic hyperglycemia may produce oxidative stress in cells, leading to the formation of an excess of "toxic end products of oxidation" including peroxides, superoxides, nitric oxide, and oxygen free radicals. • Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), FGF, etc • Cell apoptosis • Others Pathogenesis

All retinal cells were affected in diabetes Diabetes Affects all Retinal Cell Types CellType Characteristics Vascular Altered tight junctions;endothelial cell and pericyte death Glial Altered contacts with vessels;release inflammatory mediators;impaired glutamate metabolism Microglial Increased number;release inflammatory mediators Neurons Death of ganglion cells,inner nuclear layer;axonal atrophy .Microanginopathy:Retinal capillary occlusion/leakage, Neovascularization,etc .Neuropathy:Neuronal apoptosis -Low inflammation:Glial cells activation and inflammatory factors releasing (IL-1,IL-6,TNF-a,VEGF,ICAM-1,etc)
•Microanginopathy: Retinal capillary occlusion/leakage, Neovascularization, etc •Neuropathy: Neuronal apoptosis •Low inflammation: Glial cells activation and inflammatory factors releasing (IL-1, IL-6, TNF-a, VEGF, ICAM-1, etc) All retinal cells were affected in diabetes

Microvascular occlusion Microvascular Occlusion Microvascular occlusion is caused by: .Thickening of capillary Ischemia Infarction basement membranes -Abnormal proliferation of Increased VEGF Cotton- capillary endothelium wool spot Increased platelet adhesion Neovasculariz -Increased blood viscosity ation -Defective fibrinolysis Vitreous Fibrovascular Neovascular hemorrhage bands glaucoma Retina in systemic disease:a color manual of ophthalmoscopy Homayoun Tabandeh, ↓ Morton F.Goldberg 2009 Tractional retinal detachment
Microvascular occlusion is caused by: •Thickening of capillary basement membranes •Abnormal proliferation of capillary endothelium •Increased platelet adhesion •Increased blood viscosity •Defective fibrinolysis Retina in systemic disease: a color manual of ophthalmoscopy / Homayoun Tabandeh, Morton F. Goldberg 2009 Microvascular occlusion
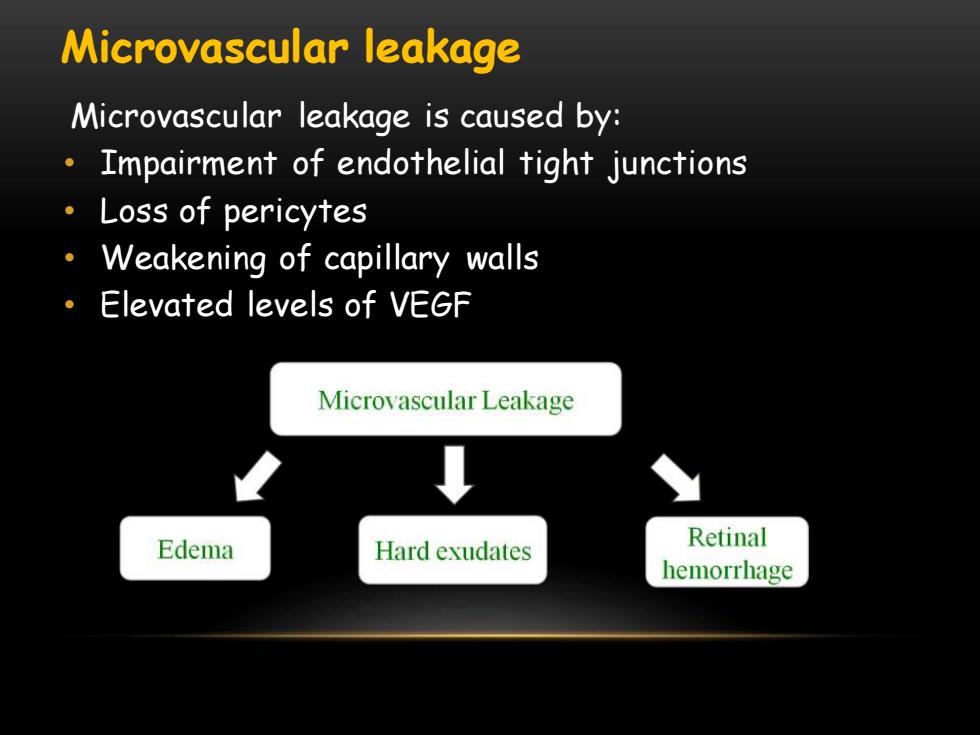
Microvascular leakage Microvascular leakage is caused by: Impairment of endothelial tight junctions ·Loss of pericytes Weakening of capillary walls Elevated levels of VEGF Microvascular Leakage Edema Hard exudates Retinal hemorrhage
Microvascular leakage is caused by: • Impairment of endothelial tight junctions • Loss of pericytes • Weakening of capillary walls • Elevated levels of VEGF Microvascular leakage

Neuropathy Below the Normal Range Contrast sensitivity ·Color vision ·ERG changes ·Neuronal apoptosis … 88 Spatial Frequency (cycles/degree) Negative control Positive control 0,0002 0.0095 0.00 C1 c2 c4 0 .04 0.06 0.08 014 0.0000 0,0001 0.00015 打ms仰到 D1 D2 04
• Contrast sensitivity • Color vision • ERG changes • Neuronal apoptosis • …… Neuropathy