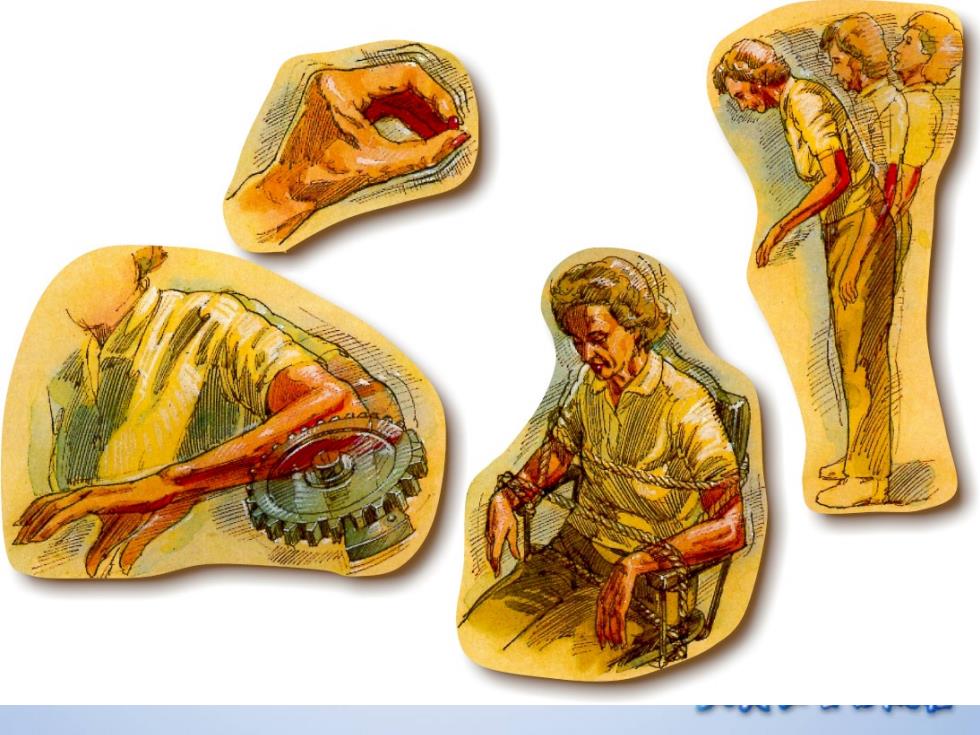

战 PARKINSON'S DISEASE Associated Clinical Features ·Micrographia写字过小症 ·Hypophonia 发声过弱 ·Shuffling gait曳行步态/festination急促步伐 ·Drooling 流涎 ·Dysphagia 吞咽困难 Autonomic dysfunction 植物神经功能紊乱 。Depression 抑郁 。Dementia 痴呆 人凤只坐公版松
PARKINSON PARKINSON’S DISEASE S DISEASE Associated Clinical Features Associated Clinical Features • Micrographia 写字过小症 • Hypophonia 发声过弱 • Shuffling gait 曳行步态/ festination急促步伐 • Drooling 流涎 • Dysphagia 吞咽困难 • Autonomic dysfunction 植物神经功能紊乱 • Depression 抑郁 • Dementia 痴呆

最 PARKINSON'S DISEASE Incidence and Epidemiology Prevalence Rate 200 per 100,000 Rare for individuals 40 years of age 1%for individuals 60 years of age 2%for individuals 85 years of age Men Women Incidence rate:20 per 100,000 (annually) 人民口生名版松
PARKINSON PARKINSON’S DISEASE S DISEASE Incidence and Epidemiology Incidence and Epidemiology Prevalence Rate : 200 per 100,000 Rare for individuals < 40 years of age 1% for individuals > 60 years of age 2% for individuals > 85 years of age Men > Women Incidence rate : 20 per 100,000 (annually)

抗帕金森病药 多巴胺能神经元 正常时黑质一纹状体有 胆碱能神经元 正常时两者处于动态平衡,参与调节机体运动机能: 多巴胺能神经元对脊髓前角运动神经起抑制作用; 胆碱能神经元对脊髓前角运动神经起兴奋作用。 轻症:抗胆碱药和MAO-B抑制药 重症:L-dopa,无效者用DA-R激动药 人凤只生公版松
正常时黑质-纹状体有 正常时两者处于动态平衡,参与调节机体运动机能: 多巴胺能神经元对脊髓前角运动神经起抑制作用; 胆碱能神经元对脊髓前角运动神经起兴奋作用。 轻症: 抗胆碱药和MAO-B抑制药 重症: L-dopa,无效者用DA-R激动药 抗帕金森病药 {多巴胺能神经元 胆碱能神经元
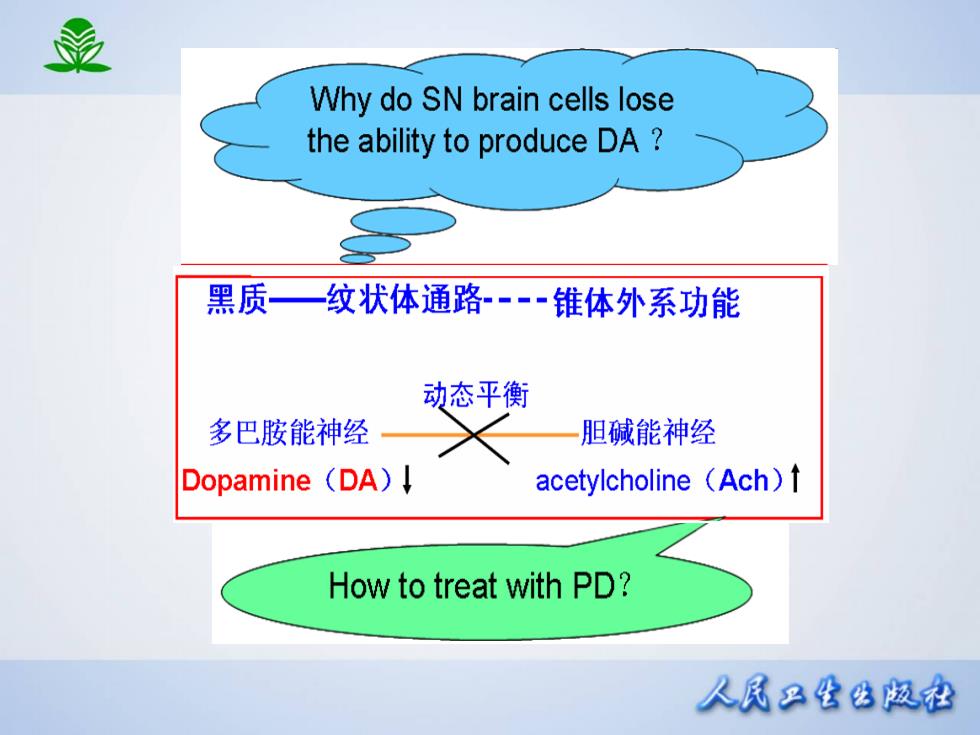
最 Why do SN brain cells lose the ability to produce DA 黑质一纹状体通路·锥体外系功能 动态平衡 多巴胺能神经 胆碱能神经 Dopamine (DA)! acetylcholine (Ach)1 How to treat with PD? 人凤只公公版松